HBA2025_results
Paloma
2025-01-27
Last updated: 2025-03-08
Checks: 6 1
Knit directory: QUAIL-Mex/
This reproducible R Markdown analysis was created with workflowr (version 1.7.1). The Checks tab describes the reproducibility checks that were applied when the results were created. The Past versions tab lists the development history.
The R Markdown file has unstaged changes. To know which version of
the R Markdown file created these results, you’ll want to first commit
it to the Git repo. If you’re still working on the analysis, you can
ignore this warning. When you’re finished, you can run
wflow_publish to commit the R Markdown file and build the
HTML.
Great job! The global environment was empty. Objects defined in the global environment can affect the analysis in your R Markdown file in unknown ways. For reproduciblity it’s best to always run the code in an empty environment.
The command set.seed(20241009) was run prior to running
the code in the R Markdown file. Setting a seed ensures that any results
that rely on randomness, e.g. subsampling or permutations, are
reproducible.
Great job! Recording the operating system, R version, and package versions is critical for reproducibility.
Nice! There were no cached chunks for this analysis, so you can be confident that you successfully produced the results during this run.
Great job! Using relative paths to the files within your workflowr project makes it easier to run your code on other machines.
Great! You are using Git for version control. Tracking code development and connecting the code version to the results is critical for reproducibility.
The results in this page were generated with repository version 7866aba. See the Past versions tab to see a history of the changes made to the R Markdown and HTML files.
Note that you need to be careful to ensure that all relevant files for
the analysis have been committed to Git prior to generating the results
(you can use wflow_publish or
wflow_git_commit). workflowr only checks the R Markdown
file, but you know if there are other scripts or data files that it
depends on. Below is the status of the Git repository when the results
were generated:
Ignored files:
Ignored: .DS_Store
Ignored: .RData
Ignored: .Rhistory
Ignored: .Rproj.user/
Ignored: analysis/.DS_Store
Ignored: analysis/.RData
Ignored: analysis/.Rhistory
Ignored: analysis/Hrs_by_HWISE score.png
Ignored: code/.DS_Store
Ignored: data/.DS_Store
Unstaged changes:
Modified: analysis/HBA2025_Analyses.Rmd
Modified: analysis/HBA2025_cleaning.Rmd
Modified: data/Cleaned_Dataset_Screening_HWISE_PSS_V3.csv
Note that any generated files, e.g. HTML, png, CSS, etc., are not included in this status report because it is ok for generated content to have uncommitted changes.
These are the previous versions of the repository in which changes were
made to the R Markdown (analysis/HBA2025_Analyses.Rmd) and
HTML (docs/HBA2025_Analyses.html) files. If you’ve
configured a remote Git repository (see ?wflow_git_remote),
click on the hyperlinks in the table below to view the files as they
were in that past version.
| File | Version | Author | Date | Message |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rmd | 7866aba | Paloma | 2025-03-07 | newplots |
| html | 7866aba | Paloma | 2025-03-07 | newplots |
| Rmd | 3704a5a | Paloma | 2025-03-04 | add more vars |
| html | 3704a5a | Paloma | 2025-03-04 | add more vars |
Introduction
Here you will find the code used to obtain results shown in the annual meeting of the HBA, 2025.
Abstract:
Coping with water insecurity: women’s strategies and emotional responses in Iztapalapa, Mexico City
Water insecurity in urban areas presents distinctive challenges, particularly in marginalized communities. While past studies have documented how households adapt to poor water services, many of these coping strategies come at a significant personal cost. Here we examine the coping strategies and emotional impacts of unreliable water services among 400 women in Iztapalapa, Mexico City. Data were collected through surveys over the Fall of 2022 and Spring of 2023. We assessed household water access, water management practices, and emotional responses to local water services.
Results indicate that during acute water shortages, women can spend extended periods (several hours, or sometimes days) waiting for water trucks. Additionally, 57% of respondents reported feeling frustrated or angry about their water situation, while around 20% experienced family conflicts over water use or community-level conflicts around water management, often involving water vendors or government services.
This study offers one of the first in-depth examinations of how water insecurity specifically affects women in Iztapalapa, a densely populated region of Mexico City with severe water access challenges. The findings highlight the urgent need for policy interventions that address water insecurity with a gender-sensitive approach, recognizing the disproportionate burden placed on women as primary water managers in their households.
# Ensure HW_TOTAL is numeric
data$HW_TOTAL <- as.numeric(data$HW_TOTAL)
# Categorize HW_TOTAL into four groups
data <- data %>%
mutate(HW_TOTAL_category = case_when(
HW_TOTAL >= 0 & HW_TOTAL <= 2 ~ "No-to-Marginal",
HW_TOTAL >= 3 & HW_TOTAL <= 11 ~ "Low",
HW_TOTAL >= 12 & HW_TOTAL <= 23 ~ "Moderate",
HW_TOTAL >= 24 & HW_TOTAL <= 36 ~ "High",
TRUE ~ NA_character_ # Assign NA if value is missing or out of range
))
# Convert to factor to maintain categorical order
data$HW_TOTAL_category <- factor(data$HW_TOTAL_category,
levels = c("No-to-Marginal", "Low", "Moderate", "High"))
# HWISE scores
summary(data$HW_TOTAL) Min. 1st Qu. Median Mean 3rd Qu. Max. NA's
0.000 3.000 8.000 8.419 12.000 27.000 11 # Check the new variable distribution
table(data$HW_TOTAL_category)
No-to-Marginal Low Moderate High
76 205 104 6 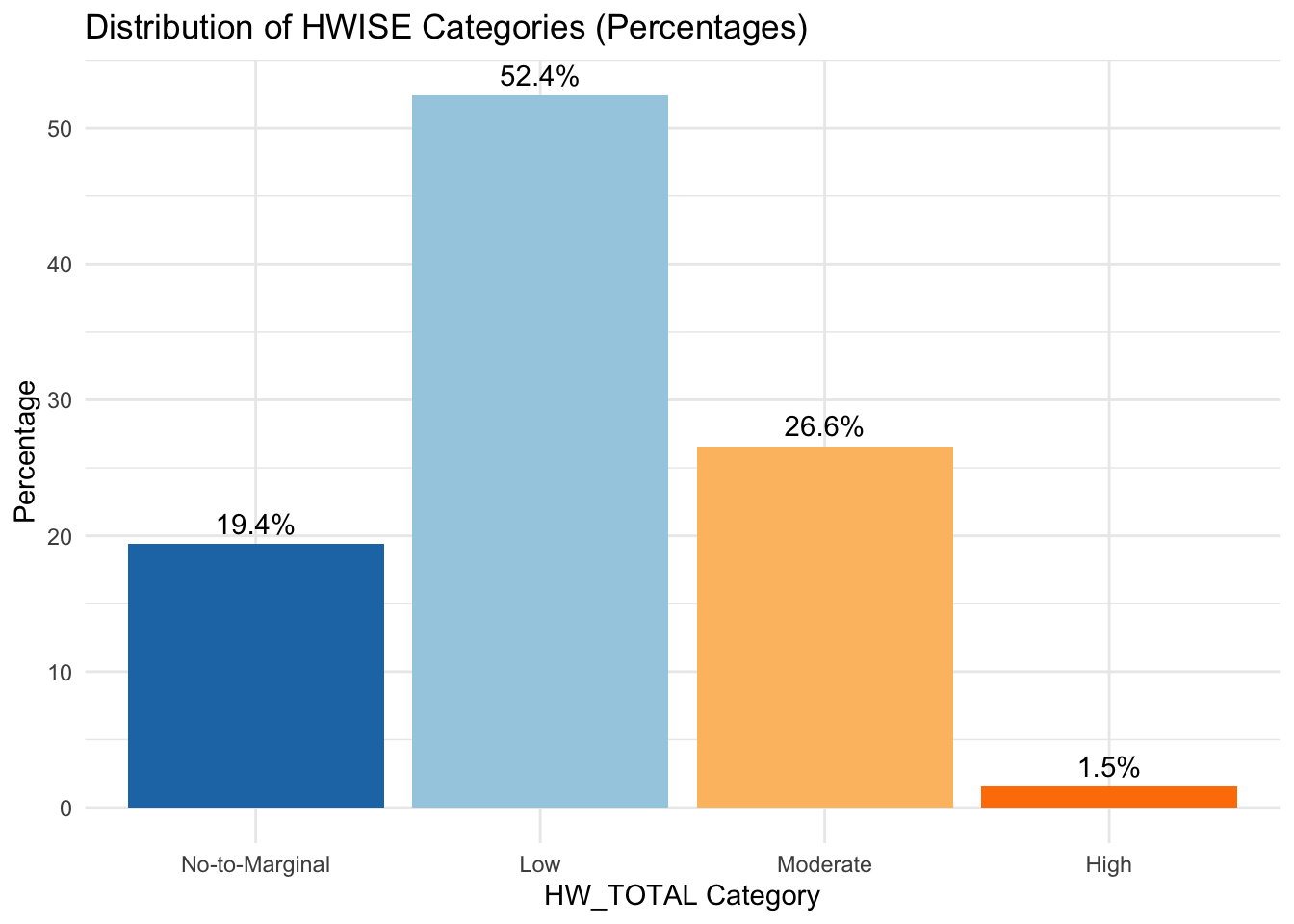
| Version | Author | Date |
|---|---|---|
| 7866aba | Paloma | 2025-03-07 |
| Version | Author | Date |
|---|---|---|
| 7866aba | Paloma | 2025-03-07 |
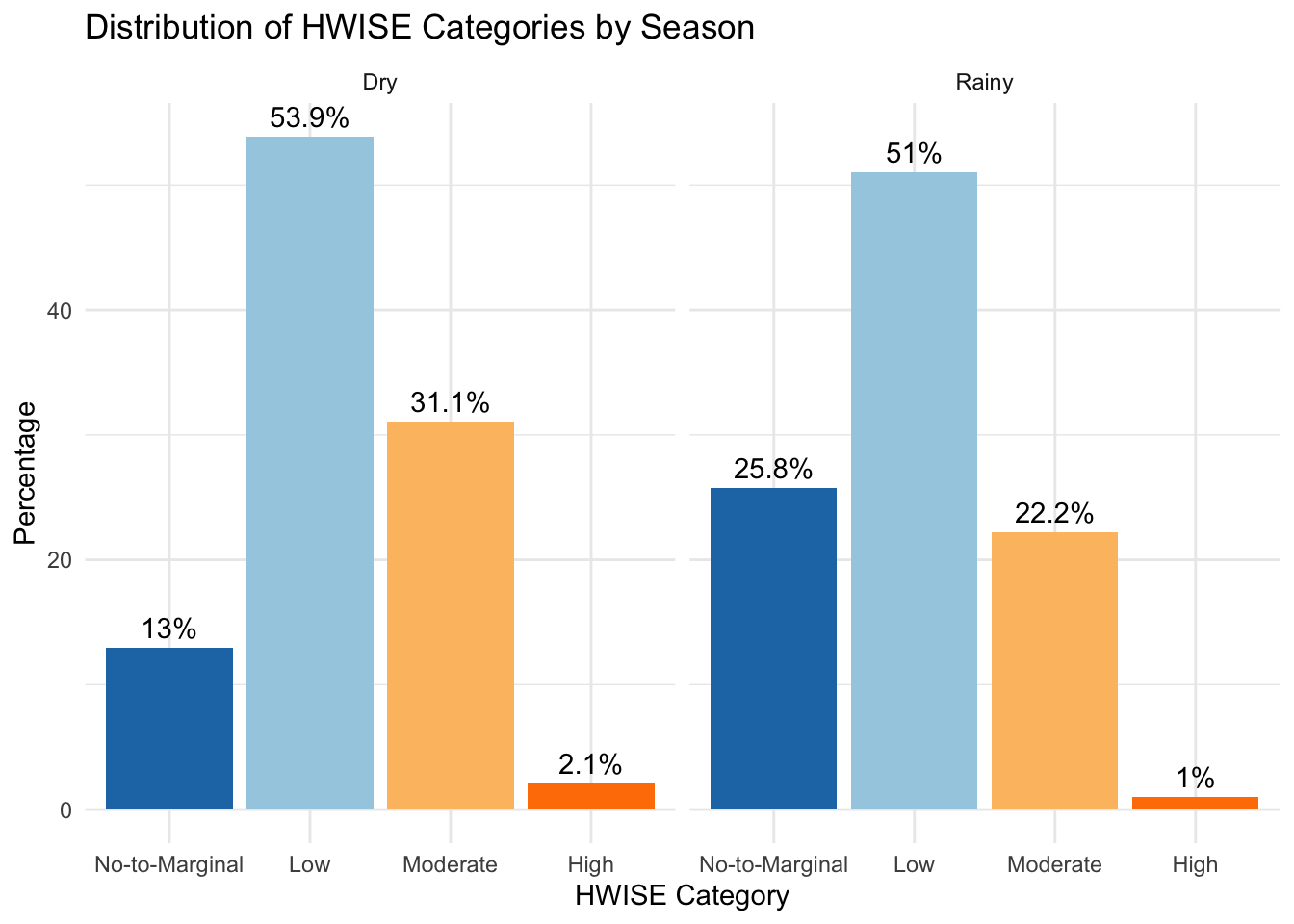
Min. 1st Qu. Median Mean 3rd Qu. Max. NA's
0.000 5.000 9.000 9.715 14.000 27.000 6 Min. 1st Qu. Median Mean 3rd Qu. Max. NA's
0.000 2.000 6.000 7.157 11.000 27.000 8
No-to-Marginal Low Moderate High
25 104 60 4
No-to-Marginal Low Moderate High
51 101 44 2 Rainy season to dry season
data <- read.csv(file.path(data_path, "Cleaned_Dataset_Screening_HWISE_PSS_V3.csv"),
stringsAsFactors = FALSE,
na.strings = c("", "N/A", "NA", "pending"))
# Define Rainy (Fall = 1) and Dry (Spring = 0) seasons
data <- data %>%
mutate(Season_Type = case_when(
SEASON == 1 ~ "Rainy",
SEASON == 0 ~ "Dry"
))
# Convert Season_Type to a factor
data$Season_Type <- factor(data$Season_Type, levels = c("Rainy", "Dry"))
# Categorize HW_TOTAL into four groups
data <- data %>%
filter(!is.na(HW_TOTAL)) %>% # Remove missing values
mutate(HW_TOTAL_category = case_when(
HW_TOTAL >= 0 & HW_TOTAL <= 2 ~ "No-to-Marginal",
HW_TOTAL >= 3 & HW_TOTAL <= 11 ~ "Low",
HW_TOTAL >= 12 & HW_TOTAL <= 23 ~ "Moderate",
HW_TOTAL >= 24 & HW_TOTAL <= 36 ~ "High"
))
# Convert to factor with correct ordering
data$HW_TOTAL_category <- factor(data$HW_TOTAL_category,
levels = c("No-to-Marginal", "Low", "Moderate", "High"))
# Calculate the percentage for each category within each season
hw_season_counts <- data %>%
filter(!is.na(HW_TOTAL_category)) %>% # Ensure no NA categories
group_by(Season_Type, HW_TOTAL_category) %>%
summarise(Count = n(), .groups = 'drop') %>%
group_by(Season_Type) %>%
mutate(Percentage = (Count / sum(Count)) * 100)
# Reshape data to calculate the percentage difference (Dry - Rainy)
hw_diff <- hw_season_counts %>%
select(Season_Type, HW_TOTAL_category, Percentage) %>%
spread(Season_Type, Percentage) %>% # Convert to wide format
mutate(Difference = Dry - Rainy) # Compute difference from Rainy to Dry
# Create the bar plot showing the percentage difference
ggplot(hw_diff, aes(x = HW_TOTAL_category, y = Difference, fill = Difference > 0)) +
geom_bar(stat = "identity") + # Use precomputed differences
theme_minimal() +
labs(title = "Change in HW_TOTAL Category Percentages (Rainy to Dry Season)",
x = "HW_TOTAL Category",
y = "Percentage Difference (Rainy to Dry season)") +
scale_fill_manual(values = c("#1f78b4", "#ff7f00"), labels = c("Decrease", "Increase")) + # Assign colors
theme(legend.position = "right") + # Keep legend
geom_text(aes(label = paste0(round(Difference, 1), "%")), vjust = -0.5) # Add percentage labels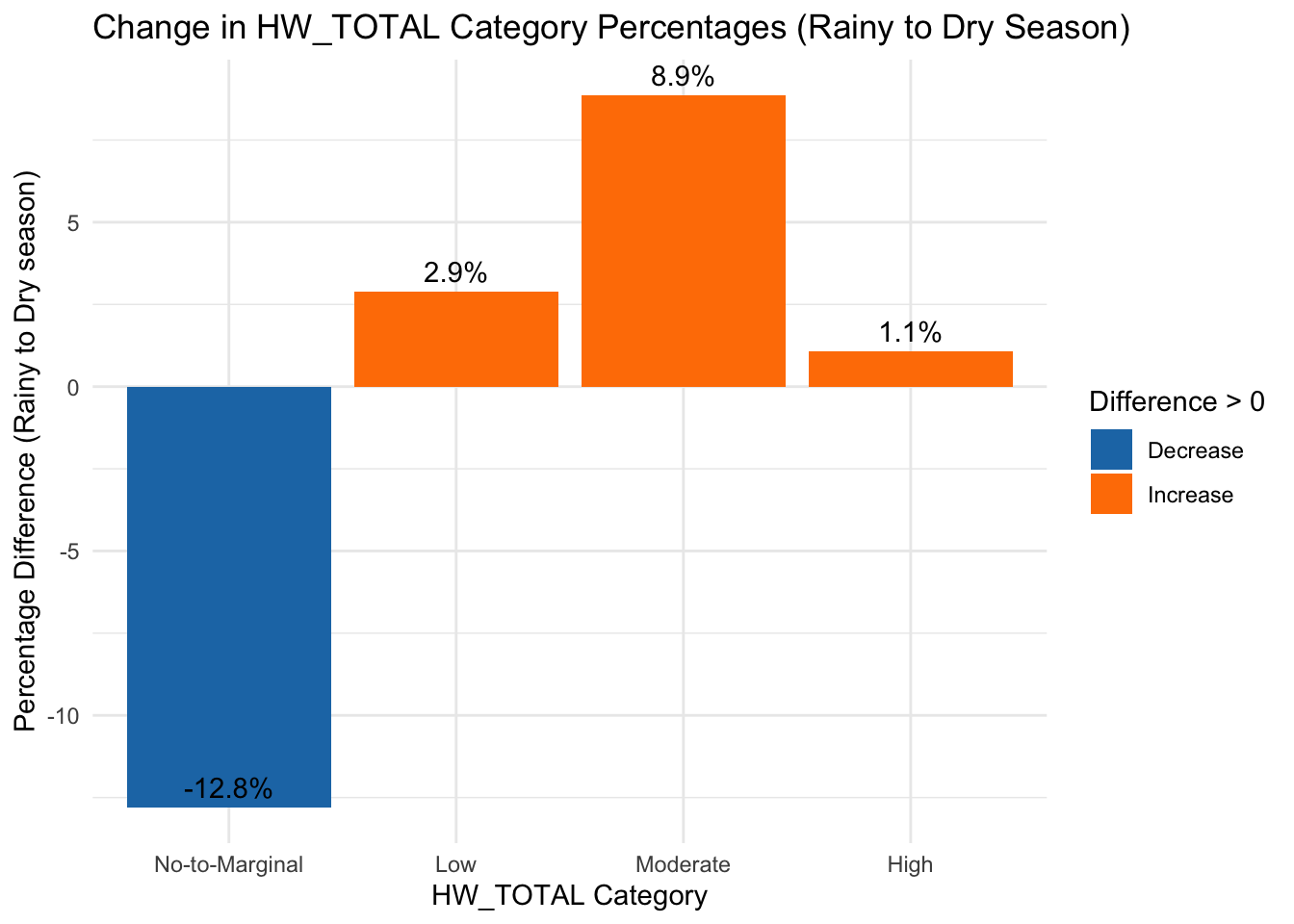
BOXPLOTS
data <- read.csv(file.path(data_path, "Cleaned_Dataset_Screening_HWISE_PSS_V3.csv"),
stringsAsFactors = FALSE,
na.strings = c("", "N/A", "NA", "pending"))
# Categorize HW_TOTAL into four groups
data <- data %>%
filter(!is.na(HW_TOTAL)) %>% # Remove missing values
mutate(HW_TOTAL_category = case_when(
HW_TOTAL >= 0 & HW_TOTAL <= 2 ~ "No-to-Marginal",
HW_TOTAL >= 3 & HW_TOTAL <= 11 ~ "Low",
HW_TOTAL >= 12 & HW_TOTAL <= 23 ~ "Moderate",
HW_TOTAL >= 24 & HW_TOTAL <= 36 ~ "High"
))
# Convert to factor with proper order
data$HW_TOTAL_category <- factor(data$HW_TOTAL_category,
levels = c("No-to-Marginal", "Low", "Moderate", "High"))
# Count the number of data points per HW_TOTAL category
summary_stats <- data %>%
group_by(HW_TOTAL_category) %>%
summarise(Count = n(), SD = sd(HRS_WEEK, na.rm = TRUE), .groups = 'drop')
hrs.w <- data$HRS_WEEK
means <- aggregate(hrs.w ~ HW_TOTAL_category, data, mean)
means$hrs.w <- round(means$hrs.w, 2)
# Define color palette
color_palette <- c("#1f78b4", "#a6cee3", "#fdbf6f", "#ff7f00")
# Create box-and-whisker plot with individual data points
ggplot(data, aes(x = HW_TOTAL_category,
y = HRS_WEEK,
fill = HW_TOTAL_category)) +
geom_jitter(aes(color = HW_TOTAL_category),
size = 1, width = 0.25) +
# Jitter adds individual data points
geom_violin(alpha = 0.6, width = 1.4) + # violin
geom_boxplot(outlier.shape = 1, alpha = 0.5,
width = 0.08, color = "grey30") + # Boxplot
geom_text(data = summary_stats,
aes(x = HW_TOTAL_category,
y = max(data$HRS_WEEK,
na.rm = TRUE) + 10,
label = paste0("SD = ", round(SD, 1))),
size = 4, fontface = "bold") + # Add SD text annotations above the boxes
geom_text(data = means,
aes(label = hrs.w, y = hrs.w + 1, hjust=-1),
size = 3, color = "darkred") + #adds average labels
theme_minimal() +
labs(title = "HRS_WEEK by HWISE Category",
x = "HWISE",
y = "Hours of Water Supply per Week") +
scale_fill_manual(values = color_palette) + # Custom colors for boxes
scale_color_manual(values = color_palette) + # Custom colors for points +
stat_summary(fun.y=mean, geom="point", shape=23,
size=5, color="darkred", fill="darkred") +
theme(legend.position = "none",
axis.text = element_text(size = 10)) + # Remove legend for clarity
scale_x_discrete(labels = paste0(summary_stats$HW_TOTAL_category,
" (n=", summary_stats$Count, ")")) # Add count to x-axis labelsWarning: The `fun.y` argument of `stat_summary()` is deprecated as of ggplot2 3.3.0.
ℹ Please use the `fun` argument instead.
This warning is displayed once every 8 hours.
Call `lifecycle::last_lifecycle_warnings()` to see where this warning was
generated.Warning: Removed 37 rows containing non-finite outside the scale range
(`stat_ydensity()`).Warning: Removed 37 rows containing non-finite outside the scale range
(`stat_boxplot()`).Warning: Removed 37 rows containing non-finite outside the scale range
(`stat_summary()`).Warning: `position_dodge()` requires non-overlapping x intervals.Warning: Removed 37 rows containing missing values or values outside the scale range
(`geom_point()`).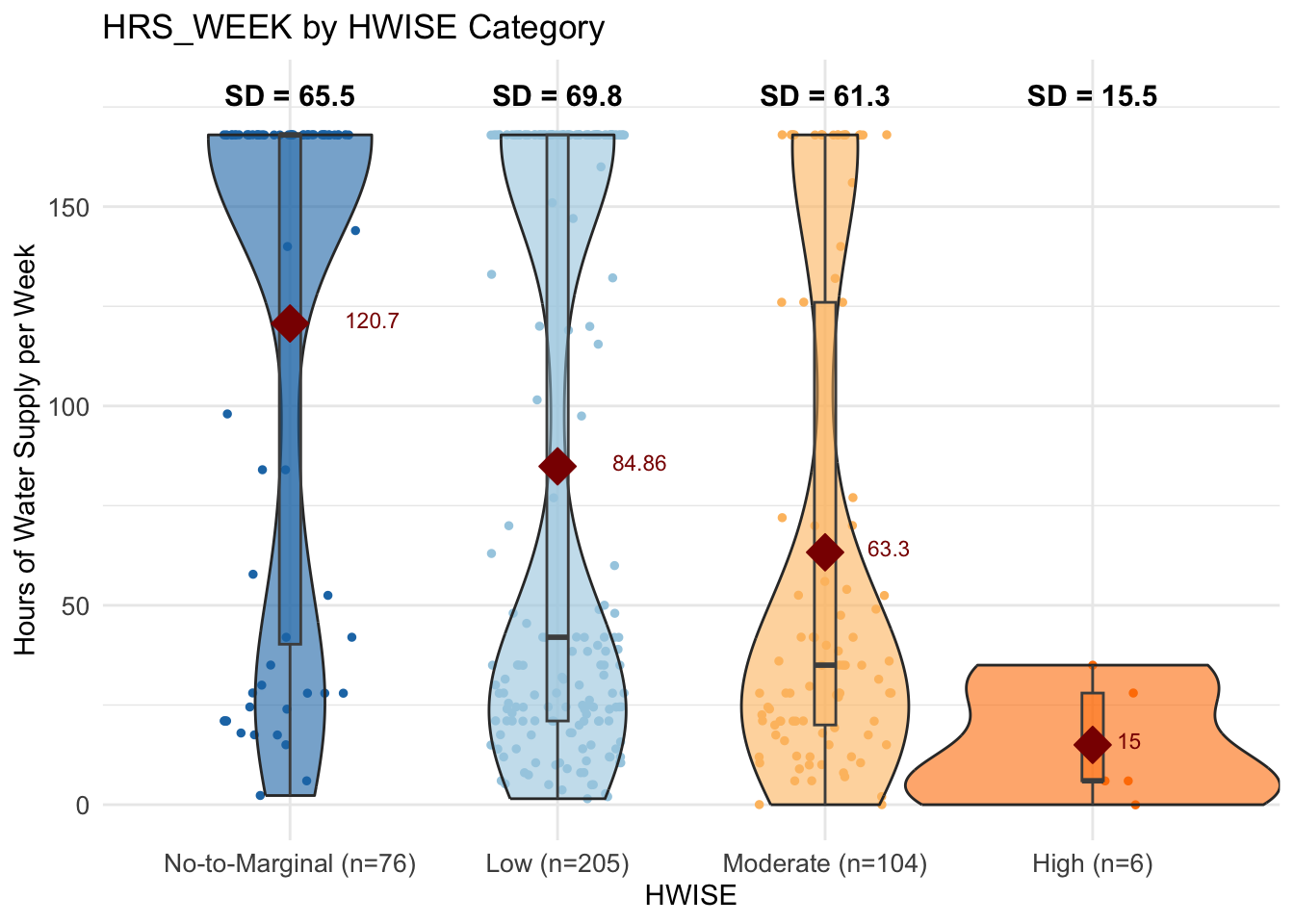
# Categorize HW_TOTAL into groups
data <- data %>%
filter(!is.na(MX28_WQ_COMP)) %>% # Remove missing values
mutate(MX28_WQ_COMP_category = case_when(
MX28_WQ_COMP == 0 ~ "Worse",
MX28_WQ_COMP == 1 ~ "Same",
MX28_WQ_COMP == 2 ~ "Better",
))
# Convert to factor with proper order
data$MX28_WQ_COMP_category <- factor(data$MX28_WQ_COMP_category,
levels = c("Worse", "Same", "Better"))
# Count the number of data points per HW_TOTAL category
summary_stats <- data %>%
group_by(MX28_WQ_COMP_category) %>%
summarise(Count = n(), SD = sd(HRS_WEEK, na.rm = TRUE), .groups = 'drop')
hrs.w <- data$HRS_WEEK
means <- aggregate(hrs.w ~ MX28_WQ_COMP_category, data, mean)
means$hrs.w <- round(means$hrs.w, 2)
color_palette <- c("#ff7f00", "#a6cee3", "#1f78b4")
# Create box-and-whisker plot with individual data points
ggplot(data, aes(x = MX28_WQ_COMP_category,
y = HRS_WEEK,
fill = MX28_WQ_COMP_category)) +
geom_jitter(aes(color = MX28_WQ_COMP_category),
size = 1, width = 0.25) +
# Jitter adds individual data points
geom_violin(alpha = 0.6, width = 1) + # violin
geom_boxplot(outlier.shape = 1, alpha = 0.5,
width = 0.08, color = "grey30") + # Boxplot
geom_text(data = means,
aes(label = hrs.w, y = hrs.w + 1, hjust=-0.8),
size = 3, color = "darkred") + #adds average labels
theme_minimal() +
labs(title = "HRS_WEEK by Group considering their water supply as worse, same or better than in other parts of the city",
x = "",
y = "Hours of Water Supply per Week") +
scale_fill_manual(values = color_palette) + # Custom colors for boxes
scale_color_manual(values = color_palette) + # Custom colors for points +
stat_summary(fun.y=mean, geom="point", shape=23,
size=5, color="darkred", fill="darkred") +
theme(legend.position = "none",
axis.text = element_text(size = 10)) +
scale_x_discrete(labels = paste0(summary_stats$MX28_WQ_COMP_category,
" (n=", summary_stats$Count, ")")) Warning: Removed 37 rows containing non-finite outside the scale range
(`stat_ydensity()`).Warning: Removed 37 rows containing non-finite outside the scale range
(`stat_boxplot()`).Warning: Removed 37 rows containing non-finite outside the scale range
(`stat_summary()`).Warning: Removed 37 rows containing missing values or values outside the scale range
(`geom_point()`).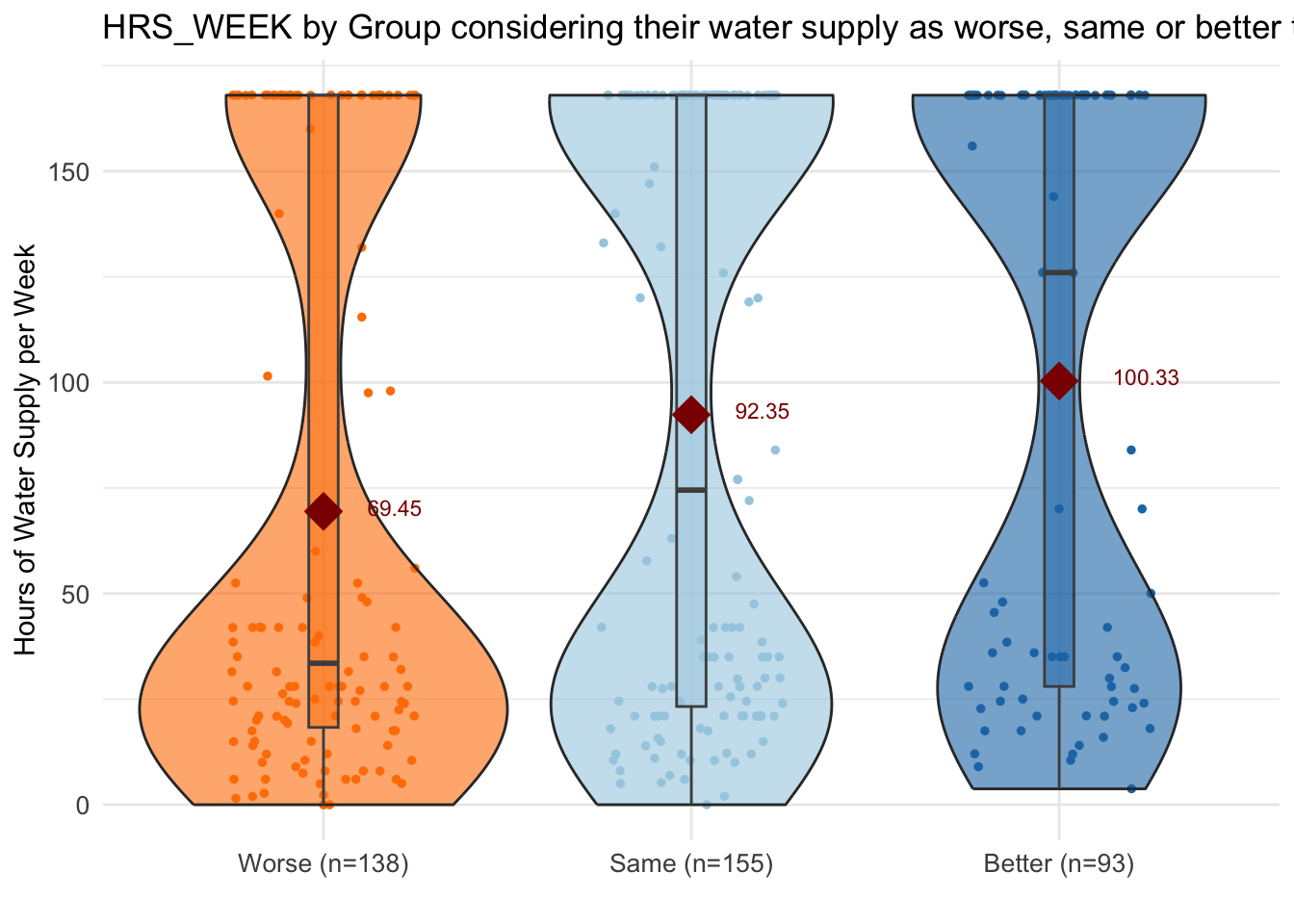
# Count the number of data points per HW_TOTAL category
summary_stats <- data %>%
group_by(MX28_WQ_COMP_category) %>%
summarise(Count = n(), SD = sd(HW_TOTAL, na.rm = TRUE), .groups = 'drop')
hrs.w <- data$HW_TOTAL
means <- aggregate(hrs.w ~ MX28_WQ_COMP_category, data, mean)
means$hrs.w <- round(means$hrs.w, 2)
# Create box-and-whisker plot with individual data points
ggplot(data, aes(x = MX28_WQ_COMP_category,
y = HW_TOTAL,
fill = MX28_WQ_COMP_category)) +
geom_jitter(aes(color = MX28_WQ_COMP_category),
size = 1, width = 0.25) +
# Jitter adds individual data points
geom_violin(alpha = 0.4, width = 1) + # violin
geom_boxplot(outlier.shape = 1, alpha = 0.3,
width = 0.15, color = "grey30") + # Boxplot
geom_text(data = means,
aes(label = hrs.w, y = hrs.w + 0.8, hjust=-0.85),
size = 3, color = "darkred") + #adds average labels
geom_text(data = summary_stats,
aes(x = MX28_WQ_COMP_category,
y = max(data$HW_TOTAL,
na.rm = TRUE) + 2,
label = paste0("SD = ", round(SD, 1))),
size = 4, fontface = "bold") + # Add SD text annotations above the boxes
theme_minimal() +
labs(title = "HWISE score by Group considering their water supply as worse, same or better than in other parts of the city",
x = "",
y = "HWISE score") +
scale_fill_manual(values = color_palette) + # Custom colors for boxes
scale_color_manual(values = color_palette) + # Custom colors for points +
stat_summary(fun.y=mean, geom="point", shape=23,
size=5, color="darkred", fill="darkred") +
theme(legend.position = "none",
axis.text = element_text(size = 10)) +
scale_x_discrete(labels = paste0(summary_stats$MX28_WQ_COMP_category,
" (n=", summary_stats$Count, ")")) 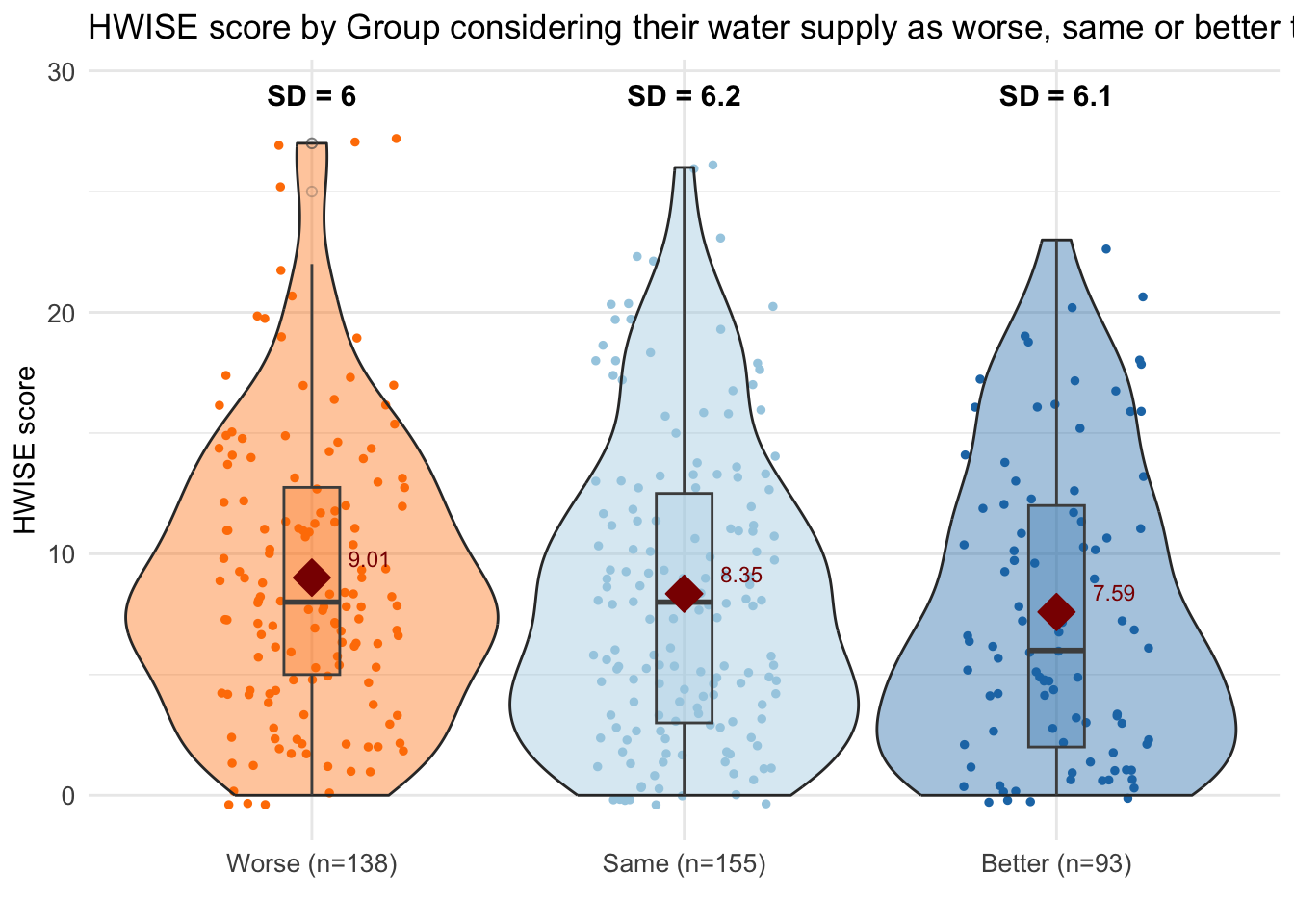
# Load the dataset
data <- read.csv(file.path(data_path, "Cleaned_Dataset_Screening_HWISE_PSS_V3.csv"),
stringsAsFactors = FALSE,
na.strings = c("", "N/A", "NA", "pending"))
# Keep only relevant columns (HW_ questions and HRS_WEEK)
data_long <- data %>%
select(HW_TOTAL, HRS_WEEK) %>%
pivot_longer(cols = HW_TOTAL, names_to = "HW_Question", values_to = "Response") %>%
filter(!is.na(HRS_WEEK), !is.na(Response)) # Remove NAs
# Compute mean HRS_WEEK for each HW_Question & Response category
summary_stats <- data_long %>%
group_by(HW_Question, Response) %>%
summarise(Mean_HRS_WEEK = mean(HRS_WEEK, na.rm = TRUE), Count = n(), SD = sd(HRS_WEEK, na.rm = TRUE), .groups = 'drop')
# Generate boxplots with mean values
ggplot(data_long, aes(x = as.factor(Response), y = HRS_WEEK, fill = as.factor(Response))) +
geom_jitter(aes(color = as.factor(Response)), size = 1.5, width = 0.2, alpha = 0.2) +
geom_boxplot(outlier.shape = NA, width = 0.5, alpha = 0.4, color = "gray70") + # Thinner boxes
geom_point(data = summary_stats, aes(x = as.factor(Response), y = Mean_HRS_WEEK),
color = "black", size = 1.5) + # Add red dot for mean value
geom_text(data = summary_stats, aes(x = as.factor(Response), y = Mean_HRS_WEEK,
label = round(Mean_HRS_WEEK, 0)), color = "black", hjust = -0.35, size = 2.8) + # Add numeric mean label
theme_minimal() +
labs(title = "Distribution of HRS_WEEK by total HWISE score",
x = "HWISE score",
y = "Hours of Water Supply per Week") +
# scale_fill_manual(values = color_palette) + # Custom colors for boxes
# scale_color_manual(values = color_palette) + # Custom colors for points
theme(legend.position = "none", axis.text.x = element_text(size = 5, angle = 45)) +
scale_x_discrete(labels = paste0(summary_stats$Response,
" (n=", summary_stats$Count, ")")) 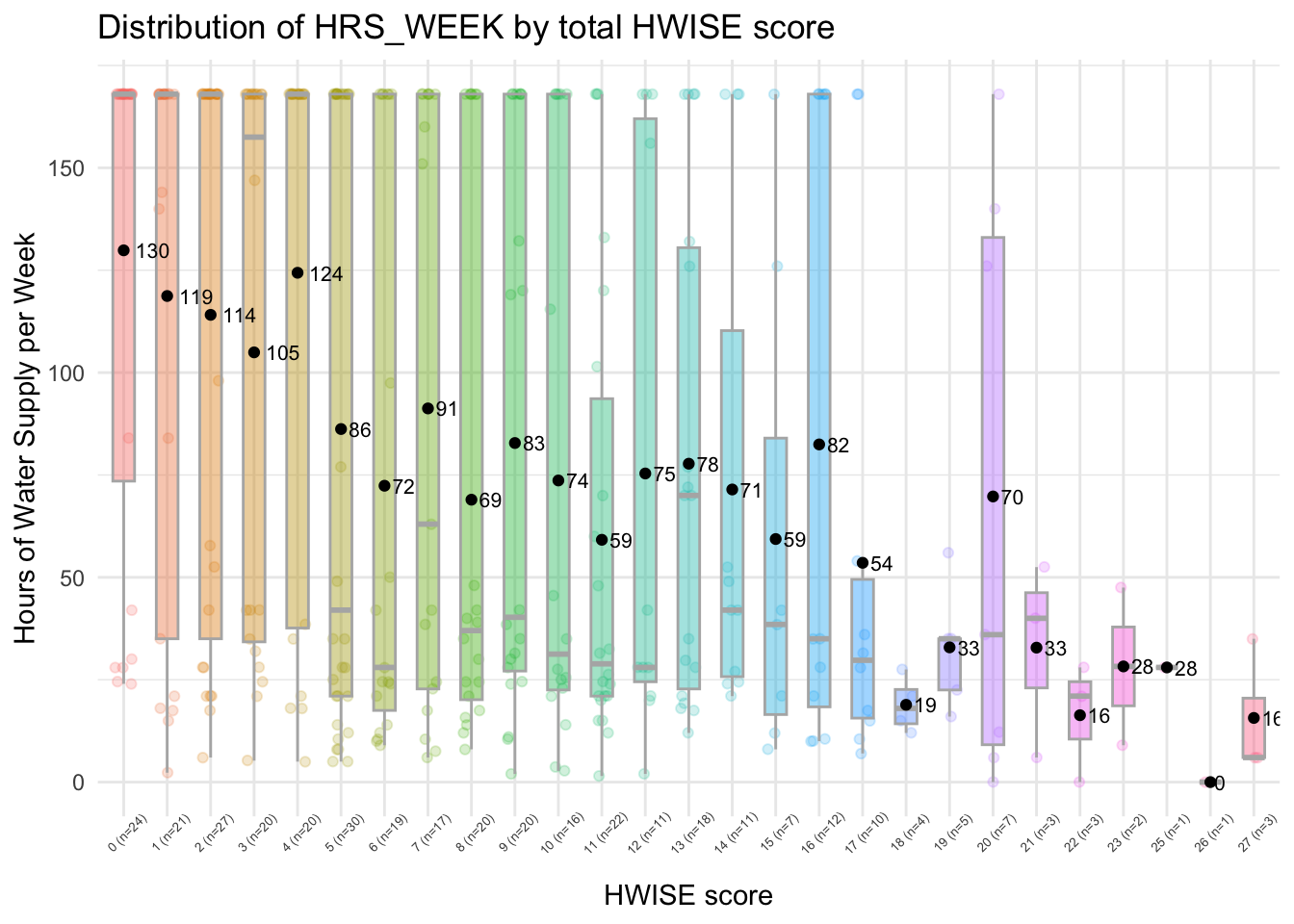
| Version | Author | Date |
|---|---|---|
| 3704a5a | Paloma | 2025-03-04 |
# Define color palette
#color_palette <- c("#1f78b4", "#a6cee3", "#fdbf6f", "#ff7f00")
# Generate boxplots
ggplot(data_long, aes(x = as.factor(Response), y = HRS_WEEK, fill = as.factor(Response))) +
geom_boxplot(outlier.shape = NA, width = 0.5, alpha = 0.7) + # Thinner boxes
geom_jitter(aes(color = as.factor(Response)), size = 1.5, width = 0.2, alpha = 0.5) +
theme_minimal() +
labs(title = "Distribution of HRS_WEEK by HW_ Questions",
x = "Response",
y = "Hours of Water Supply per Week") +
# scale_fill_manual(values = color_palette) + # Custom colors for boxes
# scale_color_manual(values = color_palette) + # Custom colors for points
theme(legend.position = "none")# + # Remove legend for clarity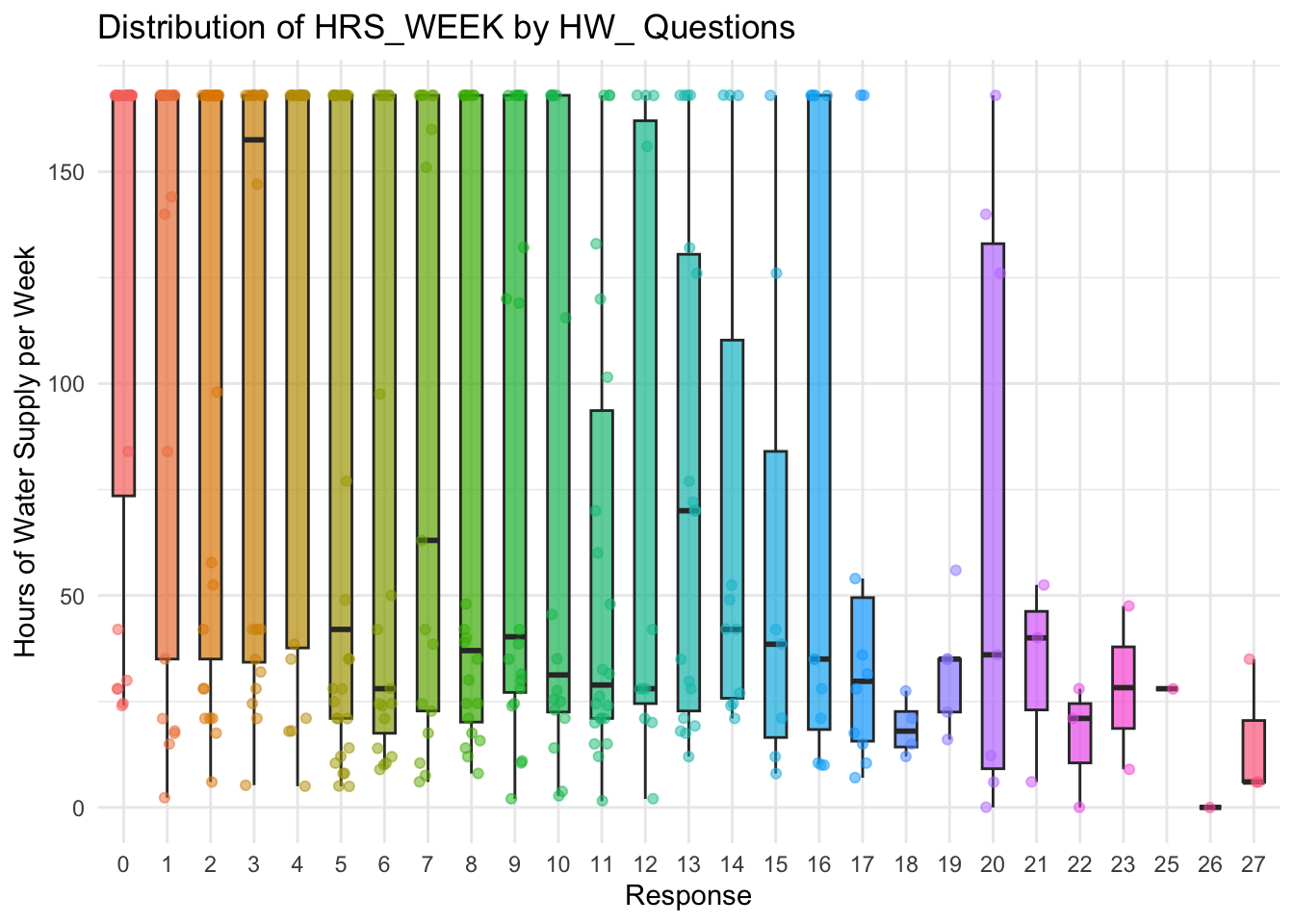
| Version | Author | Date |
|---|---|---|
| 3704a5a | Paloma | 2025-03-04 |
# Load the dataset
data <- read.csv(file.path(data_path, "Cleaned_Dataset_Screening_HWISE_PSS_V3.csv"),
stringsAsFactors = FALSE,
na.strings = c("", "N/A", "NA", "pending"))
data <- data %>%
select(-HW_TOTAL)
# Select all columns that start with "HW_"
hw_vars <- grep("^HW_", names(data), value = TRUE)
# Keep only relevant columns (HW_ questions and HRS_WEEK)
data_long <- data %>%
select(all_of(hw_vars), HRS_WEEK) %>%
pivot_longer(cols = all_of(hw_vars), names_to = "HW_Question", values_to = "Response") %>%
filter(!is.na(HRS_WEEK), !is.na(Response)) # Remove NAs
# Compute mean HRS_WEEK for each HW_Question & Response category
mean_values <- data_long %>%
group_by(HW_Question, Response) %>%
summarise(Mean_HRS_WEEK = mean(HRS_WEEK, na.rm = TRUE), .groups = 'drop')
# Generate boxplots with mean values
ggplot(data_long, aes(x = as.factor(Response), y = HRS_WEEK, fill = as.factor(Response))) +
geom_boxplot(outlier.shape = NA, alpha = 0.4, varwidth = TRUE) + # Thinner boxes
geom_jitter(aes(color = as.factor(Response)), size = 1.5, width = 0.2, alpha = 0.4) +
geom_point(data = mean_values, aes(x = as.factor(Response), y = Mean_HRS_WEEK),
color = "red", size = 2) + # Add red dot for mean value
# geom_text(data = mean_values, aes(x = as.factor(Response), y = Mean_HRS_WEEK,
# label = round(Mean_HRS_WEEK, 1)), color = "red", vjust = -0.5, size = 3.5) + # Add numeric mean label
theme_minimal() +
labs(title = "Distribution of HRS_WEEK by HW_ Questions",
x = "Response",
y = "Hours of Water Supply per Week") +
# theme(legend.position = "none") + # Remove legend for clarity
facet_wrap(~HW_Question, scales = "free_y") # Create separate plots for each HW_ question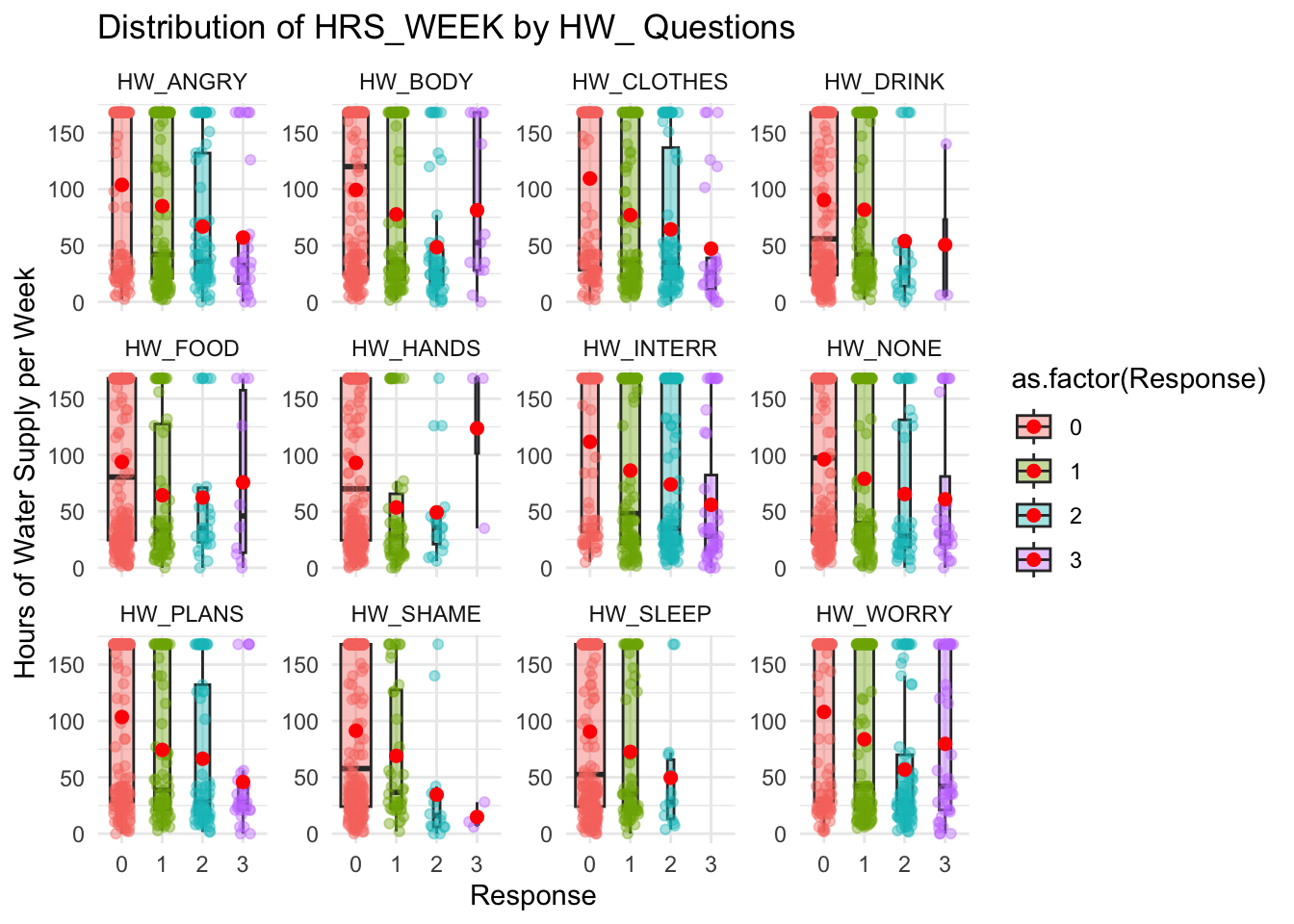
| Version | Author | Date |
|---|---|---|
| 3704a5a | Paloma | 2025-03-04 |
sessionInfo()R version 4.4.3 (2025-02-28)
Platform: aarch64-apple-darwin20
Running under: macOS Sequoia 15.3.1
Matrix products: default
BLAS: /Library/Frameworks/R.framework/Versions/4.4-arm64/Resources/lib/libRblas.0.dylib
LAPACK: /Library/Frameworks/R.framework/Versions/4.4-arm64/Resources/lib/libRlapack.dylib; LAPACK version 3.12.0
locale:
[1] en_US.UTF-8/en_US.UTF-8/en_US.UTF-8/C/en_US.UTF-8/en_US.UTF-8
time zone: America/Detroit
tzcode source: internal
attached base packages:
[1] stats graphics grDevices utils datasets methods base
other attached packages:
[1] knitr_1.49 reshape2_1.4.4 tidyr_1.3.1 ggplot2_3.5.1 dplyr_1.1.4
loaded via a namespace (and not attached):
[1] sass_0.4.9 utf8_1.2.4 generics_0.1.3 stringi_1.8.4
[5] digest_0.6.37 magrittr_2.0.3 evaluate_1.0.1 grid_4.4.3
[9] fastmap_1.2.0 rprojroot_2.0.4 workflowr_1.7.1 plyr_1.8.9
[13] jsonlite_1.8.9 whisker_0.4.1 promises_1.3.0 purrr_1.0.2
[17] fansi_1.0.6 scales_1.3.0 jquerylib_0.1.4 cli_3.6.3
[21] rlang_1.1.4 crayon_1.5.3 munsell_0.5.1 withr_3.0.2
[25] cachem_1.1.0 yaml_2.3.10 tools_4.4.3 colorspace_2.1-1
[29] httpuv_1.6.15 vctrs_0.6.5 R6_2.5.1 lifecycle_1.0.4
[33] git2r_0.35.0 stringr_1.5.1 fs_1.6.5 pkgconfig_2.0.3
[37] pillar_1.9.0 bslib_0.8.0 later_1.3.2 gtable_0.3.6
[41] glue_1.8.0 Rcpp_1.0.13-1 xfun_0.49 tibble_3.2.1
[45] tidyselect_1.2.1 rstudioapi_0.17.1 farver_2.1.2 htmltools_0.5.8.1
[49] rmarkdown_2.29 labeling_0.4.3 compiler_4.4.3