Marine Heat Waves categorisation
Marguerite Larriere & Jens Daniel Müller
22 April, 2024
Last updated: 2024-04-22
Checks: 7 0
Knit directory:
bgc_argo_r_argodata/analysis/
This reproducible R Markdown analysis was created with workflowr (version 1.7.0). The Checks tab describes the reproducibility checks that were applied when the results were created. The Past versions tab lists the development history.
Great! Since the R Markdown file has been committed to the Git repository, you know the exact version of the code that produced these results.
Great job! The global environment was empty. Objects defined in the global environment can affect the analysis in your R Markdown file in unknown ways. For reproduciblity it’s best to always run the code in an empty environment.
The command set.seed(20211008) was run prior to running
the code in the R Markdown file. Setting a seed ensures that any results
that rely on randomness, e.g. subsampling or permutations, are
reproducible.
Great job! Recording the operating system, R version, and package versions is critical for reproducibility.
Nice! There were no cached chunks for this analysis, so you can be confident that you successfully produced the results during this run.
Great job! Using relative paths to the files within your workflowr project makes it easier to run your code on other machines.
Great! You are using Git for version control. Tracking code development and connecting the code version to the results is critical for reproducibility.
The results in this page were generated with repository version 40fff85. See the Past versions tab to see a history of the changes made to the R Markdown and HTML files.
Note that you need to be careful to ensure that all relevant files for
the analysis have been committed to Git prior to generating the results
(you can use wflow_publish or
wflow_git_commit). workflowr only checks the R Markdown
file, but you know if there are other scripts or data files that it
depends on. Below is the status of the Git repository when the results
were generated:
Ignored files:
Ignored: .Rproj.user/
Untracked files:
Untracked: analysis/anomaly_SST_2023.Rmd
Untracked: analysis/draft.Rmd
Unstaged changes:
Modified: analysis/_site.yml
Modified: analysis/child/cluster_analysis_base.Rmd
Modified: analysis/coverage_maps_North_Atlantic.Rmd
Modified: analysis/load_broullon_DIC_TA_clim.Rmd
Modified: code/Workflowr_project_managment.R
Modified: code/start_background_job.R
Modified: code/start_background_job_load.R
Modified: code/start_background_job_partial.R
Note that any generated files, e.g. HTML, png, CSS, etc., are not included in this status report because it is ok for generated content to have uncommitted changes.
These are the previous versions of the repository in which changes were
made to the R Markdown (analysis/MHWs_categorisation.Rmd)
and HTML (docs/MHWs_categorisation.html) files. If you’ve
configured a remote Git repository (see ?wflow_git_remote),
click on the hyperlinks in the table below to view the files as they
were in that past version.
| File | Version | Author | Date | Message |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rmd | 40fff85 | mlarriere | 2024-04-22 | Adding SST anomaly subsection |
| Rmd | 4690882 | mlarriere | 2024-04-17 | Elbow method graph and 2 clusters |
| html | 924babc | mlarriere | 2024-04-17 | Build site. |
| Rmd | 550ab72 | mlarriere | 2024-04-17 | Cluster analysis test |
| html | 4a8157c | mlarriere | 2024-04-16 | Build site. |
| Rmd | 5acdc98 | mlarriere | 2024-04-16 | Some explanations on categorisation and beginning of cluster analysis |
| html | ad0d737 | mlarriere | 2024-04-16 | Build site. |
| Rmd | f22c4b5 | mlarriere | 2024-04-16 | Some explanations on categorisation and beginning of cluster analysis |
| Rmd | 2c60853 | mlarriere | 2024-04-15 | Some explanations on categorisation and beginning of cluster analysis |
| html | 9910de2 | mlarriere | 2024-04-14 | Build site. |
| html | 50596ee | mlarriere | 2024-04-14 | Build site. |
| Rmd | ac8de8b | mlarriere | 2024-04-14 | Figures MHWs |
| html | 718d84b | mlarriere | 2024-04-14 | Build site. |
| Rmd | a2e118c | mlarriere | 2024-04-14 | Figures MHWs |
| html | c789e3f | mlarriere | 2024-04-13 | Build site. |
| Rmd | acdc838 | mlarriere | 2024-04-13 | Figures MHWs |
| html | bbbc1bb | mlarriere | 2024-04-13 | Build site. |
| Rmd | b080fc9 | mlarriere | 2024-04-13 | Figures MHWs |
| html | 83d1fa3 | mlarriere | 2024-04-13 | Build site. |
| Rmd | c8b3f67 | mlarriere | 2024-04-13 | Figures MHWs |
| html | 1ab66f1 | mlarriere | 2024-04-13 | Build site. |
| Rmd | 25928b0 | mlarriere | 2024-04-13 | Figures MHWs |
| html | 5475def | mlarriere | 2024-04-13 | Build site. |
| Rmd | e2b710d | mlarriere | 2024-04-13 | build North Atlanatic section |
| html | c076fba | mlarriere | 2024-04-12 | Build site. |
| Rmd | a52cee0 | mlarriere | 2024-04-08 | adding subsection MHWs categorisation |
| html | efc6aab | mlarriere | 2024-04-08 | Build site. |
| Rmd | a9ea2a8 | mlarriere | 2024-04-08 | test MHWs cat |
Task
Focusing on 2023 Only core Argo - focus on temperature anomalies
Dependencies
temp_core_va.rds - temperature of core argo floats after vertical alignment.
core_metadata.rds - File with metadata concerning the floats such as platform number, cycle number, date, lat, lon and quality control results.
temp_anomaly_va.rds - file containing the temperature anomalies (temp core - climatology).
2023_mhw_raw.csv - CSV file containing the categorization of surface marine heatwaves, in 2023 and in a 0.25°x0.25° grid.
Outputs
2023_surface_mhws_1x1.rds - file containing the categorization of surface marine heatwaves in a 1°x1° grid, in 2023.
path_emlr_utilities <- "/nfs/kryo/work/jenmueller/emlr_cant/utilities/files/"
path_basin_mask <- "/nfs/kryo/work/datasets/gridded/ocean/interior/reccap2/supplementary/"
path_argo <- '/nfs/kryo/work/datasets/ungridded/3d/ocean/floats/bgc_argo'
path_argo_core <- '/nfs/kryo/work/datasets/ungridded/3d/ocean/floats/core_argo_r_argodata_2024-03-13'
path_argo_core_preprocessed <- paste0(path_argo_core, "/preprocessed_core_data")
path_argo_preprocessed <- paste0(path_argo, "/preprocessed_bgc_data")
path_mhw<- '/net/kryo/work/datasets/gridded/ocean/2d/obs/mhw'Load data
Load biomes
Load Argo floats data
MHWs category
Upscaling Surface Marine Heat Waves
#Aggregate the dataset into 1°x1° grid
argo_grid<-sst_natlantic_2023 %>%
ungroup() %>%
select(lat, lon)
mhw_1x1_natlantic_2023 <- mhw_raw_2023_north_atlantic %>% #----------->long process (few min)
mutate(lat_upscale = floor(lat) + 0.5, #rounding to the lower nearest value and add an offset of 0.5 to match with Argo data grid
lon_upscale = floor(lon) + 0.5,
row_id = row_number() #row identifier - to facilitate comparison with original dataset
) %>%
group_by(lat = lat_upscale, #group the data by lon, lat and time
lon = lon_upscale,
time) %>%
summarise(avg_intensity = mean(intensity), # average intensity
most_freq_category = names(sort(table(category), decreasing = TRUE))[1], #Most frequent category
row_id = first(row_id)
) %>%
ungroup() %>%
arrange(row_id)
test<- mhw_raw_2023_north_atlantic %>% filter(time=="2023-01-01", lat<1, lat>0, lon<1, lon>0)
print(mean(test$intensity))
test1<- mhw_1x1_natlantic_2023 %>% filter(time=="2023-01-01", lat<1, lat>0, lon<1, lon>0)
print(test1)
#Adding biomes value to the surface MHWs
mhw_1x1_natlantic_2023_biomes<-left_join(mhw_1x1_natlantic_2023, biomes_subset, by=c("lat", "lon")) %>%
filter(!is.na(biome_value))
mhw_1x1_natlantic_2023_biomes$month <- format( as.Date(mhw_1x1_natlantic_2023_biomes$time), "%m")#adding month attribute
#Write upscaled MHWs dataset (1°x1°)
mhw_1x1_natlantic_2023_biomes %>% write_rds(file = paste0(path_argo_core_preprocessed,"/", "2023_surface_mhws_1x1.rds"))Surface intensity maps
#Read upscale data
mhw_1x1_natlantic_2023_biomes <- read_rds(file = paste0(path_argo_core_preprocessed,"/", "2023_surface_mhws_1x1.rds"))
# original_plot <- base_map +
# geom_point(data=mhw_raw_2023_north_atlantic, aes(x = lon, y = lat, color = intensity), size=0.1) +
# scale_color_gradient(low = "blue", high = "red") +
# labs(title = "MHW intensity - Original Data") +
# theme_minimal()
# print(original_plot)
mhw_biomes_plot <- base_map +
geom_point(data= mhw_1x1_natlantic_2023_biomes, aes(x = lon, y = lat, color = avg_intensity)) +
scale_color_gradient(low = "blue", high = "red") +
labs(title = "MHW intensity - Upscaled Data") +
theme_minimal()
print(mhw_biomes_plot)
Surface category maps per season
mhw_season_plot_comparison<-function(original_dataset, upscale_dataset, season_of_interest, name_season){
#Select data in season_of_interest
season_original<-original_dataset %>%
filter(month %in% season_of_interest)
season_1x1<-upscale_dataset %>%
filter(month %in% season_of_interest)
#Plot
plot_original<- base_map +
geom_point(data = season_original, aes(x = lon, y = lat, color = factor(category))) +
scale_color_manual(values = c("I Moderate" = "darkgoldenrod1",
"II Strong" = "darkorange",
"III Severe" = "darkred",
"IV Extreme" = "#21152B"), name = "Category")+
guides(color = guide_legend(override.aes = list(shape = 15, size = 10)))+
labs(title = paste0("Surface MHWs in ", name_season, " 2023 - resolution 0.25°x0.25°"))
plot_upscale<- base_map +
geom_point(data = season_1x1, aes(x = lon, y = lat, color = factor(most_freq_category)), size = 0.3) +
scale_color_manual(values = c("I Moderate" = "darkgoldenrod1",
"II Strong" = "darkorange",
"III Severe" = "darkred",
"IV Extreme" = "#21152B"), name = "Category")+
guides(color = guide_legend(override.aes = list(shape = 15, size = 10)))+
labs(title = paste0("Surface MHWs in ", name_season, " 2023 - resolution 1°x1°"))
combined_plot <- grid.arrange(plot_original, plot_upscale, ncol = 2)
print(combined_plot)
}
mhw_season_plot_comparison(mhw_raw_2023_north_atlantic, mhw_1x1_natlantic_2023_biomes, c("03", "04", "05"), "spring")
mhw_season_plot_comparison(mhw_raw_2023_north_atlantic, mhw_1x1_natlantic_2023_biomes, c("06", "07", "08"), "summer")
mhw_season_plot_comparison(mhw_raw_2023_north_atlantic, mhw_1x1_natlantic_2023_biomes, c("09", "10", "11", "12"), "autumn")
mhw_season_plot_comparison(mhw_raw_2023_north_atlantic, mhw_1x1_natlantic_2023_biomes, c("01", "02"), "winter")mhw_season_plot<-function(upscale_dataset, months){
months<-unique(format(as.Date(upscale_dataset$time), "%m"))
print(months)
#Plot
plot_upscale<- base_map +
geom_point(data = upscale_dataset, aes(x = lon, y = lat, color = factor(most_freq_category)), size = 0.3) +
scale_color_manual(values = c("I Moderate" = "darkgoldenrod1",
"II Strong" = "darkorange",
"III Severe" = "darkred",
"IV Extreme" = "#21152B"), name = "Category")+
guides(color = guide_legend(override.aes = list(shape = 15, size = 10)))+
labs(title = paste0("Surface MHWs in 2023"),
subtitle = paste0("Months: ", paste(months, collapse = ", ") ,"\nresolution 1°x1°"))
return(plot_upscale)
}
#Select data in season_of_interest
spring_1x1<-mhw_1x1_natlantic_2023_biomes %>%
filter(month %in% c("03", "04", "05"))
summer_1x1<-mhw_1x1_natlantic_2023_biomes %>%
filter(month %in% c("06", "07", "08"))
autumn_1x1<-mhw_1x1_natlantic_2023_biomes %>%
filter(month %in% c("09", "10", "11", "12"))
winter_1x1<-mhw_1x1_natlantic_2023_biomes %>%
filter(month %in% c("01", "02"))
#Plot MHWs
spring_plot_1x1<-mhw_season_plot(spring_1x1, "spring")[1] "03" "04" "05"summer_plot_1x1<-mhw_season_plot(summer_1x1, "summer")[1] "06" "07" "08"autumn_plot_1x1<-mhw_season_plot(autumn_1x1, "autumn")[1] "09" "10" "11" "12"winter_plot_1x1<-mhw_season_plot(winter_1x1, "winter")[1] "01" "02"combined_plot <- grid.arrange(winter_plot_1x1, spring_plot_1x1, summer_plot_1x1, autumn_plot_1x1, ncol = 2, nrow=2)
print(combined_plot)TableGrob (2 x 2) "arrange": 4 grobs
z cells name grob
1 1 (1-1,1-1) arrange gtable[layout]
2 2 (1-1,2-2) arrange gtable[layout]
3 3 (2-2,1-1) arrange gtable[layout]
4 4 (2-2,2-2) arrange gtable[layout]Argo floats
Strong MHWs regions
#Time in the same format in the 2 dataframes
argo_data_2023 <- sst_with_platform_2023 %>%
mutate(time = as.Date(date))
mhw_1x1_natlantic_2023_biomes <- mhw_1x1_natlantic_2023_biomes %>%
mutate(time = as.Date(time))
#Associating mhws category to the argo profiles
argo_mhws_categ<-left_join(mhw_1x1_natlantic_2023_biomes, argo_data_2023, by=c("lat", "lon", "time")) %>%
filter(!is.na(platform_number)) %>% #select only locations where there is an argo float
rename(biome_value=biome_value.x) %>%
select(platform_number,cycle_number,
depth, lat, lon, time,
avg_intensity, most_freq_category,
biome_value, temp) #Cleaning dataset
#Adding temperature anomaly
argo_anomaly_2023 <- argo_anomaly_2023 %>%
mutate(time = as.Date(date))
#Datasets for each surface MHWs category
mhws_surface_categorisation<- function(argo_categ_dataset, anomaly_dataset, category){
argo_surf_cat<-filter(argo_categ_dataset, most_freq_category==category)
argo_anomaly_cat<- left_join(anomaly_dataset, argo_surf_cat,
by=c("platform_number", "cycle_number","lat", "lon", "depth", "time", "biome_value")) %>%
filter(!is.na(anomaly), !is.na(most_freq_category))
return(argo_anomaly_cat)
}
argo_anomaly_moderate<- mhws_surface_categorisation(argo_mhws_categ, argo_anomaly_2023, category='I Moderate')
argo_anomaly_strong<- mhws_surface_categorisation(argo_mhws_categ, argo_anomaly_2023, category='II Strong')
argo_anomaly_severe<- mhws_surface_categorisation(argo_mhws_categ, argo_anomaly_2023, category='III Severe')
argo_anomaly_extreme<- mhws_surface_categorisation(argo_mhws_categ, argo_anomaly_2023, category='IV Extreme')
final_mhw_argo_cat<-bind_rows(argo_anomaly_moderate,
argo_anomaly_strong,
argo_anomaly_severe,
argo_anomaly_extreme)plot_float_location <- function(data, month_chosen) {
month_biome_dataset <- data %>%
filter(month == sprintf("%02d", match(month_chosen, month.abb)))
#Changing subtitle and color based on biome_value
subtitles <- c("SPSS", "STSS", "STPS")
colors <- c("darkblue", "darkorange", "darkred")
base_map +
geom_point(data = month_biome_dataset, aes(x = lon, y = lat, color = factor(biome_value)), size = 2) +
scale_color_manual(values = colors, name = "Biome", labels = subtitles) +
labs(title = paste("Float Locations in North Atlantic Ocean in 2023"),
subtitle = paste0("Month: ", month_chosen))
}
#Anomaly T°C plot for each month
plot_list <- list()
for (month in month.abb) {
plot <- plot_float_location(argo_data_2023, month)
plot_list[[month]]<- plot
}
plot_list$Jan
$Feb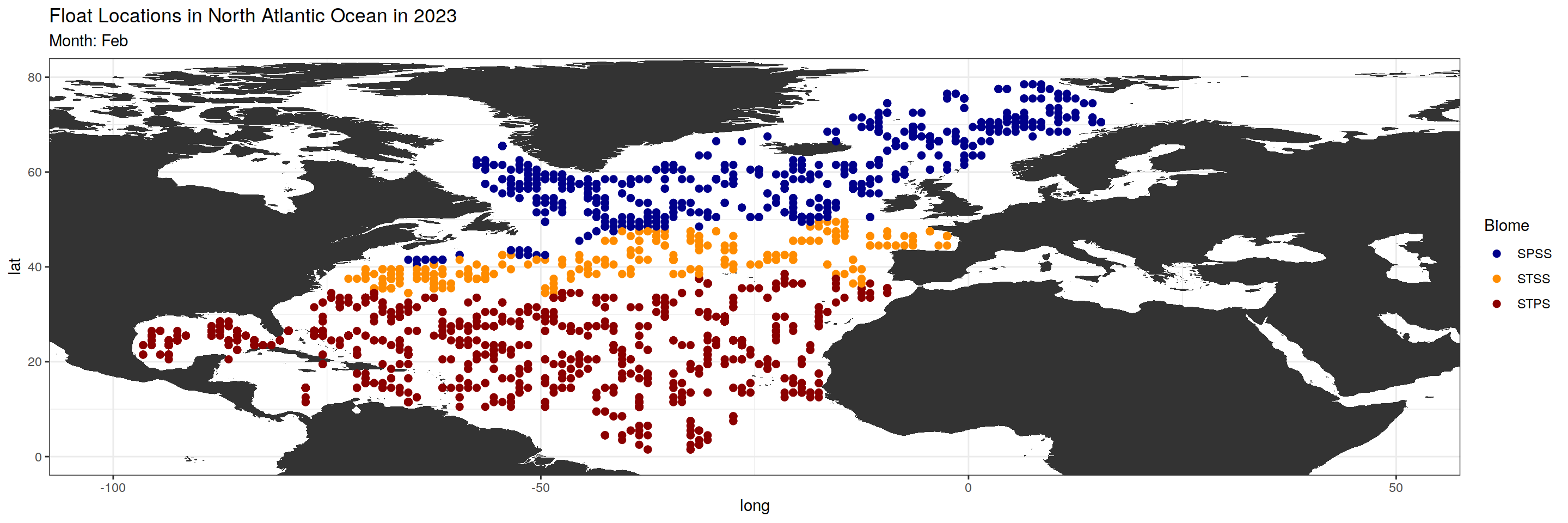
$Mar
$Apr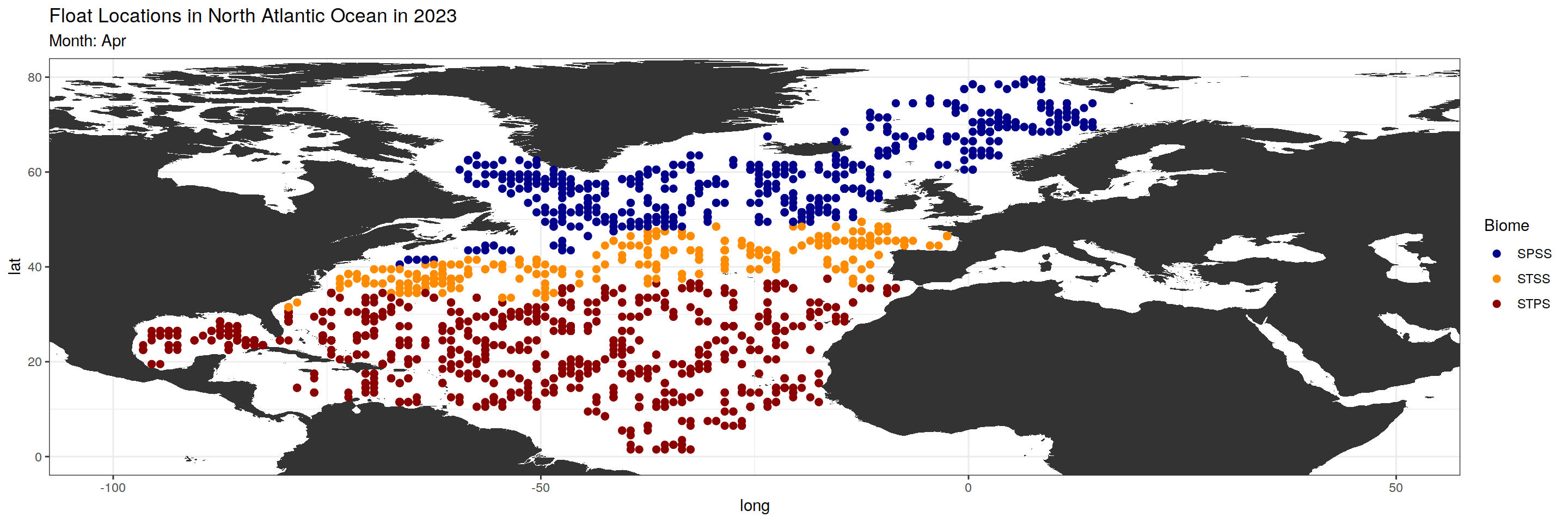
$May
$Jun
$Jul
$Aug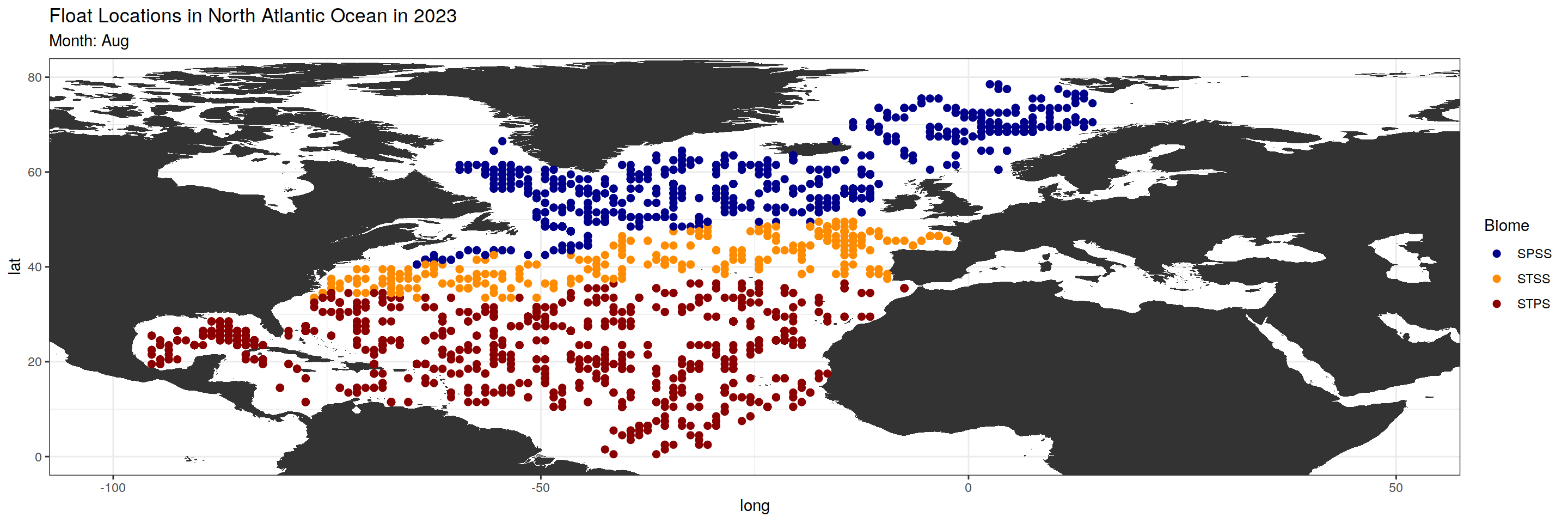
$Sep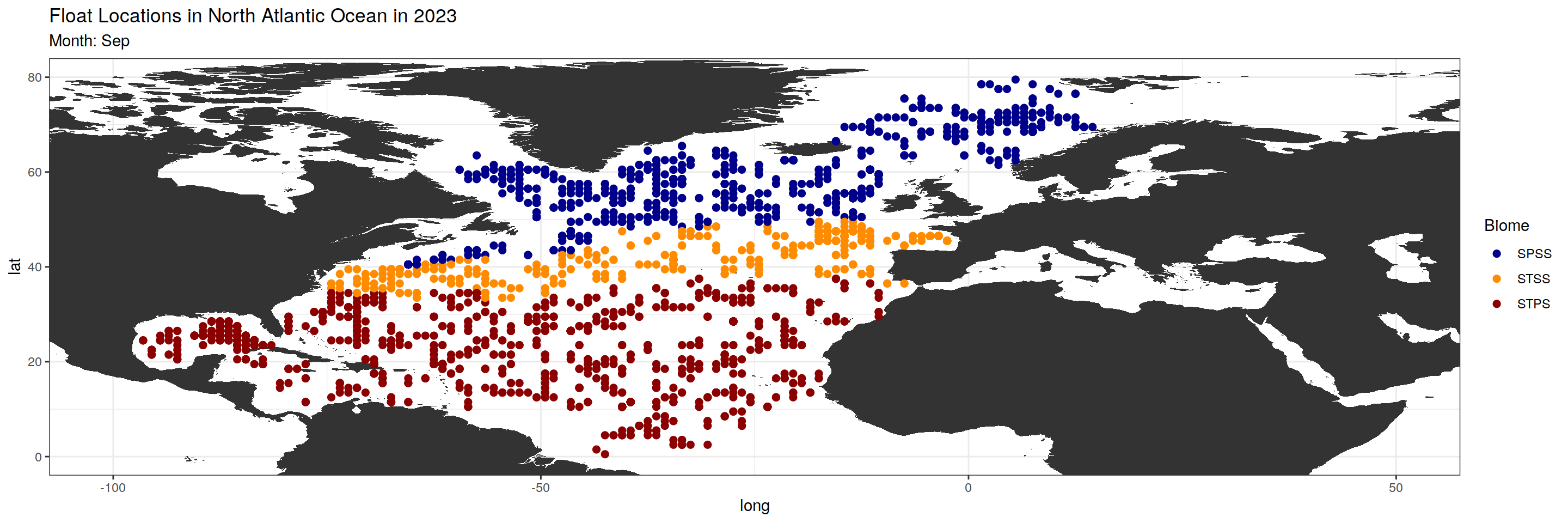
$Oct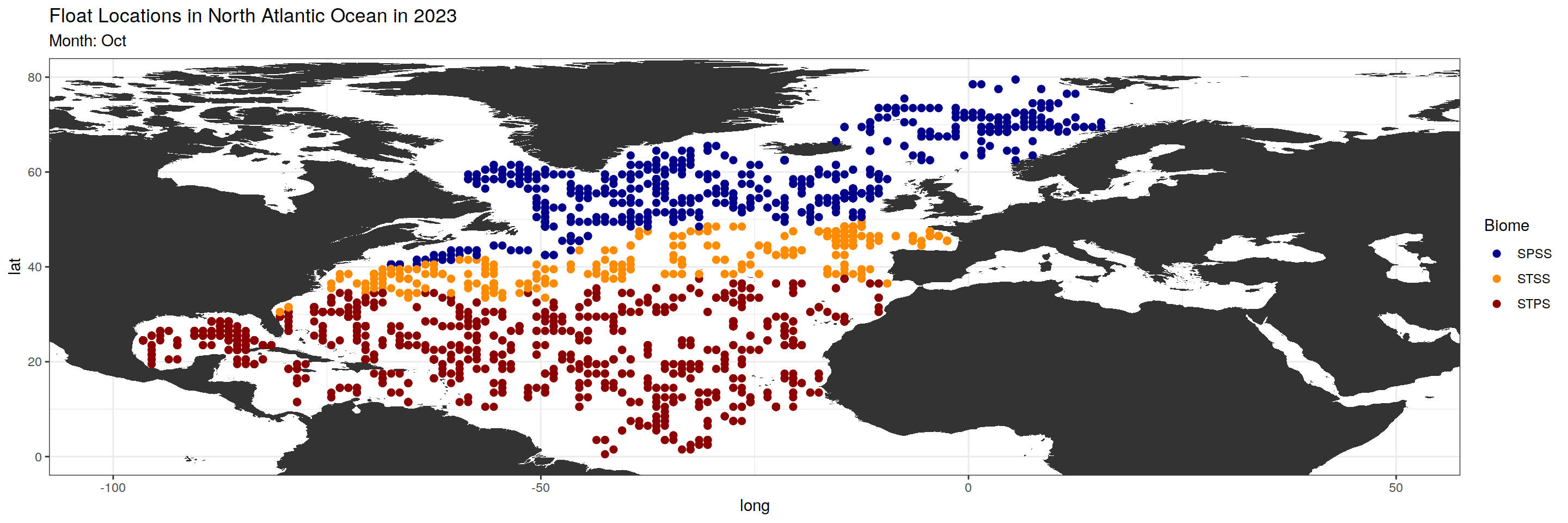
$Nov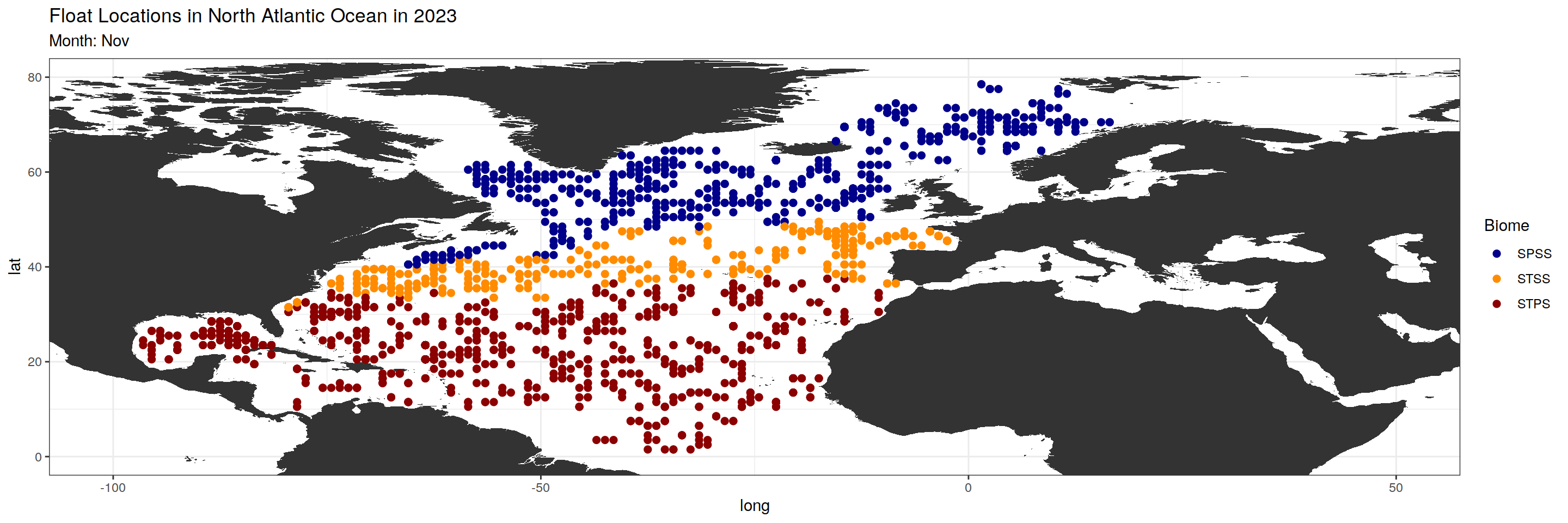
$Dec
#Histogram -- number of floats per month and biome
unique_platforms_per_month <- argo_data_2023 %>%
group_by(month, biome_value) %>%
summarize(unique_platforms = n_distinct(platform_number))
hist <- ggplot(unique_platforms_per_month, aes(x = factor(month), y = unique_platforms, fill=factor(biome_value))) +
geom_bar(stat = "identity")+#, position = "dodge") +
labs(title= paste0("Amount of platform per month and per biome, in 2023"),
x = "Months", y = "Number of argo floats", fill = "Biomes") +
scale_fill_manual(values = c("1" = "#1034A6", "2" = "#f59c04", "3" = "darkred"),
labels = c("1" = "SPSS", "2" = "STSS", "3" = "STPS")) +
theme_minimal()
print(hist)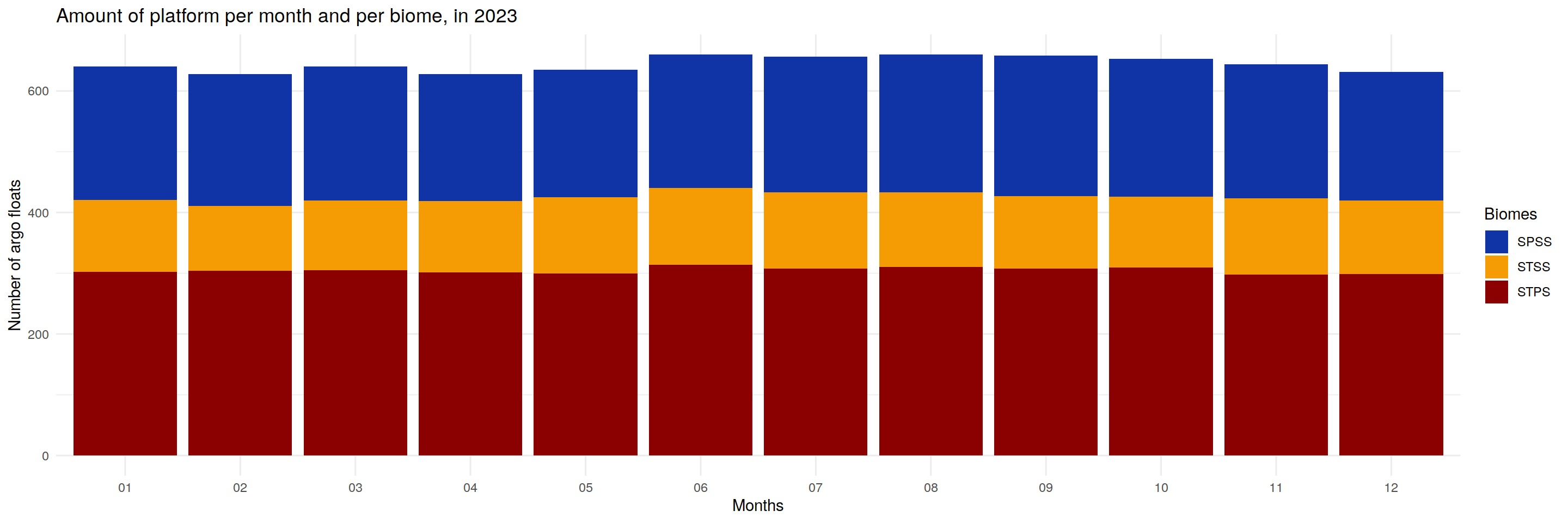 # SST anomaly
# SST anomaly
#Read SST anomaly, computed using climatology:2009-2019 (from anomaly_SST_2023.Rmd)
sst_anomaly<- read_rds(paste(path_argo_core_preprocessed, "/SST_anomaly2023_clim2004-2019.rds", sep = ""))Area of interest
#Defining are of interest spatially and temporally depending on SST anomaly
#hotpost in JJA + SON in agreement with climate reanaliser
lat_max<-55
lat_min<-40
lon_max<--40
lon_min<- -60
july_heatwave<-
#Annual hotpost (+MAM + JJA + a bit SON) in agreement with climate reanaliser
lat_max<-55
lat_min<-5
lon_max<--5
lon_min<- -30
hotspot_extent<- Mean anomaly temperature profile
Per biomes and months
We investigate the mean temperature anomaly profile for each biome and over months in 2023.
plot_anomaly_profiles_biomes <- function(data, biome_chosen) {
# Filter data for the chosen biome
biome_data <- filter(data, biome_value == biome_chosen)
# Anomaly statistics
anomaly_overall_mean <- biome_data %>%
group_by(depth, month, biome_value) %>%
summarise(temp_count = n(),
temp_anomaly_mean = mean(anomaly, na.rm = TRUE),
temp_anomaly_sd = sd(anomaly, na.rm = TRUE))
# Subtitle and color based on biome chosen
subtitle <- switch(biome_chosen,
"1" = "SPSS",
"2" = "STSS",
"3" = "STPS")
color_SPSS <- "darkblue"
color_STSS <- "darkorange"
color_STPS <- "darkred"
colors <- c("1" = color_SPSS, "2" = color_STSS, "3" = color_STPS)
# Anomaly plot
ggplot(anomaly_overall_mean) +
geom_path(aes(x = temp_anomaly_mean, y = depth, color = factor(month))) +
geom_ribbon(aes(xmax = temp_anomaly_mean + temp_anomaly_sd,
xmin = temp_anomaly_mean - temp_anomaly_sd,
y = depth, fill = factor(biome_value)), alpha = 0.4) +
geom_vline(xintercept = 0) +
scale_y_reverse() +
coord_cartesian(xlim = c(-4.5, 6)) +
scale_x_continuous(breaks = c(-4, -2, 0, 2, 4, 6)) +
labs(title = paste0('Mean Temperature anomaly profiles - up to 600m depth'),
x = "Temperature anomaly (°C)", y = 'depth (m)', color = "Biome") +
scale_color_manual(values = colors[biome_chosen],
labels = subtitle) +
scale_fill_manual(values = colors[biome_chosen],
name = "Biome", labels = subtitle) +
facet_wrap(~ month, ncol = 3, labeller = labeller(month.abb)) +
theme(axis.text.x = element_text(angle = 0, hjust = 1)) +
theme(legend.position = "bottom")
}
plot_anomaly_profiles_biomes(final_mhw_argo_cat, 1)
plot_anomaly_profiles_biomes(final_mhw_argo_cat, 2)
plot_anomaly_profiles_biomes(final_mhw_argo_cat, 3)Floats classification
We classify marine heat waves according to their intensity and propagation over the water column:
When the temperature anomaly is equal to or greater than 1°C, we consider the anomaly to be big, otherwise it is considered as small.
Then we look at the vertical propagation of the MHWS: - Shallow MHWs: When a big anomaly is detected between 0 and 100 meters depth.
- Medium MHWs: When a big anomaly is detected between 0 and 200 meters depth.
- Deep MHWs: When a big anomaly is detected between 0 and 600 meters depth.# Defining the anomaly class as a function of anomaly value and depth
threshold <- argo_anomaly_moderate %>%
filter(anomaly >= 1) %>% # Look only at positive anomaly values
group_by(depth) %>%
summarise(depth_threshold = max(depth))
argo_anomaly_dataset <- argo_anomaly_moderate %>%
mutate(anomaly_class = ifelse(anomaly >= 1 & depth <= threshold$depth_threshold, "Big", "Small")) %>%
mutate(anomaly_class = factor(anomaly_class, levels = c("Big", "Small")))
# Group the data by float identifiers
max_depth_by_float <- argo_anomaly_moderate %>%
filter(anomaly >= 1) %>%
group_by(file_id, lat, lon) %>%
summarise(max_depth = max(depth))
# Define mhw_class based on the maximum depth
max_depth_by_float <- max_depth_by_float %>%
mutate(mhw_class = case_when(
max_depth <= 100 ~ "Shallow",
max_depth <= 200 ~ "Medium",
TRUE ~ "Deep"
))
#Combining datasets
final_mhw_argo_cat<-left_join(max_depth_by_float, argo_anomaly_dataset, by=c("file_id", "lat","lon") )
plot_anomaly_categorisation <- function(anomaly_data) {
anomaly_classes <- anomaly_data %>%
distinct(depth, anomaly_class)
ggplot(anomaly_data) +
geom_rect(data = anomaly_data %>% distinct(depth, anomaly_class),
aes(xmin = -Inf, xmax = Inf, ymin = lag(depth), ymax = depth, fill = anomaly_class),
inherit.aes = FALSE) +
geom_path(aes(x = anomaly , y = depth)) +
geom_vline(xintercept = 0) +
scale_fill_manual(values = c("Big" = "lightblue", "Small" = "lightyellow"),
name = "Anomaly Class", labels = c("Big Anomaly", "Small Anomaly")
) +
scale_y_reverse() +
coord_cartesian(xlim = c(-4.5, 6)) +
scale_x_continuous(breaks = c(-4, -2, 0, 2, 4, 6)) +
labs(title = paste0('Anomaly profile in ', month.name[unique(month(anomaly_data$time))], ' 2023'),
subtitle = paste0('Location: (', unique(anomaly_data$lat), ',', unique(anomaly_data$lon),')\n',
'Type of surface MHW: ', unique(anomaly_data$most_freq_category),"\n",
'Type of argo MHW: ', unique(anomaly_data$mhw_class)),
x = "Temperature anomaly (°C)", y = 'depth (m)')
}
shallow<-plot_anomaly_categorisation(final_mhw_argo_cat %>% filter(file_id==20))
medium<-plot_anomaly_categorisation(final_mhw_argo_cat %>% filter(file_id==10))
deep<-plot_anomaly_categorisation(final_mhw_argo_cat %>% filter(file_id==6396))
combined_plot <- grid.arrange(shallow, medium, deep, ncol = 3)
print(combined_plot)
sessionInfo()R version 4.2.2 (2022-10-31)
Platform: x86_64-pc-linux-gnu (64-bit)
Running under: openSUSE Leap 15.5
Matrix products: default
BLAS: /usr/local/R-4.2.2/lib64/R/lib/libRblas.so
LAPACK: /usr/local/R-4.2.2/lib64/R/lib/libRlapack.so
locale:
[1] LC_CTYPE=en_US.UTF-8 LC_NUMERIC=C
[3] LC_TIME=en_US.UTF-8 LC_COLLATE=en_US.UTF-8
[5] LC_MONETARY=en_US.UTF-8 LC_MESSAGES=en_US.UTF-8
[7] LC_PAPER=en_US.UTF-8 LC_NAME=C
[9] LC_ADDRESS=C LC_TELEPHONE=C
[11] LC_MEASUREMENT=en_US.UTF-8 LC_IDENTIFICATION=C
attached base packages:
[1] stats graphics grDevices utils datasets methods base
other attached packages:
[1] broom_1.0.5 paletteer_1.6.0 cluster_2.1.6
[4] gridExtra_2.3 scatterplot3d_0.3-44 viridis_0.6.2
[7] viridisLite_0.4.1 ggOceanMaps_1.3.4 ggspatial_1.1.7
[10] oce_1.7-10 gsw_1.1-1 lubridate_1.9.0
[13] timechange_0.1.1 forcats_0.5.2 stringr_1.5.0
[16] dplyr_1.1.3 purrr_1.0.2 readr_2.1.3
[19] tidyr_1.3.0 tibble_3.2.1 ggplot2_3.4.4
[22] tidyverse_1.3.2 workflowr_1.7.0
loaded via a namespace (and not attached):
[1] googledrive_2.0.0 colorspace_2.0-3 ellipsis_0.3.2
[4] class_7.3-20 rprojroot_2.0.3 fs_1.5.2
[7] rstudioapi_0.15.0 proxy_0.4-27 farver_2.1.1
[10] fansi_1.0.3 xml2_1.3.3 codetools_0.2-18
[13] cachem_1.0.6 knitr_1.41 jsonlite_1.8.3
[16] dbplyr_2.2.1 rgeos_0.5-9 compiler_4.2.2
[19] httr_1.4.4 backports_1.4.1 assertthat_0.2.1
[22] fastmap_1.1.0 gargle_1.2.1 cli_3.6.1
[25] later_1.3.0 htmltools_0.5.8.1 tools_4.2.2
[28] gtable_0.3.1 glue_1.6.2 maps_3.4.1
[31] Rcpp_1.0.10 cellranger_1.1.0 jquerylib_0.1.4
[34] RNetCDF_2.6-1 raster_3.6-11 vctrs_0.6.4
[37] lwgeom_0.2-10 xfun_0.35 ps_1.7.2
[40] rvest_1.0.3 lifecycle_1.0.3 ncmeta_0.3.5
[43] googlesheets4_1.0.1 terra_1.7-65 getPass_0.2-2
[46] scales_1.2.1 hms_1.1.2 promises_1.2.0.1
[49] parallel_4.2.2 rematch2_2.1.2 yaml_2.3.6
[52] sass_0.4.4 stringi_1.7.8 highr_0.9
[55] e1071_1.7-12 rlang_1.1.1 pkgconfig_2.0.3
[58] evaluate_0.18 lattice_0.20-45 sf_1.0-9
[61] labeling_0.4.2 processx_3.8.0 tidyselect_1.2.0
[64] magrittr_2.0.3 R6_2.5.1 generics_0.1.3
[67] DBI_1.2.2 pillar_1.9.0 haven_2.5.1
[70] whisker_0.4 withr_2.5.0 units_0.8-0
[73] stars_0.6-0 abind_1.4-5 sp_1.5-1
[76] modelr_0.1.10 crayon_1.5.2 KernSmooth_2.23-20
[79] utf8_1.2.2 tzdb_0.3.0 rmarkdown_2.18
[82] grid_4.2.2 readxl_1.4.1 callr_3.7.3
[85] git2r_0.30.1 reprex_2.0.2 digest_0.6.30
[88] classInt_0.4-8 httpuv_1.6.6 munsell_0.5.0
[91] bslib_0.4.1