QGT-Columbia-analysis-plan
Hae Kyung Im
2020-06-03
Last updated: 2020-06-10
Checks: 7 0
Knit directory: QGT-Columbia-lab/
This reproducible R Markdown analysis was created with workflowr (version 1.6.2). The Checks tab describes the reproducibility checks that were applied when the results were created. The Past versions tab lists the development history.
Great! Since the R Markdown file has been committed to the Git repository, you know the exact version of the code that produced these results.
Great job! The global environment was empty. Objects defined in the global environment can affect the analysis in your R Markdown file in unknown ways. For reproduciblity it’s best to always run the code in an empty environment.
The command set.seed(20200603) was run prior to running the code in the R Markdown file. Setting a seed ensures that any results that rely on randomness, e.g. subsampling or permutations, are reproducible.
Great job! Recording the operating system, R version, and package versions is critical for reproducibility.
Nice! There were no cached chunks for this analysis, so you can be confident that you successfully produced the results during this run.
Great job! Using relative paths to the files within your workflowr project makes it easier to run your code on other machines.
Great! You are using Git for version control. Tracking code development and connecting the code version to the results is critical for reproducibility.
The results in this page were generated with repository version f5ab5b9. See the Past versions tab to see a history of the changes made to the R Markdown and HTML files.
Note that you need to be careful to ensure that all relevant files for the analysis have been committed to Git prior to generating the results (you can use wflow_publish or wflow_git_commit). workflowr only checks the R Markdown file, but you know if there are other scripts or data files that it depends on. Below is the status of the Git repository when the results were generated:
Ignored files:
Ignored: .DS_Store
Ignored: .Rhistory
Ignored: .Rproj.user/
Ignored: extras/.DS_Store
Note that any generated files, e.g. HTML, png, CSS, etc., are not included in this status report because it is ok for generated content to have uncommitted changes.
These are the previous versions of the repository in which changes were made to the R Markdown (analysis/analysis_plan.Rmd) and HTML (docs/analysis_plan.html) files. If you’ve configured a remote Git repository (see ?wflow_git_remote), click on the hyperlinks in the table below to view the files as they were in that past version.
| File | Version | Author | Date | Message |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rmd | f5ab5b9 | HKI qgt test | 2020-06-10 | edits |
| Rmd | b2b8f8b | HKI qgt test | 2020-06-10 | torus |
| Rmd | 13520bc | HKI qgt test | 2020-06-09 | edits |
| Rmd | 7df918e | Hae Kyung Im | 2020-06-09 | edits |
| html | 7df918e | Hae Kyung Im | 2020-06-09 | edits |
| Rmd | 64a96f7 | Hae Kyung Im | 2020-06-09 | edits |
| html | 64a96f7 | Hae Kyung Im | 2020-06-09 | edits |
| Rmd | e65d451 | Hae Kyung Im | 2020-06-09 | moved def up |
| html | e65d451 | Hae Kyung Im | 2020-06-09 | moved def up |
| html | e8079a7 | Hae Kyung Im | 2020-06-09 | figure moved |
| Rmd | 09f235e | Hae Kyung Im | 2020-06-09 | added figure assoc |
| Rmd | 7fc9808 | Hae Kyung Im | 2020-06-09 | editing preliminary notices |
| html | 7fc9808 | Hae Kyung Im | 2020-06-09 | editing preliminary notices |
| Rmd | b1c4d69 | Hae Kyung Im | 2020-06-09 | heads up and questionnaire |
| html | b1c4d69 | Hae Kyung Im | 2020-06-09 | heads up and questionnaire |
| Rmd | bc78582 | meliao | 2020-06-09 | Improved method of reading predicted expression (Thanks Tyson) |
| Rmd | e5b04c3 | HKI qgt test | 2020-06-09 | height to cad |
| Rmd | ad4f80b | HKI qgt test | 2020-06-09 | height to cad |
| Rmd | db5a1ae | Hae Kyung Im | 2020-06-09 | edits |
| html | db5a1ae | Hae Kyung Im | 2020-06-09 | edits |
| Rmd | 83e040c | Hae Kyung Im | 2020-06-09 | edits |
| Rmd | 3fc9ab8 | Hae Kyung Im | 2020-06-08 | edits |
| Rmd | d4f7c78 | meliao | 2020-06-08 | Fixed merge |
| Rmd | ca165eb | meliao | 2020-06-08 | Added to code directory and updated analysis plan |
| Rmd | b7047c7 | Hae Kyung Im | 2020-06-08 | more comments |
| html | b7047c7 | Hae Kyung Im | 2020-06-08 | more comments |
| Rmd | c9cedba | Hae Kyung Im | 2020-06-08 | added brief explanation to chunks |
| Rmd | f754512 | Hae Kyung Im | 2020-06-08 | removed - in spredixcan folder name |
| html | f754512 | Hae Kyung Im | 2020-06-08 | removed - in spredixcan folder name |
| Rmd | 0ae4586 | meliao | 2020-06-08 | Committing before merging in master |
| html | 0ae4586 | meliao | 2020-06-08 | Committing before merging in master |
| Rmd | 3489f1b | meliao | 2020-06-08 | Unfinished plotting changes. Committing before merge |
| Rmd | b52e06a | Hae Kyung Im | 2020-06-08 | edits |
| html | b52e06a | Hae Kyung Im | 2020-06-08 | edits |
| Rmd | a2b9918 | Hae Kyung Im | 2020-06-07 | testing, reducing size of genotype file |
| html | a2b9918 | Hae Kyung Im | 2020-06-07 | testing, reducing size of genotype file |
| Rmd | 2257a0f | Hae Kyung Im | 2020-06-06 | raw figure links |
| html | 2257a0f | Hae Kyung Im | 2020-06-06 | raw figure links |
| Rmd | efbfceb | Hae Kyung Im | 2020-06-06 | raw urls for figures |
| Rmd | 973fc2b | Hae Kyung Im | 2020-06-05 | prelim notes |
| Rmd | 517e8f7 | meliao | 2020-06-05 | Merge branch ‘master’ of https://github.com/hakyimlab/QGT-Columbia-HKI |
| Rmd | 409558f | Yanyu Liang | 2020-06-05 | updated some paths |
| html | 409558f | Yanyu Liang | 2020-06-05 | updated some paths |
| Rmd | 0deee3c | Hae Kyung Im | 2020-06-05 | added TWMR |
| html | 0deee3c | Hae Kyung Im | 2020-06-05 | added TWMR |
| Rmd | 064f6ee | Hae Kyung Im | 2020-06-05 | added figures and slides under extras |
| html | 064f6ee | Hae Kyung Im | 2020-06-05 | added figures and slides under extras |
| Rmd | 1b70eb7 | Hae Kyung Im | 2020-06-05 | updated prerequisites |
| html | 1b70eb7 | Hae Kyung Im | 2020-06-05 | updated prerequisites |
| Rmd | 339f40c | Hae Kyung Im | 2020-06-05 | added plan |
| html | 339f40c | Hae Kyung Im | 2020-06-05 | added plan |
| Rmd | a3aa03e | Hae Kyung Im | 2020-06-05 | prerequisites added |
| Rmd | 09f5dae | Hae Kyung Im | 2020-06-05 | fastenloc |
| Rmd | ccb1167 | Hae Kyung Im | 2020-06-05 | knit |
| html | ccb1167 | Hae Kyung Im | 2020-06-05 | knit |
| Rmd | d427aee | Hae Kyung Im | 2020-06-05 | minor comment sort1 |
| Rmd | 4ca65b9 | Hae Kyung Im | 2020-06-05 | edits 2 |
| Rmd | f59cd02 | Hae Kyung Im | 2020-06-04 | edits |
| html | f59cd02 | Hae Kyung Im | 2020-06-04 | edits |
| Rmd | 1ad820c | meliao | 2020-06-04 | Added shell source command |
| Rmd | d65c555 | Hae Kyung Im | 2020-06-04 | twmr |
| html | d65c555 | Hae Kyung Im | 2020-06-04 | twmr |
| html | 682b6e2 | Hae Kyung Im | 2020-06-04 | Build site. |
| Rmd | d3502e8 | Hae Kyung Im | 2020-06-04 | wflow_publish(“analysis/analysis_plan.Rmd”) |
| Rmd | 4420fc7 | Hae Kyung Im | 2020-06-04 | wflow_rename(“analysis/predixcan_analysis.Rmd”, “analysis/analysis_plan.Rmd”) |
| html | 4420fc7 | Hae Kyung Im | 2020-06-04 | wflow_rename(“analysis/predixcan_analysis.Rmd”, “analysis/analysis_plan.Rmd”) |
Set up
- download data and software from Box. This will have copies of all the software repositories and the models
Linux is the operating system of choice to run bioinformatics software. We are offering two options
- Option 1: full setup, recommended for the linux-savvy with full setup
- Option 2: pre-installed RStudio in Google cloud, recommended for people less familiar with linux
The latest version of the analysis plan markdown document that generated this page is on github here rendered here as an html page
Option 1
- install anaconda/miniconda
- define imlabtools conda environment how to here, which will install all the python modules needed for this analysis session
-
download software (copies of the repos are already included in the course folder QCT-Columbia-HKI/repos/)
- download metaxcan repo
- download torus repo
- download fastenloc repo
- download TMWR repo
- download prediction models from predictdb.org (a few models are included in the course folder QCT-Columbia-HKI/repos/)
- install R/RStudio/tidyverse package
- (optional) install workflowr package in R
- git clone https://github.com/hakyimlab/QGT-Columbia-HKI.git
- start Rstudio (if you installed workflowr, you can just open the QGT-Columbia-HKI.Rproj)
Option 2
- claim your Rstudio server IP address and get the username and password here (https://docs.google.com/spreadsheets/d/1PKVfywvTu1RZuDCyHV4xt_cCngzhmjzw60_dHzLbLrc/edit#gid=145770066)
- connect to the Rstudio server using the url you claimed (http://xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx:8787) using a web browser
- log into the server using the username and password of the server you claimed
Both options
Summary of analysis plan
- predict whole blood expression
- check how well the prediction works with GEUVADIS expression data
- run association between predicted expression and a simulated phenotype
- calculate association between expression levels and coronary artery disease risk using s-predixcan
- fine-map the coronary artery disease gwas results using torus
- calculate colocalization probability using fastenloc
- run transcriptome-wide mendelian randomization in one locus of interestgi
Initial remarks
We ask you to actively participate in today’s hands on activities. Notice that we may ask you to share your screen for pedagogic purposes.
As you run the analysis and programs, we ask you to respond the questions in this document. Find the tab with your name and fill out the questions as you go along.
You are welcome to check other people’s answers as guidelines but please make sure you write down your own answers.
If you have any concerns about this, please ask me or one of the TAs for assistance. We are here to help you learn.
Preliminary definitions
- Go to the terminal tab on the RStudio server and update the analysis document to the most recent version. The commands are shown below. Copy the text (without the lines with apostrophes: ```), paste them to the terminal, and hit enter.
PRE="/home/student/"
cd $PRE/lab/
git pull - activate the the imlabtools environment, which will make sure all the necessary python modules are available to the software we will be running.
conda activate imlabtoolsReminder: the bash chunks need to be copy-pasted to the terminal, not performed within the chunk.
- execute the following chunk (you can use the green arrow below to the right)
suppressPackageStartupMessages(library(tidyverse))- define some variables to access the data more easily within the R session. Run the following r chunk
print(getwd())
lab="/home/student/lab"
CODE=glue::glue("{lab}/code")
source(glue::glue("{CODE}/extra_functions.R"))
#source(glue::glue("code/extra_functions.R"))
PRE="/home/student/QGT-Columbia-HKI"
MODEL=glue::glue("{PRE}/models")
DATA=glue::glue("{PRE}/data")
RESULTS=glue::glue("{PRE}/results")
METAXCAN=glue::glue("{PRE}/repos/MetaXcan-master/software")
FASTENLOC=glue::glue("{PRE}/repos/fastenloc-master")
TORUS=glue::glue("{PRE}/repos/torus-master")
TWMR=glue::glue("{PRE}/repos/TWMR-master")- define some variables to access the data more easily in the terminal. Run the following bash chunk. You will need to copy and paste the following chunk in the terminal
export PRE="/home/student/QGT-Columbia-HKI"
export LAB="/home/student/lab"
export CODE=$LAB/code
export DATA=$PRE/data
export MODEL=$PRE/models
export RESULTS=$PRE/results
export METAXCAN=$PRE/repos/MetaXcan-master/software
export TWMR=$PRE/repos/TWMR-masterTranscriptome-wide association methods
Transcriptome-wide association methods
predict expression
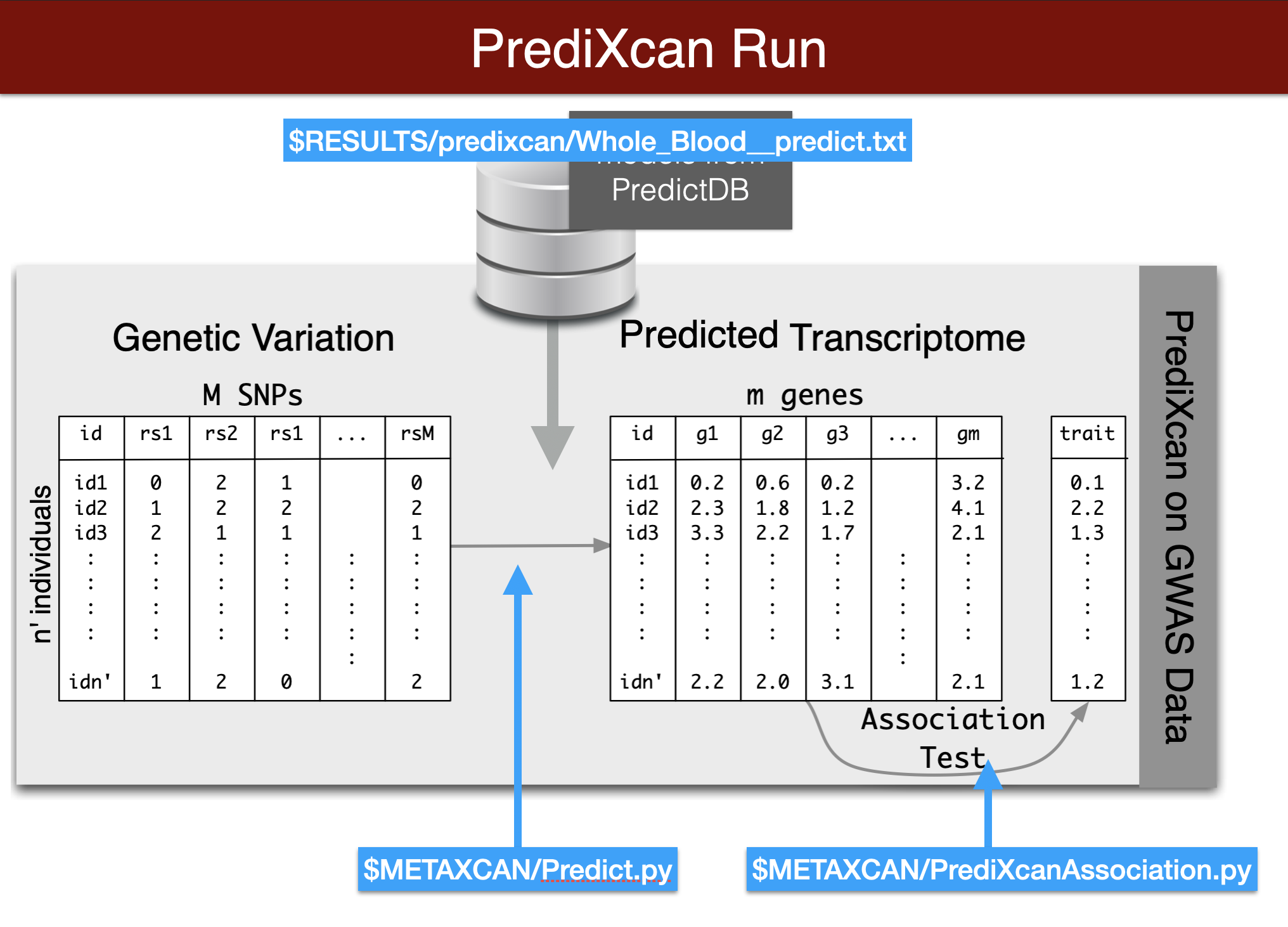
Visual summary of predixcan runs
We will predict expression of genes in whole blood using the Predict.py code in the METAXCAN folder.
Prediction models are located in the MODEL folder. Additional models for different tissues and transcriptome studies can be downloaded from predictdb.org
Remember you need to copy and paste this code chunk into the terminal to run it. Also make sure you activated the imlabtools environment which has all the necessary python modules.
Make sure all the paths and file names are correct
This run should take about one minute.
printf "Predict expression\n\n"
python3 $METAXCAN/Predict.py \
--model_db_path $PRE/models/gtex_v8_en/en_Whole_Blood.db \
--vcf_genotypes $DATA/predixcan/genotype/filtered.vcf.gz \
--vcf_mode genotyped \
--variant_mapping $DATA/predixcan/gtex_v8_eur_filtered_maf0.01_monoallelic_variants.txt.gz id rsid \
--on_the_fly_mapping METADATA "chr{}_{}_{}_{}_b38" \
--prediction_output $RESULTS/predixcan/Whole_Blood__predict.txt \
--prediction_summary_output $RESULTS/predixcan/Whole_Blood__summary.txt \
--verbosity 9 \
--throw
check predicted values
prediction_fp = glue::glue("{RESULTS}/predixcan/Whole_Blood__predict.txt")
## Read the Predict.py output into a dataframe
predicted_expression = read.table(file=prediction_fp, sep="\t", quote="", comment.char="", skip = 1, header = TRUE)
# Retain the column names
cols = read.table(file=prediction_fp, sep="\t", quote="", comment.char="", nrows = 1)
# Fill the column names
colnames(predicted_expression) = unname(unlist(cols[1,]))
## Melt the data so each row is FID, IID, gene_id, predicted_expression
predicted_expression = predicted_expression %>%
pivot_longer(
cols = starts_with("ENSG"),
names_to = "gene_id",
values_to = "predicted_expression",
values_drop_na =
)
## read summary of prediction, number of SNPs per gene, cross validated prediction performance
prediction_summary = read_tsv(glue::glue("{RESULTS}/predixcan/Whole_Blood__summary.txt"))
## number of genes with a prediction model
dim(prediction_summary)
head(prediction_summary)
print("distribution of prediction performance r2")
summary(prediction_summary$pred_perf_r2)assess prediction performance (optional)
## download and read observed expression data from GEUVADIS
## from https://uchicago.box.com/s/4y7xle5l0pnq9d1fwmthe2ewhogrnlrv
## Remove the version number from the gene_id's (ENSG000XXX.ver)
predicted_expression$gene_id = gsub("\\..*","",predicted_expression$gene_id)
head(predicted_expression)
## merge predicted expression with observed expression data (by IID and gene)
## plot observes vs predicted expressioni for
## ERAP1 (ENSG00000164307)
## PEX6 (ENSG00000124587)
## calculate spearman correlation for all genes
## what's the best performing gene?run association with a simulated phenotype
\(Y = \sum_k T_k \beta_k + \epsilon\)
with random effects \(\beta_k \sim (1-\pi)\cdot \delta_0 + \pi\cdot N(0,1)\)
export PHENO="sim.spike_n_slab_0.01_pve0.1"
printf "association\n\n"
python3 $METAXCAN/PrediXcanAssociation.py \
--expression_file $RESULTS/predixcan/Whole_Blood__predict.txt \
--input_phenos_file $DATA/predixcan/phenotype/$PHENO.txt \
--input_phenos_column pheno \
--output $RESULTS/predixcan/$PHENO/Whole_Blood__association.txt \
--verbosity 9 \
--throw
More predicted phenotypes can be downloaded from here. The naming of the phenotypes provides information about the genic architecture: the number after pve is the proportion of variance of Y explained by the genetic component of expression. The number after spike_n_slab represents the probability that a gene is causal \(\pi\)(i.e. prob \(\beta \ne 0\))
read association results
## read association results
PHENO="sim.spike_n_slab_0.01_pve0.1"
predixcan_association = read_tsv(glue::glue("{RESULTS}/predixcan/{PHENO}/Whole_Blood__association.txt"))
## take a look at the results
dim(predixcan_association)
predixcan_association %>% arrange(pvalue) %>% head
predixcan_association %>% arrange(pvalue) %>% ggplot(aes(pvalue)) + geom_histogram(bins=20)
## compare distribution against the null (uniform)
gg_qqplot(predixcan_association$pvalue, max_yval = 40)truebetas = read_tsv(glue::glue("{DATA}/predixcan/phenotype/gene-effects/{PHENO}.txt"))
betas = (predixcan_association %>%
inner_join(truebetas,by=c("gene"="gene_id")) %>%
select(c('predicted_beta'='effect', 'true_beta'='effect_size','pvalue')))
betas %>% ggplot(aes(predicted_beta, true_beta))+geom_point()+geom_abline()## get chr and position of genes (transcription start site)
## do you see examples of potential LD contamination?Summary PrediXcan
Now we will use the summary results from a GWAS of coronary artery disease to calculate the association between the genetic component of the expression of genes and coronary artery disease risk. We will use the SPrediXcan.py.
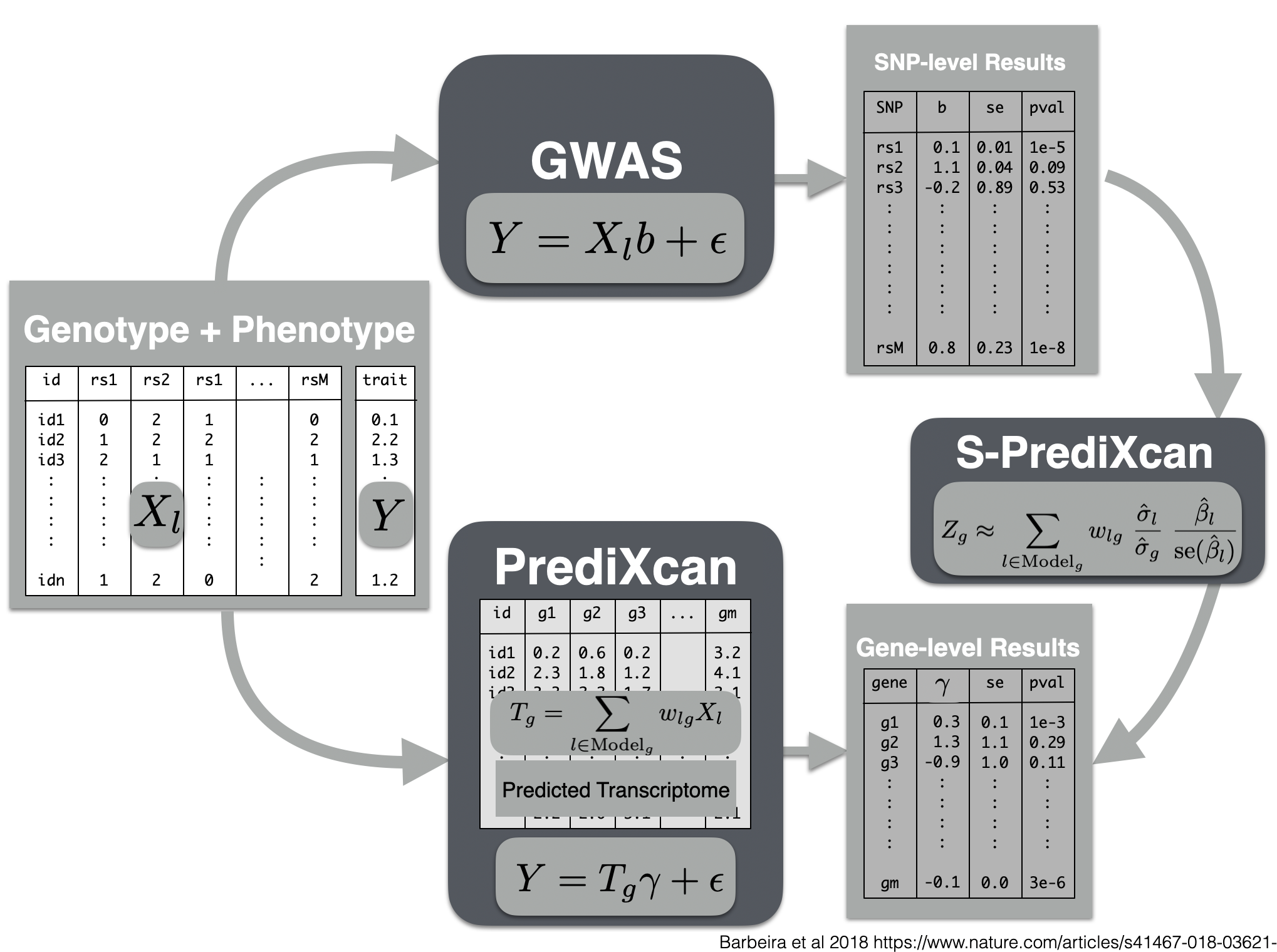
Visual summary of s-predixcan
- harmonized and imputed GWAS result for coronary artery disease is available in $PRE/spredixcan/data/
run s-predixcan
python $METAXCAN/SPrediXcan.py \
--gwas_file $DATA/spredixcan/imputed_CARDIoGRAM_C4D_CAD_ADDITIVE.txt.gz \
--snp_column panel_variant_id --effect_allele_column effect_allele --non_effect_allele_column non_effect_allele --zscore_column zscore \
--model_db_path $MODEL/gtex_v8_mashr/mashr_Whole_Blood.db \
--covariance $MODEL/gtex_v8_mashr/mashr_Whole_Blood.txt.gz \
--keep_non_rsid --additional_output --model_db_snp_key varID \
--throw \
--output_file $RESULTS/spredixcan/eqtl/CARDIoGRAM_C4D_CAD_ADDITIVE__PM__Whole_Blood.csv
plot and interpret s-predixcan results
spredixcan_association = read_csv(glue::glue("{RESULTS}/spredixcan/eqtl/CARDIoGRAM_C4D_CAD_ADDITIVE__PM__Whole_Blood.csv"))
dim(spredixcan_association)
spredixcan_association %>% arrange(pvalue) %>% head
spredixcan_association %>% arrange(pvalue) %>% ggplot(aes(pvalue)) + geom_histogram(bins=20)
gg_qqplot(spredixcan_association$pvalue)- SORT1, considered to be a causal gene for LDL cholesterol and as a consequence of coronary artery disease, is not found here. Why? (tissue)
Exercise
run s-predixcan with liver model, do you find SORT1? Is it significant?
compare zscores in liver and whole blood.
run multixcan (optional)
python $METAXCAN/SMulTiXcan.py \
--models_folder $MODEL/gtex_v8_mashr \
--models_name_pattern "mashr_(.*).db" \
--snp_covariance $MODEL/gtex_v8_expression_mashr_snp_smultixcan_covariance.txt.gz \
--metaxcan_folder $RESULTS/spredixcan/eqtl/ \
--metaxcan_filter "CARDIoGRAM_C4D_CAD_ADDITIVE__PM__(.*).csv" \
--metaxcan_file_name_parse_pattern "(.*)__PM__(.*).csv" \
--gwas_file $DATA/spredixcan/imputed_CARDIoGRAM_C4D_CAD_ADDITIVE.txt.gz \
--snp_column panel_variant_id --effect_allele_column effect_allele --non_effect_allele_column non_effect_allele --zscore_column zscore --keep_non_rsid --model_db_snp_key varID \
--cutoff_condition_number 30 \
--verbosity 7 \
--throw \
--output $RESULTS/smultixcan/eqtl/CARDIoGRAM_C4D_CAD_ADDITIVE_smultixcan.txt
Colocalization methods
- Colocalization methods seek to estimate the probability that the complex trait and expression causal variants are the same. We favor methods that calculate the probability of causality for each trait (posterior inclusion probability), called fine-mapping methods. Here we use torus for fine-mapping and fastENLOC for colocalization.
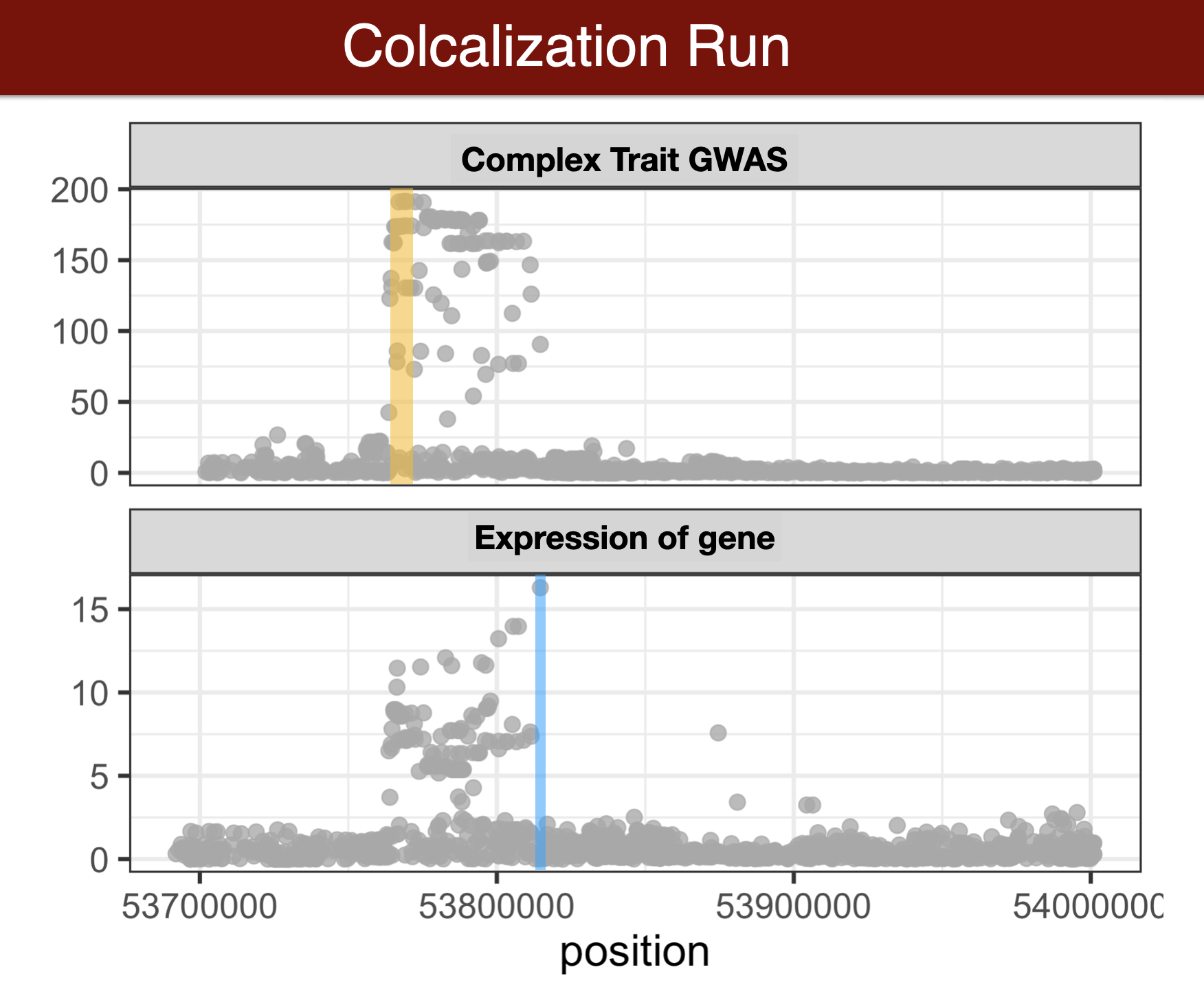
Visual summary of colocalization
GWAS summary statistics to torus format
the following code will format GWAS summary statistics into a format that the fine-mapping method torus can understand.
we precalculated this for you so there is no need to recalculate
##TODO CAD GWAS is in hg38
python $CODE/gwas_to_torus_zscore.py \
-input_gwas $DATA/spredixcan/imputed_CARDIoGRAM_C4D_CAD_ADDITIVE.txt.gz \
-input_ld_regions $DATA/spredixcan/eur_ld_hg38.txt.gz \
-output_fp $DATA/fastenloc/CARDIoGRAM_C4D_CAD_ADDITIVE.zval.gz
fine-map GWAS results
We will run torus due to time limitation but ideally we would like to run a method that allows multiple causal variants per locus, such as DAP-G or SusieR.
torus has been precompiled and placed within the PATH
export TORUSOFT=torus
$TORUSOFT -d $PRE/data/fastenloc/CARDIoGRAM_C4D_CAD_ADDITIVE.zval.gz --load_zval -dump_pip $PRE/data/fastenloc/CARDIoGRAM_C4D_CAD_ADDITIVE.gwas.pip
cd $PRE/data/fastenloc
gzip CARDIoGRAM_C4D_CAD_ADDITIVE.gwas.pip
cd $PRE
We can take a quick look at the z-values and finemapping PIPs:
cd $PRE/data/fastenloc
zless CARDIoGRAM_C4D_CAD_ADDITIVE.zval.gz
zless CARDIoGRAM_C4D_CAD_ADDITIVE.gwas.pip.gzcalculate colocalization with fastENLOC
## check out tutorial https://github.com/xqwen/fastenloc/tree/master/tutorial
export eqtl_annotation_gzipped=$PRE/data/fastenloc/FASTENLOC-gtex_v8.eqtl_annot.vcf.gz
export gwas_data_gzipped=$PRE/data/fastenloc/CARDIoGRAM_C4D_CAD_ADDITIVE.gwas.pip.gz
export TISSUE=Whole_Blood
export FASTENLOCSOFT=fastenloc
##export FASTENLOCSOFT=/Users/owenmelia/projects/finemapping_bin/src/fastenloc/src/fastenloc
mkdir $RESULTS/fastenloc/
cd $RESULTS/fastenloc/
$FASTENLOCSOFT -eqtl $eqtl_annotation_gzipped -gwas $gwas_data_gzipped -t $TISSUE
#[-total_variants total_snp] [-thread n] [-prefix prefix_name] [-s shrinkage]
analyze results
## optional - compare with s-predixcan results
fastenloc_results = load_fastenloc_coloc_result(glue::glue("{RESULTS}/fastenloc/enloc.sig.out"))
spredixcan_and_fastenloc = inner_join(spredixcan_association, fastenloc_results, by=c('gene'='Signal'))
ggplot(spredixcan_and_fastenloc, aes(RCP, -log10(pvalue))) + geom_point()Mendelian randomization methods
run TWMR (for a locus)
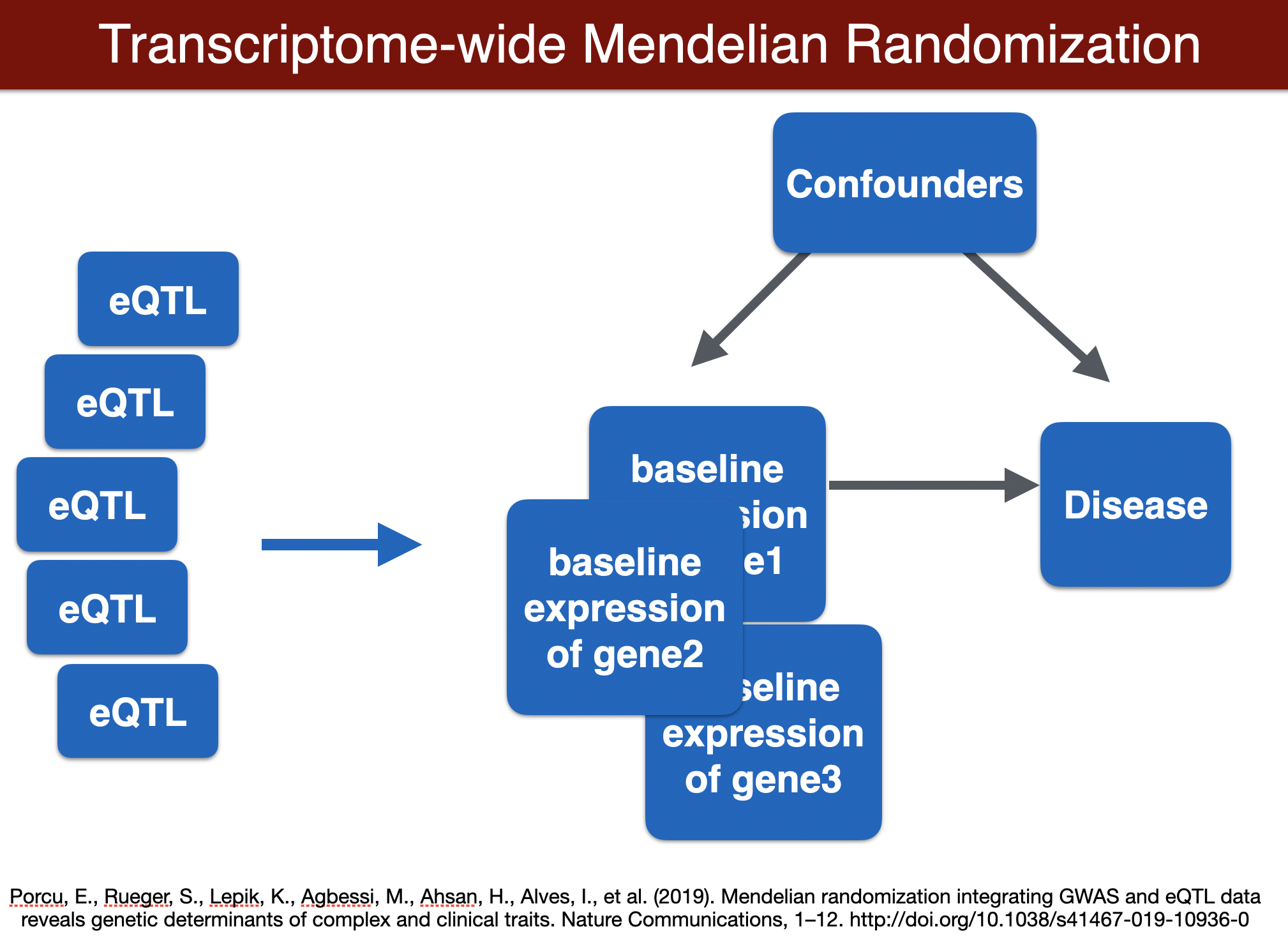
TWMR
GENE=ENSG00000002919
cd $TWMR
R < $TWMR/MR.R --no-save $GENE
cd $PRE
## output: /home/student/QGT-Columbia-HKI/repos/TWMR-master/ENSG00000002919.alpha
sessionInfo()R version 3.6.3 (2020-02-29)
Platform: x86_64-apple-darwin15.6.0 (64-bit)
Running under: macOS Catalina 10.15.2
Matrix products: default
BLAS: /Library/Frameworks/R.framework/Versions/3.6/Resources/lib/libRblas.0.dylib
LAPACK: /Library/Frameworks/R.framework/Versions/3.6/Resources/lib/libRlapack.dylib
locale:
[1] en_US.UTF-8/en_US.UTF-8/en_US.UTF-8/C/en_US.UTF-8/en_US.UTF-8
attached base packages:
[1] stats graphics grDevices utils datasets methods base
loaded via a namespace (and not attached):
[1] workflowr_1.6.2 Rcpp_1.0.4.6 rprojroot_1.3-2 digest_0.6.25
[5] later_1.0.0 R6_2.4.1 backports_1.1.6 git2r_0.26.1
[9] magrittr_1.5 evaluate_0.14 stringi_1.4.6 rlang_0.4.5
[13] fs_1.4.1 promises_1.1.0 whisker_0.4 rmarkdown_2.1
[17] tools_3.6.3 stringr_1.4.0 glue_1.4.1 httpuv_1.5.2
[21] xfun_0.13 yaml_2.2.1 compiler_3.6.3 htmltools_0.4.0
[25] knitr_1.28