Environmental Audio AI
Example
toni.heittola@tuni.fi
 |
 |
 |
PANNS¶
Large-scale pretrained audio neural networks for audio pattern recognition
- State-of-the-art pretrained audio tagging model released in 2019
- Model architecture is inspired by VGG architecture, model (CNN14) has 80M parameters
- Trained with AudioSet dataset
- Data collected from YouTube
- 2M human-labeled 10-second clips organized into ontology with 632 sound classes
- Designed for single-channel audio with a 32kHz sampling rate
- Model outputs:
- Score for 527 sound classes
- Per-analysis-frame embedding (2048 values)
- Two modes: Audio tagger and Sound event detector
Qiuqiang Kong, Yin Cao, Turab Iqbal, Yuxuan Wang, Wenwu Wang, and Mark D. Plumbley. "PANNS: Large-scale pretrained audio neural networks for audio pattern recognition." IEEE/ACM Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing 28 (2020): 2880-2894. PDF
Example audio¶
Usage as audio tagger¶
# Import
from panns_inference import AudioTagging, labels
# Create audio tagger
audio_tagger = AudioTagging(
checkpoint_path=model_storage_filename,
device='cuda'
)
# Apply to test audio
(clipwise_output, embeddings) = audio_tagger.inference(
test_audio_32k.data[None, :] # (batch_size, audio_samples)
)
Top 5 tags based on outputted scores:
Score Tag ----- ------- 0.724 Whistle 0.453 Whistling 0.334 Speech 0.079 Music 0.053 Inside, small room
Usage as a sound event detector¶
# Import
from panns_inference import SoundEventDetection, labels
# Create sound event detector
detector = SoundEventDetection(
checkpoint_path=model_storage_filename,
device='cuda'
)
# Apply to test audio
framewise_output = detector.inference(test_audio_32k.data[None, :])
YAMNet¶
Pretrained neural network for sound recognition
- Released by Google in 2019
- Model uses Mobilenet_v1 architecture
- Depthwise-separable convolution architecture with 3.7M parameters
- Trained with AudioSet dataset
- Data collected from YouTube
- 2M human-labeled 10-second clips organized into ontology with 632 sound classes
- Designed for single-channel audio with a 16kHz sampling rate
- Internally audio is framed into 0.96-second analysis window with 0.48 seconds hop
- Model outputs:
- Score for 512 sound classes
- Per-analysis-frame embedding (1024 values)
Usage¶
# Import
import tensorflow_hub as hub
# Load model
yamnet_model_handle = 'https://tfhub.dev/google/yamnet/1'
yamnet_model = hub.load(yamnet_model_handle)
# Load class names
class_map_path = yamnet_model.class_map_path().numpy().decode('utf-8')
class_names = list(pd.read_csv(class_map_path)['display_name'])
# Run the model, check the output.
scores, embeddings, spectrogram = yamnet_model(test_audio_16k.data)
scores matrix shape (analysis segments, class-wise scores): (10, 521)
Example audio¶
Analyze content¶
# Run the model
scores, embeddings, spectrogram_data = yamnet_model(test_audio_16k.data)
# Get top class
infered_class = class_names[scores.numpy().mean(axis=0).argmax()]
infered_class: Whistle
Scores of the top 5 classes across the sample¶
Transfer Learning¶
We need to make a robust classifier, however, we only have small amount of examples per class
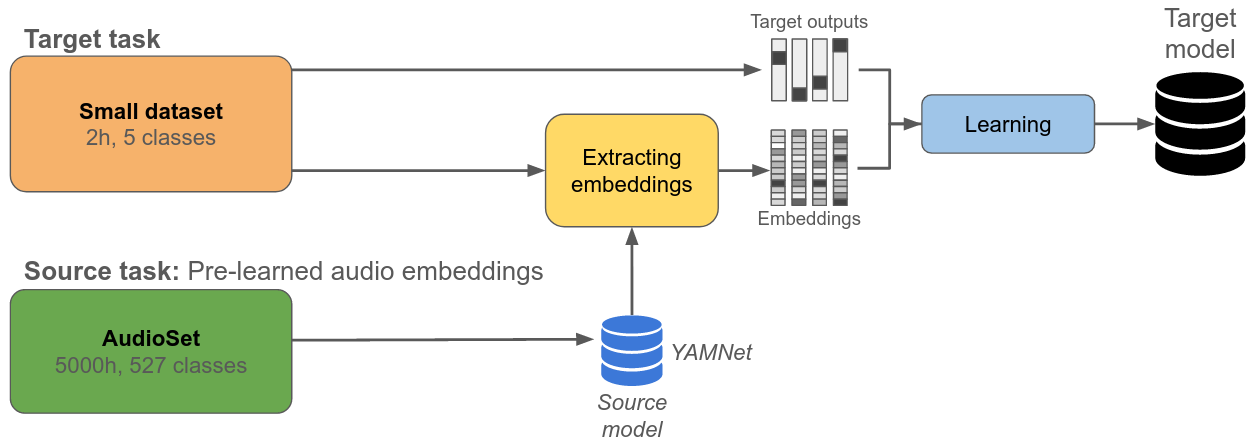
Transfer Learning¶
Advantage: Many pre-trained models available, enables including a large amount of knowledge into the learning process with minimal computational power
Disadvantage: No guarantee that it works; in some cases can make the learning process even harder (negative transfer)
Application example¶
Target task: Animal vocalization classifier with 10 classes
Source task: Generic sound classifier YAMNet
A new model will be trained, and YAMNet embeddings will be used as input features
Application¶
ESC-50 dataset will be used as target data
- 5-second environmental audio recordings collected from FreeSound.org
- Recordings are organized into 50 classes each having 40 examples
target_classes = [
'cat', # YAMNet class
'cow',
'crickets',
'crow', # YAMNet class
'dog', # YAMNet class
'frog', # YAMNet class
'hen',
'pig', # YAMNet class
'rooster',
'sheep' # YAMNet class
]
Only six of the target classes could be recognized directly by YAMNet.
Select material from ESC-50 dataset¶
Identify suitable items in the dataset
# Load dataset meta
dataset_meta = pd.read_csv(meta_csv)
# Filter data
dataset_meta_filtered = dataset_meta[dataset_meta.category.isin(target_classes)]
class_id = dataset_meta_filtered['category'].apply(
lambda name: map_class_to_id[name]
)
dataset_meta_filtered = dataset_meta_filtered.assign(target=class_id)
| filename | category | |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | data/datasets/ESC-50-master/audio16k/1-100032-... | dog |
| 8 | data/datasets/ESC-50-master/audio16k/1-103298-... | crow |
| 14 | data/datasets/ESC-50-master/audio16k/1-110389-... | dog |
| 29 | data/datasets/ESC-50-master/audio16k/1-121951-... | sheep |
| 45 | data/datasets/ESC-50-master/audio16k/1-15689-A... | frog |
Extract embeddings¶
main_ds = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices(
(dataset_meta_filtered['filename'],
dataset_meta_filtered['target'],
dataset_meta_filtered['fold'])
)
def load_audio_for_map_function(filename, label, fold):
return load_audio(filename), label, fold
main_ds = main_ds.map(load_audio_for_map_function)
# Function to extract embeddings
def extract_embedding(wav_data, label, fold):
scores, embeddings, spectrogram = yamnet_model(wav_data)
num_embeddings = tf.shape(embeddings)[0]
return (embeddings,
tf.repeat(label, num_embeddings),
tf.repeat(fold, num_embeddings))
# Extract embedding
main_ds = main_ds.map(extract_embedding).unbatch()
Create neural network¶
finetuned_model = tf.keras.Sequential([
tf.keras.layers.Input(
shape=(1024),
dtype=tf.float32,
name='input_embedding'
),
tf.keras.layers.Dense(512, activation='relu', name='fully-connected'),
tf.keras.layers.Dense(len(target_classes), name='output')
], name='my_model')
| Layer name | Layer type | Output shape | Parameters |
|---|---|---|---|
| fully-connected | Dense | (None, 512) | 524800 |
| output | Dense | (None, 10) | 5130 |
Training¶
finetuned_model.compile(
loss=tf.keras.losses.SparseCategoricalCrossentropy(from_logits=True),
optimizer='adam',
metrics=['accuracy']
)
callback = tf.keras.callbacks.EarlyStopping(monitor='loss', patience=10, restore_best_weights=True)
# Track power consumption and time
tracker = EmissionsTracker("Transfer learning example", output_dir=os.path.join('data', 'training_codecarbon'))
tracker.start()
start_time = time.time()
history = finetuned_model.fit(train_ds, epochs=100, validation_data=val_ds, callbacks=callback, verbose=0)
# Stop tracking
stop_time = time.time()
tracker.stop()
Time used for training: 28.55 sec Total energy consumed during training: 0.00083 kWh
Evaluation¶
| Scene label | Accuracy |
|---|---|
| cat | 100.0 |
| cow | 100.0 |
| crickets | 87.5 |
| crow | 100.0 |
| dog | 100.0 |
| frog | 62.5 |
| hen | 100.0 |
| pig | 62.5 |
| rooster | 100.0 |
| sheep | 100.0 |
| Average | 91.2 |
Confusion matrix¶
Sound Event Detection¶
The task of simultaneously estimating what is happening and when it is happening
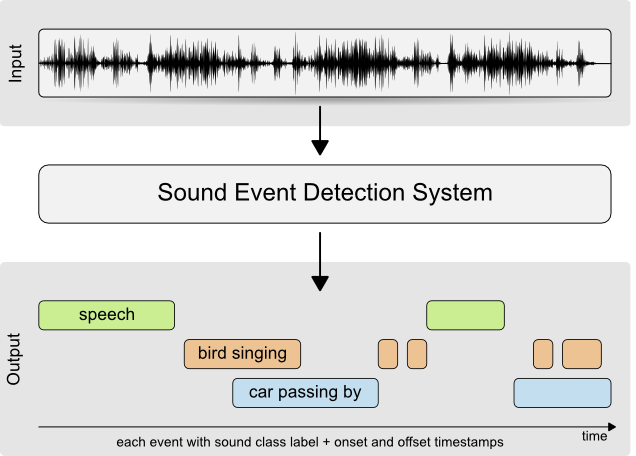
System structure¶
A simple sound event detector can be implemented by applying a sound classifier or audio tagger in consecutive segments and joining activity information into sound events with start and end times.
- Model trained in the transfer learning section will be used
- Analysis is done in segments (0.96 sec) that are moved through the signal with 0.5-sec hops
- In each segment, the model is used to get class-wise scores
- Class with the highest score is outputted if the score is over the threshold (0.99)
- This system can detect only a single sound event at a time with a time resolution of 0.5 sec
Example input signal¶
Signal generated with dog, cat, rooster, and cow samples in a metro station