results
Last updated: 2021-04-14
Checks: 6 1
Knit directory: funcFinemapping/
This reproducible R Markdown analysis was created with workflowr (version 1.6.2). The Checks tab describes the reproducibility checks that were applied when the results were created. The Past versions tab lists the development history.
The R Markdown file has unstaged changes. To know which version of the R Markdown file created these results, you'll want to first commit it to the Git repo. If you're still working on the analysis, you can ignore this warning. When you're finished, you can run wflow_publish to commit the R Markdown file and build the HTML.
Great job! The global environment was empty. Objects defined in the global environment can affect the analysis in your R Markdown file in unknown ways. For reproduciblity it's best to always run the code in an empty environment.
The command set.seed(20210404) was run prior to running the code in the R Markdown file. Setting a seed ensures that any results that rely on randomness, e.g. subsampling or permutations, are reproducible.
Great job! Recording the operating system, R version, and package versions is critical for reproducibility.
Nice! There were no cached chunks for this analysis, so you can be confident that you successfully produced the results during this run.
Great job! Using relative paths to the files within your workflowr project makes it easier to run your code on other machines.
Great! You are using Git for version control. Tracking code development and connecting the code version to the results is critical for reproducibility.
The results in this page were generated with repository version 66c75b9. See the Past versions tab to see a history of the changes made to the R Markdown and HTML files.
Note that you need to be careful to ensure that all relevant files for the analysis have been committed to Git prior to generating the results (you can use wflow_publish or wflow_git_commit). workflowr only checks the R Markdown file, but you know if there are other scripts or data files that it depends on. Below is the status of the Git repository when the results were generated:
Ignored files:
Ignored: analysis/results.nb.html
Untracked files:
Untracked: data/joint_torus_annotations.txt.gz
Untracked: data/torus_enrichment.est
Untracked: output/constrained_and_OPC.txt
Untracked: output/prop_constrained_variants_with_OCR.txt
Unstaged changes:
Modified: analysis/results.Rmd
Deleted: data/enrichment_table.ext
Note that any generated files, e.g. HTML, png, CSS, etc., are not included in this status report because it is ok for generated content to have uncommitted changes.
These are the previous versions of the repository in which changes were made to the R Markdown (analysis/results.Rmd) and HTML (docs/results.html) files. If you've configured a remote Git repository (see ?wflow_git_remote), click on the hyperlinks in the table below to view the files as they were in that past version.
| File | Version | Author | Date | Message |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| html | 1a76b29 | Jing Gu | 2021-04-06 | Build site. |
| Rmd | ae12e8a | Jing Gu | 2021-04-06 | evaluate sequence constraints |
| html | 752cb39 | Jing Gu | 2021-04-05 | Build site. |
| html | f1c5950 | Jing Gu | 2021-04-05 | Build site. |
| html | d16a5e0 | Jing Gu | 2021-04-05 | Build site. |
| Rmd | 6f7214b | Jing Gu | 2021-04-05 | edit index page |
Fine-mapping with functional annotations as priors has shown improved results in identifying causal variants. This project is to evaluate the utility of novel annotation features and adopt ones that can improve fine mapping results.
Evaluation
GWAS summary statistics
Schizopherenia - Pardinas et al., 2018
- 40675 cases and 64643 controls
- CLOZUK sample + PGC sample (independent)
- 179 independent GWAS significant SNPs mapped to 145 independent loci
- SNPs were imputed using a combination of the 1KGPp3 and UK 10K datasets.
- SNPs were filtered by NFO > 0.6 and MAF > 0.01
- LD-score regression analysis: An LD reference was generated from 1KGPp3 after restricting this dataset to strictly unrelated individuals and retaining only markers with MAF > 0.01.
GWAS QC Procedures
- Current procedures was based on Alan's finemappeR pipeline
- Criteria for filtering gwas SNPs
- Remove all non-biallelic SNPs
- Remove all SNPs with strand-ambiguous alleles (SNPs with A/T, C/G alleles)
- Removed SNPs without rs IDs, duplicated rs IDs or base pair position.
- Removed SNPs not in the reference panels
- Removed SNPs whose base pair positions or alleles doesn’t match the reference panels
- Removed all SNPs on chromosome X, Y, and MT
After filtering, there are around 6 million variants remained.
Plots for GWAS summary statistics
Features
- Sequence constraints:
- context-dependent tolerance scores(CDTS) in percentiles
- A score was computed for each 10bp bin in the genome.
- The lower the score is, the more intolerant to variation is the bin.
Procedures
- GWAS summary statistics was pre-processed to remove sex chromosomes, indels, ambiguous and duplicated SNPs.
- Currently, genotypes from 1kg European samples are used to compute LD between SNPs.
- SNPs in GWAS summary statistics were matched with the reference panel and assigned to in total 1687 independent LD blocks.
- Run TORUS to perform genome-wide enrichment analyses.
Results
All variants were catogrized into whether or not they occur in genomic bins with CDTS up to 1 percentile or 5 percentile.
Examine the CDTS feature
check the proportion of variants with high sequencing constraints that also have functional annotations in brain
| iN_Dopa | iN_GABA | iN_Glut | iPSC | NPC | Any_OCR | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CDTS_1% | 53.7% | 62.6% | 53.2% | 70.8% | 51.9% | 76.4% |
| CDTS_5% | 24.4% | 27.8% | 21.6% | 33.9% | 20.6% | 40.4% |
Check the percent of constrained sequences that overlaps with open chromatin regions from neurons
| iN_Dopa | iN_GABA | iN_Glut | iPSC | NPC | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CDTS_1% | 46.9% | 55.6% | 45.4% | 62.2% | 44.2% |
| CDTS_5% | 18% | 21.3% | 17.4% | 23.8% | 16.9% |
Enrichment analysis for sequence constraints 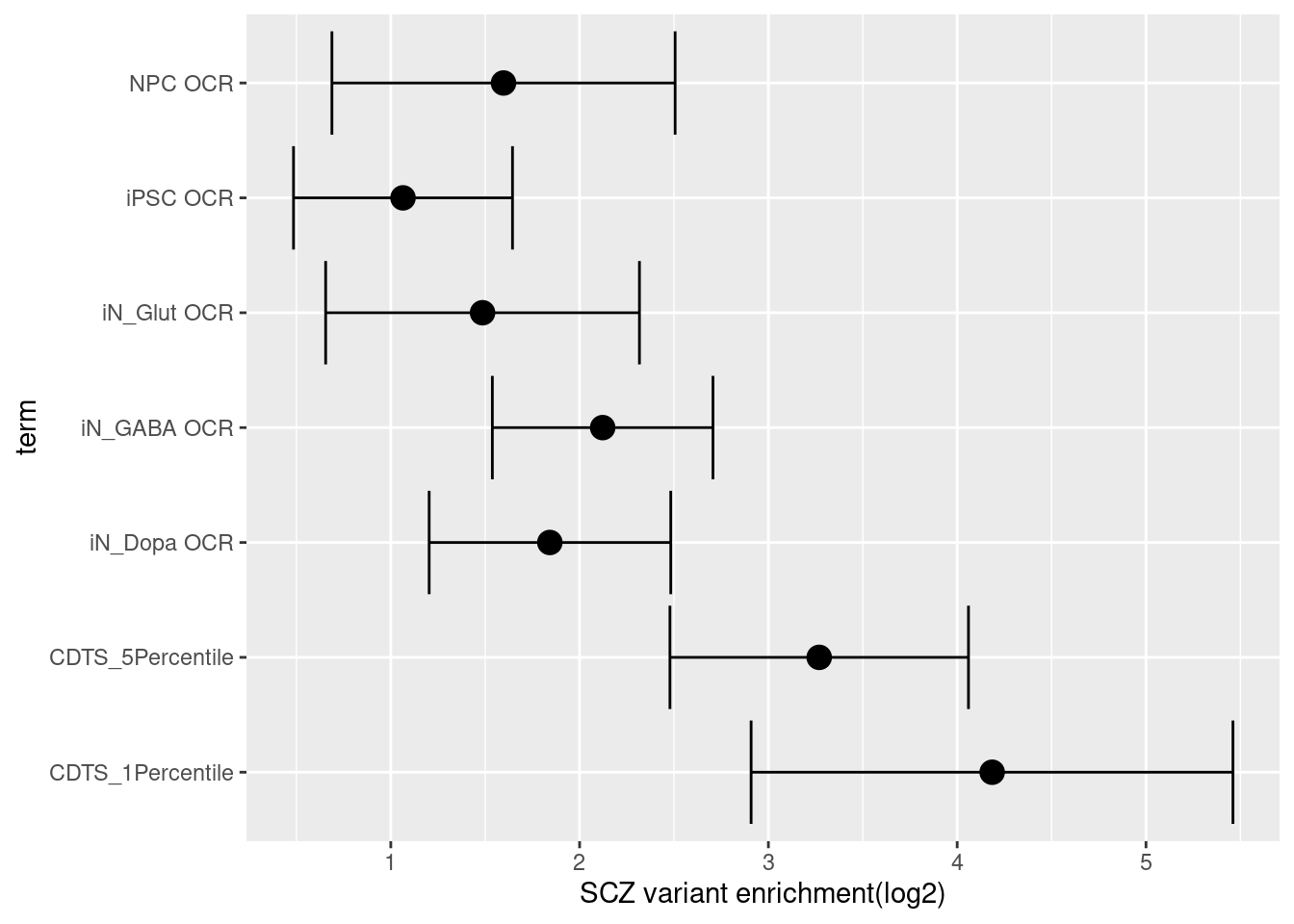 The enrichment estimate has a confience level above zero for CDTS and positive controls. This shows SNPs associated with SCZ are on average ~ 9 fold enriched in genomic bins with up to 5 percentile of CDTS.
The enrichment estimate has a confience level above zero for CDTS and positive controls. This shows SNPs associated with SCZ are on average ~ 9 fold enriched in genomic bins with up to 5 percentile of CDTS.
sessionInfo()R version 4.0.4 (2021-02-15)
Platform: x86_64-pc-linux-gnu (64-bit)
Running under: Scientific Linux 7.4 (Nitrogen)
Matrix products: default
BLAS/LAPACK: /software/openblas-0.3.13-el7-x86_64/lib/libopenblas_haswellp-r0.3.13.so
locale:
[1] LC_CTYPE=en_US.UTF-8 LC_NUMERIC=C
[3] LC_TIME=en_US.UTF-8 LC_COLLATE=en_US.UTF-8
[5] LC_MONETARY=en_US.UTF-8 LC_MESSAGES=en_US.UTF-8
[7] LC_PAPER=en_US.UTF-8 LC_NAME=C
[9] LC_ADDRESS=C LC_TELEPHONE=C
[11] LC_MEASUREMENT=en_US.UTF-8 LC_IDENTIFICATION=C
attached base packages:
[1] stats graphics grDevices utils datasets methods base
other attached packages:
[1] ggplot2_3.3.3 knitr_1.31 data.table_1.14.0 workflowr_1.6.2
loaded via a namespace (and not attached):
[1] Rcpp_1.0.6 pillar_1.5.0 compiler_4.0.4 bslib_0.2.4
[5] later_1.1.0.1 jquerylib_0.1.3 git2r_0.28.0 highr_0.8
[9] tools_4.0.4 digest_0.6.27 gtable_0.3.0 jsonlite_1.7.2
[13] evaluate_0.14 lifecycle_1.0.0 tibble_3.0.6 pkgconfig_2.0.3
[17] rlang_0.4.10 DBI_1.1.1 yaml_2.2.1 xfun_0.21
[21] withr_2.4.1 dplyr_1.0.4 stringr_1.4.0 generics_0.1.0
[25] fs_1.5.0 vctrs_0.3.6 sass_0.3.1 tidyselect_1.1.0
[29] rprojroot_2.0.2 grid_4.0.4 glue_1.4.2 R6_2.5.0
[33] fansi_0.4.2 rmarkdown_2.7 farver_2.0.3 purrr_0.3.4
[37] magrittr_2.0.1 whisker_0.4 scales_1.1.1 promises_1.2.0.1
[41] ellipsis_0.3.1 htmltools_0.5.1.1 assertthat_0.2.1 colorspace_2.0-0
[45] httpuv_1.5.5 labeling_0.4.2 utf8_1.1.4 stringi_1.5.3
[49] munsell_0.5.0 crayon_1.4.1