PEM vs. PAM split point sensitivity
Last updated: 2018-05-23
workflowr checks: (Click a bullet for more information)-
✔ R Markdown file: up-to-date
Great! Since the R Markdown file has been committed to the Git repository, you know the exact version of the code that produced these results.
-
✔ Environment: empty
Great job! The global environment was empty. Objects defined in the global environment can affect the analysis in your R Markdown file in unknown ways. For reproduciblity it’s best to always run the code in an empty environment.
-
✔ Seed:
set.seed(20180517)The command
set.seed(20180517)was run prior to running the code in the R Markdown file. Setting a seed ensures that any results that rely on randomness, e.g. subsampling or permutations, are reproducible. -
✔ Session information: recorded
Great job! Recording the operating system, R version, and package versions is critical for reproducibility.
-
Great! You are using Git for version control. Tracking code development and connecting the code version to the results is critical for reproducibility. The version displayed above was the version of the Git repository at the time these results were generated.✔ Repository version: 4ddf7b2
Note that you need to be careful to ensure that all relevant files for the analysis have been committed to Git prior to generating the results (you can usewflow_publishorwflow_git_commit). workflowr only checks the R Markdown file, but you know if there are other scripts or data files that it depends on. Below is the status of the Git repository when the results were generated:
Note that any generated files, e.g. HTML, png, CSS, etc., are not included in this status report because it is ok for generated content to have uncommitted changes.Ignored files: Ignored: analysis/pem_vs_pam_cache/ Untracked files: Untracked: output/sim-lag-lead-registry/ Untracked: output/sim-pem-vs-pam-registry/ Untracked: sandbox/ Unstaged changes: Modified: analysis/_site.yml Modified: analysis/about.Rmd Modified: analysis/index.Rmd
Expand here to see past versions:
| File | Version | Author | Date | Message |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rmd | 4ddf7b2 | adibender | 2018-05-23 | wflow_publish(“analysis/pem_vs_pam.Rmd”) |
| html | da628e9 | adibender | 2018-05-22 | Build site. |
| Rmd | 870faf5 | adibender | 2018-05-22 | wflow_publish(c(“analysis/pem_vs_pam.Rmd”)) |
| html | 2542e6b | adibender | 2018-05-22 | Build site. |
| Rmd | e7b4b2d | adibender | 2018-05-22 | wflow_publish(c(“analysis/pem_vs_pam.Rmd”)) |
| html | e9f8507 | adibender | 2018-05-22 | Build site. |
| Rmd | 14e326b | adibender | 2018-05-22 | wflow_publish(c(“analysis/pem_vs_pam.Rmd”)) |
| html | 1e706df | adibender | 2018-05-22 | Build site. |
| Rmd | f963aae | adibender | 2018-05-22 | wflow_publish(c(“analysis/pem_vs_pam.Rmd”)) |
library(ggplot2)
theme_set(theme_bw())
library(batchtools)Motivation
This is a light-weight simulation study to investigate how sensitive the different approaches (PEM vs. PAM) to the estimation of the baseline-hazard function are to the placement of the interval split points.
Setup
The setup is as follows:
\(n=250\) survival times are simulated from a distribution with log-hazard \(-3.5 + f(8,2)*6\), where \(f(8,2)\) is the density function of the Gamma distribution with respective parameters.
The baseline hazard is estimated by a PEM and PAM respectively
Three different settings are used for the interval split point definition
- “default”: Unique event times from each simulated data set is used
- “fine”: A fine, equidistant grid with interval lengths \(0.2\)
- “rough”: A rough, equidistant grid with interval lengths \(0.5\)
For each setting, 20 replications are run
Function for data simulation (using pammtools::sim_pexp):
## simulation function
sim_wrapper <- function(data, job, n = 250, time_grid = seq(0, 10, by = 0.05)) {
# create data set with covariates
df <- tibble::tibble(x1 = runif(n, -3, 3), x2 = runif(n, 0, 6))
# baseline hazard
f0 <- function(t) {dgamma(t, 8, 2) * 6}
# define function that generates nz exposures z(t_{z,1}), ..., z(t_{z,Q})
sim_pexp(formula = ~ -3.5 + f0(t), data = df, cut = time_grid)
}Function to estimate hazard from simulated data, either by a PEM or PAM
## estimation function
pam_wrapper <- function(data, job, instance,
cut = NA,
bs = "ps",
mod_type = c("pem", "pam") ,
max_time = 10) {
if(is.na(cut)) {
cut <- NULL
} else {
if(cut == "rough") {
cut <- seq(0, max_time, by = 0.5)
} else {
if(cut == "fine") {
cut <- seq(0, max_time, by = 0.2)
}
}
}
ped <- as_ped(data = instance, formula = Surv(time, status) ~ ., cut = cut, id="id")
form <- "ped_status ~ s(tend) + s(x1) + s(x2)"
if(mod_type == "pem") {
form <- ped_status ~ interval
time_var <- "interval"
} else {
form <- ped_status ~ s(tend, bs = bs, k = 10)
time_var <- "tend"
}
mod <- gam(formula = form, data = ped, family = poisson(), offset = offset, method = "REML")
# summary(mod)
make_newdata(ped, tend=unique(tend)) %>%
add_hazard(mod, type="link", se_mult = qnorm(0.975), time_var = time_var) %>%
mutate(truth = -3.5 + dgamma(tend, 8, 2) * 6)
}Setup simulation registry
Setup simulation using batchtools:
if(!checkmate::test_directory_exists("output/sim-pem-vs-pam-registry")) {
reg <- makeExperimentRegistry("output/sim-pem-vs-pam-registry",
packages = c("mgcv", "dplyr", "tidyr", "pammtools"),
seed = 20052018)
reg$cluster.functions = makeClusterFunctionsMulticore(ncpus = 2)
addProblem(name = "pem-vs-pam", fun = sim_wrapper)
addAlgorithm(name = "pem-vs-pam", fun = pam_wrapper)
algo_df <- tidyr::crossing(
cut = c(NA, "fine", "rough"),
mod_type = c("pem", "pam"))
addExperiments(algo.design = list("pem-vs-pam" = algo_df), repls = 20)
submitJobs()
waitForJobs()
}Warning: replacing previous import 'dplyr::vars' by 'ggplot2::vars' when
loading 'pammtools'[1] TRUEEvaluate Simulation
reg <- loadRegistry("output/sim-pem-vs-pam-registry", writeable = TRUE)
ids_pam <- findExperiments(prob.name="pem-vs-pam", algo.name="pem-vs-pam")
pars <- unwrap(getJobPars()) %>% as_tibble()
res <- reduceResultsDataTable(ids=findDone(ids_pam)) %>%
as_tibble() %>%
tidyr::unnest() %>%
left_join(pars) %>%
mutate(cut = case_when(is.na(cut) ~ "default", TRUE ~ cut))
res %>%
mutate(
sq_error = (truth - hazard)^2,
covered = (truth >= ci_lower) & (truth <= ci_upper)) %>%
group_by(job.id, mod_type, cut) %>%
summarize(
RMSE = sqrt(mean(sq_error)),
coverage = mean(covered)) %>%
group_by(mod_type, cut) %>%
summarize(
RMSE = mean(RMSE),
coverage = mean(coverage))# A tibble: 6 x 4
# Groups: mod_type [?]
mod_type cut RMSE coverage
<chr> <chr> <dbl> <dbl>
1 pam default 0.223 0.881
2 pam fine 0.268 0.916
3 pam rough 0.281 0.920
4 pem default 1.38 0.870
5 pem fine 6.84 0.966
6 pem rough 3.02 0.920Visualize Estimations
ggplot(res, aes(x=tend, y = hazard)) +
geom_step(aes(group = job.id), alpha = 0.3) +
geom_line(aes(y = truth, col = "truth"), lwd = 2) +
facet_grid(cut ~ mod_type) +
coord_cartesian(ylim=c(-5, 0)) +
geom_smooth(aes(col="average estimate"), method="gam", formula = y ~ s(x),
se=FALSE) +
scale_color_brewer("Method", palette = "Dark2") +
xlab("time")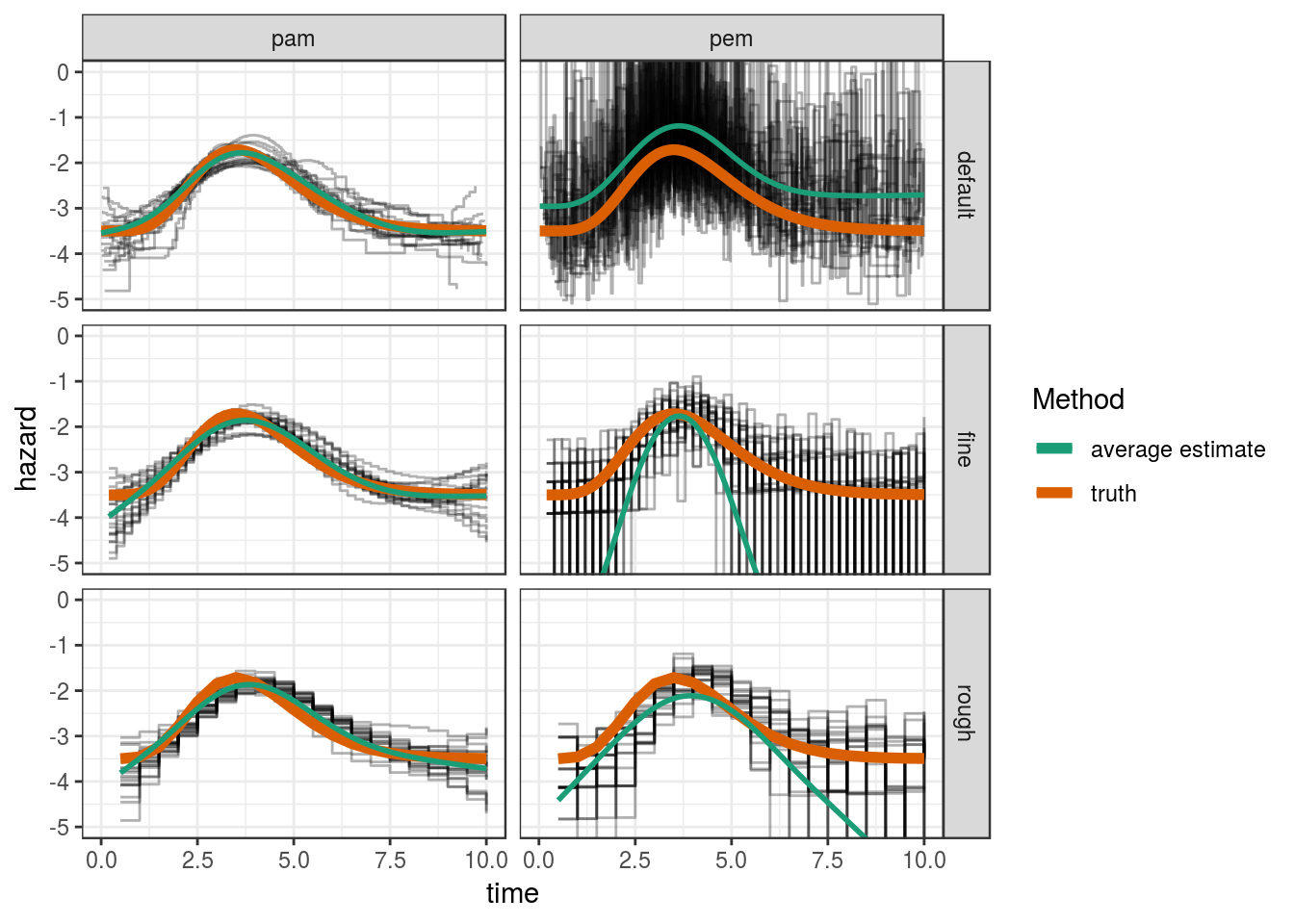
Expand here to see past versions of unnamed-chunk-5-1.png:
| Version | Author | Date |
|---|---|---|
| 1e706df | adibender | 2018-05-22 |
Conclusion
For the PAM, the RMSE has about the same magnitude for all three split point settings
For the PEM, the RMSE is highly dependent on the RMSE, partly because even for the “rough” split point setting, in some simulations some intervals have no events and the hazard is estimated close to zero (very small log-hazard values) and for the “default” setting, where each interval contains at least one event, appears to overestimate the hazard on average
Session information
sessionInfo()R version 3.4.4 (2018-03-15)
Platform: x86_64-pc-linux-gnu (64-bit)
Running under: Ubuntu 16.04.4 LTS
Matrix products: default
BLAS: /usr/lib/openblas-base/libblas.so.3
LAPACK: /usr/lib/libopenblasp-r0.2.18.so
locale:
[1] LC_CTYPE=en_US.UTF-8 LC_NUMERIC=C
[3] LC_TIME=de_DE.UTF-8 LC_COLLATE=en_US.UTF-8
[5] LC_MONETARY=de_DE.UTF-8 LC_MESSAGES=en_US.UTF-8
[7] LC_PAPER=de_DE.UTF-8 LC_NAME=C
[9] LC_ADDRESS=C LC_TELEPHONE=C
[11] LC_MEASUREMENT=de_DE.UTF-8 LC_IDENTIFICATION=C
attached base packages:
[1] stats graphics grDevices utils datasets methods base
other attached packages:
[1] bindrcpp_0.2.2 pammtools_0.0.9.9003 tidyr_0.8.0
[4] dplyr_0.7.4 mgcv_1.8-23 nlme_3.1-137
[7] batchtools_0.9.8 data.table_1.10.4-3 ggplot2_2.2.1.9000
loaded via a namespace (and not attached):
[1] progress_1.1.2 tidyselect_0.2.4 reshape2_1.4.3
[4] purrr_0.2.4 splines_3.4.4 lattice_0.20-35
[7] expm_0.999-2 colorspace_1.3-2 htmltools_0.3.6
[10] yaml_2.1.18 utf8_1.1.3 survival_2.42-3
[13] rlang_0.2.0.9001 R.oo_1.21.0 pillar_1.2.1
[16] glue_1.2.0 withr_2.1.2 R.utils_2.6.0
[19] rappdirs_0.3.1 RColorBrewer_1.1-2 plyr_1.8.4
[22] bindr_0.1.1 stringr_1.3.0 munsell_0.4.3
[25] gtable_0.2.0 workflowr_1.0.1 R.methodsS3_1.7.1
[28] mvtnorm_1.0-7 evaluate_0.10.1 labeling_0.3
[31] knitr_1.20 Rcpp_0.12.16 scales_0.5.0.9000
[34] backports_1.1.2 checkmate_1.8.5 debugme_1.1.0
[37] brew_1.0-6 digest_0.6.15 stringi_1.1.7
[40] msm_1.6.6 grid_3.4.4 rprojroot_1.3-2
[43] cli_1.0.0 tools_3.4.4 magrittr_1.5
[46] base64url_1.3 lazyeval_0.2.1 tibble_1.4.2
[49] Formula_1.2-3 crayon_1.3.4 whisker_0.3-2
[52] pkgconfig_2.0.1 Matrix_1.2-13 prettyunits_1.0.2
[55] assertthat_0.2.0 rmarkdown_1.9 R6_2.2.2
[58] git2r_0.21.0 compiler_3.4.4 This reproducible R Markdown analysis was created with workflowr 1.0.1