Matrix factorization of binary data
Jason Willwerscheid
9/22/2018
Last updated: 2018-09-25
workflowr checks: (Click a bullet for more information)-
✔ R Markdown file: up-to-date
Great! Since the R Markdown file has been committed to the Git repository, you know the exact version of the code that produced these results.
-
✔ Environment: empty
Great job! The global environment was empty. Objects defined in the global environment can affect the analysis in your R Markdown file in unknown ways. For reproduciblity it’s best to always run the code in an empty environment.
-
✔ Seed:
set.seed(20180714)The command
set.seed(20180714)was run prior to running the code in the R Markdown file. Setting a seed ensures that any results that rely on randomness, e.g. subsampling or permutations, are reproducible. -
✔ Session information: recorded
Great job! Recording the operating system, R version, and package versions is critical for reproducibility.
-
Great! You are using Git for version control. Tracking code development and connecting the code version to the results is critical for reproducibility. The version displayed above was the version of the Git repository at the time these results were generated.✔ Repository version: 2303a6c
Note that you need to be careful to ensure that all relevant files for the analysis have been committed to Git prior to generating the results (you can usewflow_publishorwflow_git_commit). workflowr only checks the R Markdown file, but you know if there are other scripts or data files that it depends on. Below is the status of the Git repository when the results were generated:
Note that any generated files, e.g. HTML, png, CSS, etc., are not included in this status report because it is ok for generated content to have uncommitted changes.Ignored files: Ignored: .DS_Store Ignored: .Rhistory Ignored: .Rproj.user/ Ignored: docs/.DS_Store Ignored: docs/figure/.DS_Store Untracked files: Untracked: data/greedy19.rds
Expand here to see past versions:
| File | Version | Author | Date | Message |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rmd | 2303a6c | Jason Willwerscheid | 2018-09-25 | wflow_publish(“analysis/binary_data.Rmd”) |
Introduction
I repeat the previous analysis but here I treat the GTEx donation matrix as binary data. (This is probably more appropriate; it is much more natural to assume that each donor will contribute a given tissue with a particular probability than that each donor will generate samples of a given tissue such that the count of samples is distributed as a Poisson random variable.)
Model
Here the model is \[ Y_{ij} \sim \text{Bernoulli}(p_{ij}), \] with \[ \log \left( \frac{p}{1 - p} \right) = LF'. \] As in the previous analysis, one could also put \[ \log \left( \frac{p}{1 - p} \right) = LF' + E, \] with the “errors” \(E_{ij}\) distributed i.i.d. \(N(0, \sigma^2)\).
Setting \(\eta = \log (p / (1 - p))\), one has that \[ \begin{aligned} \ell(\eta) &= \sum_{i, j} - \log (1 + e^{\eta_{ij}}) + Y_{ij} \eta_{ij} \\ \ell'(\eta) &= \sum_{i, j} -\frac{e^{\eta_{ij}}}{1 + e^{\eta_{ij}}} + Y_{ij} = \sum_{i, j} Y_{ij} - p_{ij} \\ \ell''(\eta) &= \sum_{i, j} - \frac{e^{\eta_{ij}}}{(1 + e^{\eta_{ij}})^2} = \sum_{i, j} -p_{ij}(1 - p_{ij}) \end{aligned}\]
Using the same trick as before, one obtains pseudo-data \[ X = \log \left( \frac{p^\star}{1 - p^\star} \right) + \frac{Y - p^\star}{p^\star(1 - p^\star)} \] with standard errors \[ S = \frac{1}{\sqrt{p^\star(1 - p^\star)}} \]
The objective can be calculated as the FLASH objective plus \[\sum_{i, j} Y_{ij} \log p^\star_{ij} + (1 - Y_{ij}) \log (1 - p^\star_{ij}) + \frac{1}{2}\log \left( \frac{2 \pi}{p^\star_{ij}(1 - p^\star_{ij})} \right) + \frac{(Y_{ij} - p^\star_{ij})^2}{2p^\star_{ij}(1 - p^\star_{ij})}. \]
Code
This is largely cut and pasted from the previous analysis.
devtools::load_all("~/GitHub/flashr")
#> Loading flashr
devtools::load_all("~/GitHub/ebnm")
#> Loading ebnm
raw <- read.csv("https://storage.googleapis.com/gtex_analysis_v6/annotations/GTEx_Data_V6_Annotations_SampleAttributesDS.txt",
header=TRUE, sep='\t')
data <- raw[, c("SAMPID", "SMTSD")] # sample ID, tissue type
# Extract donor ID:
tmp <- strsplit(as.character(data$SAMPID), "-")
data$SAMPID <- as.factor(sapply(tmp, function(x) {x[[2]]}))
names(data) <- c("DonorID", "TissueType")
data <- suppressMessages(reshape2::acast(data, TissueType ~ DonorID))
missing.tissues <- c(1, 8, 9, 20, 21, 24, 26, 27, 33, 36, 39)
data <- data[-missing.tissues, ]
# Drop columns with no samples:
data <- data[, colSums(data) > 0]
# Convert to binary data:
data[data > 0] <- 1
gtex.colors <- read.table("https://github.com/stephenslab/gtexresults/blob/master/data/GTExColors.txt?raw=TRUE",
sep = '\t', comment.char = '')
gtex.colors <- gtex.colors[-c(7, 8, 19, 20, 24, 25, 31, 34, 37), 2]
gtex.colors <- as.character(gtex.colors)
# Computing objective (ELBO) -------------------------------------------
calc_obj <- function(fl, the_data, p) {
return(fl$objective +
sum(the_data * log(p) + (1 - the_data) * log(1 - p) +
0.5 * (log(2 * pi / (p * (1 - p))) +
(the_data - p)^2 / (p * (1 - p)))))
}
# Calculating pseudo-data ----------------------------------------------
calc_X <- function(the_data, p) {
return(log(p / (1 - p)) + (the_data - p) / (p * (1 - p)))
}
calc_S <- function(the_data, p) {
return(1 / sqrt(p * (1 - p)))
}
set_pseudodata <- function(the_data, p) {
return(flash_set_data(calc_X(the_data, p), S = calc_S(the_data, p)))
}
# Setting FLASH parameters ---------------------------------------------
# Initialization function for nonnegative loadings
# (but arbitrary factors):
my_init_fn <- function(Y, K = 1) {
ret = udv_svd(Y, K)
sum_pos = sum(ret$u[ret$u > 0]^2)
sum_neg = sum(ret$u[ret$u < 0]^2)
if (sum_neg > sum_pos) {
return(list(u = -ret$u, d = ret$d, v = -ret$v))
} else
return(ret)
}
get_init_fn <- function(nonnegative = FALSE) {
if (nonnegative) {
return("my_init_fn")
} else {
return("udv_svd")
}
}
get_ebnm_fn <- function(nonnegative = FALSE) {
if (nonnegative) {
return(list(l = "ebnm_ash", f = "ebnm_pn"))
} else {
return(list(l = "ebnm_pn", f = "ebnm_pn"))
}
}
get_ebnm_param <- function(nonnegative = FALSE) {
if (nonnegative) {
return(list(l = list(mixcompdist = "+uniform"),
f = list(warmstart = TRUE)))
} else {
return(list(l = list(warmstart = TRUE),
f = list(warmstart = TRUE)))
}
}
# Initializing p and running FLASH -------------------------------------
stabilize_p <- function(p) {
p[p < 1e-6] <- 1e-6
p[p > 1 - 1e-6] <- 1 - 1e-6
return(p)
}
init_p <- function(the_data, f_init) {
if (is.null(f_init)) {
return(matrix(colMeans(the_data),
nrow = nrow(the_data), ncol = ncol(the_data),
byrow = TRUE))
} else {
p <- 1 / (1 + exp(-f_init$fitted_values))
return(stabilize_p(p))
}
}
update_p <- function(fl, pseudodata, var_type) {
if (var_type == "constant") {
LF <- fl$fitted_values
X <- pseudodata$Y
S2 <- pseudodata$S^2
s2 <- 1 / fl$fit$tau[1, 1] - S2[1,1]
eta <- LF + ((1 / S2) / (1 / S2 + 1 / s2)) * (X - LF)
p <- 1 / (1 + exp(-eta))
} else { # var_type = "zero"
p <- 1 / (1 + exp(-fl$fitted_values))
}
return(stabilize_p(p))
}
greedy_iter <- function(pseudodata, f_init, niter,
nonnegative = FALSE, var_type = "zero") {
suppressWarnings(
flash_greedy_workhorse(pseudodata,
Kmax = 1,
f_init = f_init,
var_type = var_type,
ebnm_fn = get_ebnm_fn(nonnegative),
ebnm_param = get_ebnm_param(nonnegative),
init_fn = get_init_fn(nonnegative),
verbose_output = "",
nullcheck = FALSE,
maxiter = niter)
)
}
backfit_iter <- function(pseudodata, f_init, kset, niter,
nonnegative = FALSE, var_type = "zero") {
suppressWarnings(
flash_backfit_workhorse(pseudodata,
kset = kset,
f_init = f_init,
var_type = var_type,
ebnm_fn = get_ebnm_fn(nonnegative),
ebnm_param = get_ebnm_param(nonnegative),
verbose_output = "",
nullcheck = FALSE,
maxiter = niter)
)
}
run_one_fit <- function(the_data, f_init, greedy, maxiter = 200,
n_subiter = 200, nonnegative = FALSE,
var_type = "zero",
verbose = TRUE, tol = .01) {
p <- init_p(the_data, f_init)
if (greedy) {
pseudodata <- set_pseudodata(the_data, p)
fl <- greedy_iter(pseudodata, f_init, n_subiter,
nonnegative, var_type)
kset <- ncol(fl$fit$EL) # Only "backfit" the greedily added factor
p <- update_p(fl, pseudodata, var_type)
} else {
fl <- f_init
kset <- 1:ncol(fl$fit$EL) # Backfit all factor/loadings
}
# The objective can get stuck oscillating between two values, so we
# need to track the last two values attained:
old_old_obj <- -Inf
old_obj <- -Inf
diff <- Inf
iter <- 0
while (diff > tol && iter < maxiter) {
iter <- iter + 1
pseudodata <- set_pseudodata(the_data, p)
fl <- backfit_iter(pseudodata, fl, kset, n_subiter,
nonnegative, var_type)
fl$objective <- calc_obj(fl, the_data, p)
diff <- min(abs(fl$objective - old_obj),
abs(fl$objective - old_old_obj))
old_old_obj <- old_obj
old_obj <- fl$objective
p <- update_p(fl, pseudodata, var_type)
if (verbose) {
message("Iteration ", iter, ": ", fl$objective)
}
}
return(fl)
}
flash_fit <- function(the_data, n_subiter, nonnegative = FALSE,
var_type = "zero", maxiter = 100, tol = .01,
verbose = FALSE) {
fl <- run_one_fit(the_data, f_init = NULL, greedy = TRUE,
maxiter = maxiter, n_subiter = n_subiter,
nonnegative = nonnegative, var_type = var_type,
verbose = verbose)
old_obj <- fl$objective
# Keep greedily adding factors until the objective no longer improves:
diff <- Inf
while (diff > tol) {
fl <- run_one_fit(the_data, fl, greedy = TRUE,
maxiter = maxiter, n_subiter = n_subiter,
nonnegative = nonnegative, var_type = var_type,
verbose = verbose)
diff <- fl$objective - old_obj
old_obj <- fl$objective
}
# Now backfit the whole thing:
fl <- run_one_fit(the_data, fl, greedy = FALSE,
maxiter = maxiter, n_subiter = n_subiter,
nonnegative = nonnegative, var_type = var_type,
verbose = verbose)
return(fl)
}Results
I fit factors using var_type = "zero" (as in the previous analysis, var_type = "constant" gives the same result):
fl_zero <- flash_fit(data, 1, var_type = "zero")
fl_zero$objective
#> [1] -12075.66
plot(fl_zero, plot_loadings = TRUE, loading_colors = gtex.colors,
loading_legend_size = 3, plot_scree = FALSE)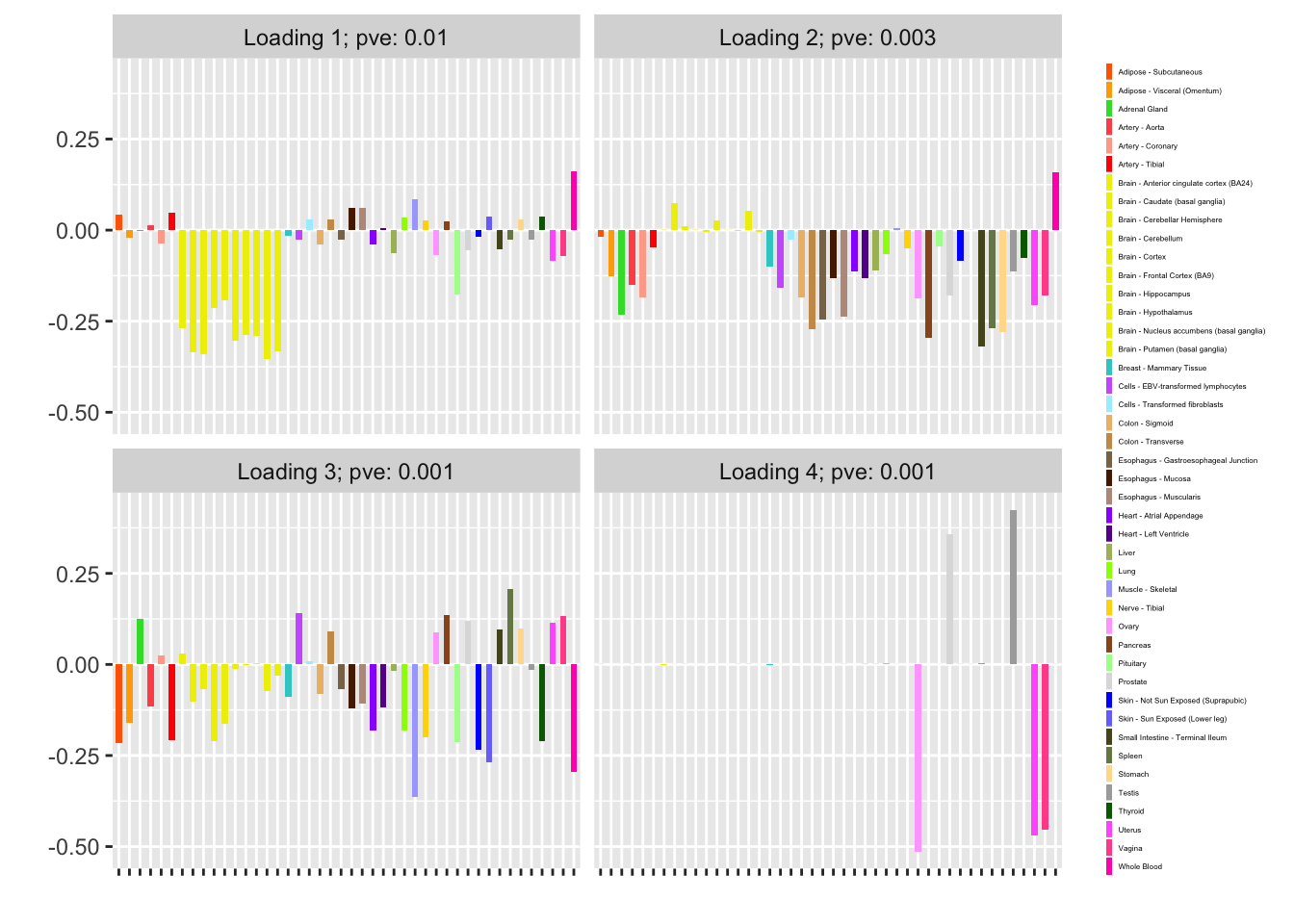
Nonnegative loadings are not as compelling (but I’m not sure that they make much sense in this scenario anyway):
fl_nonneg <- flash_fit(data, 1, var_type = "zero", nonnegative = TRUE)
fl_nonneg$objective
#> [1] -12448.13
plot(fl_nonneg, plot_loadings = TRUE, loading_colors = gtex.colors,
loading_legend_size = 3, plot_scree = FALSE)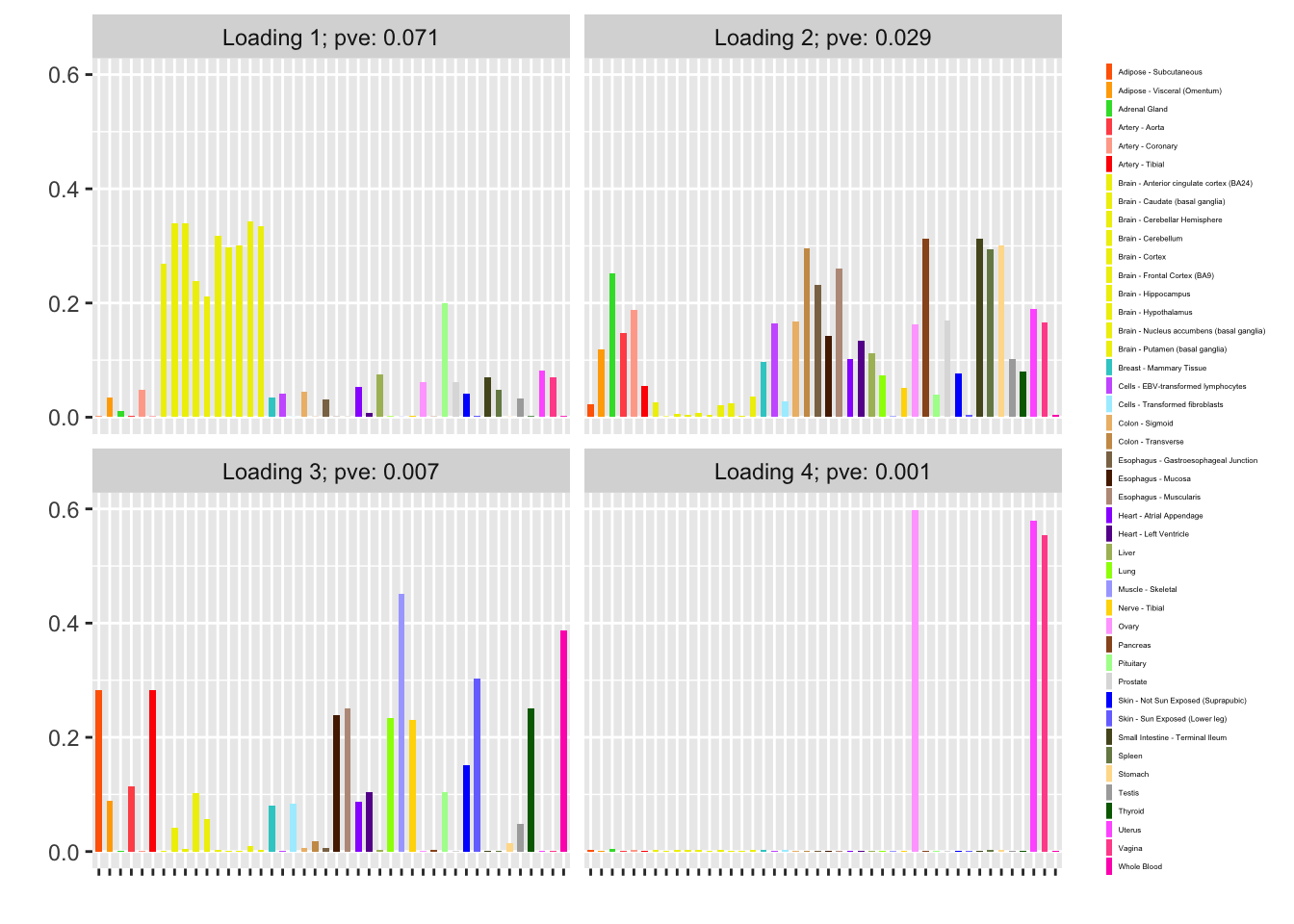
Session information
sessionInfo()
#> R version 3.4.3 (2017-11-30)
#> Platform: x86_64-apple-darwin15.6.0 (64-bit)
#> Running under: macOS High Sierra 10.13.6
#>
#> Matrix products: default
#> BLAS: /Library/Frameworks/R.framework/Versions/3.4/Resources/lib/libRblas.0.dylib
#> LAPACK: /Library/Frameworks/R.framework/Versions/3.4/Resources/lib/libRlapack.dylib
#>
#> locale:
#> [1] en_US.UTF-8/en_US.UTF-8/en_US.UTF-8/C/en_US.UTF-8/en_US.UTF-8
#>
#> attached base packages:
#> [1] stats graphics grDevices utils datasets methods base
#>
#> other attached packages:
#> [1] ebnm_0.1-15 flashr_0.6-2
#>
#> loaded via a namespace (and not attached):
#> [1] Rcpp_0.12.18 pillar_1.2.1 plyr_1.8.4
#> [4] compiler_3.4.3 git2r_0.21.0 workflowr_1.0.1
#> [7] R.methodsS3_1.7.1 R.utils_2.6.0 iterators_1.0.9
#> [10] tools_3.4.3 testthat_2.0.0 digest_0.6.15
#> [13] tibble_1.4.2 evaluate_0.10.1 memoise_1.1.0
#> [16] gtable_0.2.0 lattice_0.20-35 rlang_0.2.0
#> [19] Matrix_1.2-12 foreach_1.4.4 commonmark_1.4
#> [22] yaml_2.1.17 parallel_3.4.3 withr_2.1.1.9000
#> [25] stringr_1.3.0 roxygen2_6.0.1.9000 xml2_1.2.0
#> [28] knitr_1.20 REBayes_1.2 devtools_1.13.4
#> [31] rprojroot_1.3-2 grid_3.4.3 R6_2.2.2
#> [34] rmarkdown_1.8 reshape2_1.4.3 ggplot2_2.2.1
#> [37] ashr_2.2-13 magrittr_1.5 whisker_0.3-2
#> [40] backports_1.1.2 scales_0.5.0 codetools_0.2-15
#> [43] htmltools_0.3.6 MASS_7.3-48 assertthat_0.2.0
#> [46] softImpute_1.4 colorspace_1.3-2 labeling_0.3
#> [49] stringi_1.1.6 Rmosek_7.1.3 lazyeval_0.2.1
#> [52] doParallel_1.0.11 pscl_1.5.2 munsell_0.4.3
#> [55] truncnorm_1.0-8 SQUAREM_2017.10-1 R.oo_1.21.0This reproducible R Markdown analysis was created with workflowr 1.0.1