Comparison of cant estimates to results of Gruber et al 2019
Jens Daniel Müller
06 January, 2021
Last updated: 2021-01-06
Checks: 7 0
Knit directory: emlr_mod_v_XXX/
This reproducible R Markdown analysis was created with workflowr (version 1.6.2). The Checks tab describes the reproducibility checks that were applied when the results were created. The Past versions tab lists the development history.
Great! Since the R Markdown file has been committed to the Git repository, you know the exact version of the code that produced these results.
Great job! The global environment was empty. Objects defined in the global environment can affect the analysis in your R Markdown file in unknown ways. For reproduciblity it’s best to always run the code in an empty environment.
The command set.seed(20200707) was run prior to running the code in the R Markdown file. Setting a seed ensures that any results that rely on randomness, e.g. subsampling or permutations, are reproducible.
Great job! Recording the operating system, R version, and package versions is critical for reproducibility.
Nice! There were no cached chunks for this analysis, so you can be confident that you successfully produced the results during this run.
Great job! Using relative paths to the files within your workflowr project makes it easier to run your code on other machines.
Great! You are using Git for version control. Tracking code development and connecting the code version to the results is critical for reproducibility.
The results in this page were generated with repository version 1d55c11. See the Past versions tab to see a history of the changes made to the R Markdown and HTML files.
Note that you need to be careful to ensure that all relevant files for the analysis have been committed to Git prior to generating the results (you can use wflow_publish or wflow_git_commit). workflowr only checks the R Markdown file, but you know if there are other scripts or data files that it depends on. Below is the status of the Git repository when the results were generated:
Ignored files:
Ignored: .Rhistory
Ignored: .Rproj.user/
Unstaged changes:
Modified: code/Workflowr_project_managment.R
Note that any generated files, e.g. HTML, png, CSS, etc., are not included in this status report because it is ok for generated content to have uncommitted changes.
These are the previous versions of the repository in which changes were made to the R Markdown (analysis/analysis_this_study_vs_Gruber_2019.Rmd) and HTML (docs/analysis_this_study_vs_Gruber_2019.html) files. If you’ve configured a remote Git repository (see ?wflow_git_remote), click on the hyperlinks in the table below to view the files as they were in that past version.
| File | Version | Author | Date | Message |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| html | e5cb81a | Donghe-Zhu | 2021-01-05 | Build site. |
| Rmd | 608cc45 | Donghe-Zhu | 2021-01-05 | modification of analysis |
| html | a499f10 | Donghe-Zhu | 2021-01-05 | Build site. |
| Rmd | 5855606 | Donghe-Zhu | 2021-01-05 | first model-based run |
| Rmd | 715bdb4 | Donghe-Zhu | 2021-01-02 | model modification |
| html | fb8a752 | Donghe-Zhu | 2020-12-23 | Build site. |
| html | 8fae0b2 | Donghe-Zhu | 2020-12-21 | Build site. |
| html | c8b76b3 | jens-daniel-mueller | 2020-12-19 | Build site. |
| Rmd | b5fedce | jens-daniel-mueller | 2020-12-19 | first build after creating model template |
| Rmd | 8e8abf5 | Jens Müller | 2020-12-18 | Initial commit |
1 Data sources
Following Cant estimates are used:
- Zonal mean (basin, lat, depth)
- Inventories (lat, lon)
1.1 This study
Results from this study are referred to as JDM.
cant_zonal_JDM <-
read_csv(paste(path_version_data,
"cant_zonal.csv",
sep = ""))
cant_zonal_JDM <- cant_zonal_JDM %>%
filter(eras == unique(cant_zonal_JDM$eras)[1]) %>%
select(lat,
depth,
basin_AIP,
cant_mean,
cant_pos_mean,
cant_sd,
cant_pos_sd)
cant_inv_JDM <-
read_csv(paste(path_version_data,
"cant_inv.csv",
sep = ""))
cant_inv_JDM <- cant_inv_JDM %>%
filter(eras == unique(cant_inv_JDM$eras)[1],
inv_depth == params_global$inventory_depth_standard) %>%
select(-c(eras))1.2 Modeled Cant
Results from modeled Cant is referred to as M.
tref <-
read_csv(paste(path_version_data,
"tref.csv",
sep = ""))
cant_tref_1 <-
read_csv(paste(
path_preprocessing,
"cant_annual_field_AD/cant_",
unique(tref$year[1]),
".csv",
sep = ""
))
cant_tref_1 <- cant_tref_1 %>%
rename(cant_tref_1 = cant_total) %>%
select(-year)
cant_tref_2 <-
read_csv(paste(
path_preprocessing,
"cant_annual_field_AD/cant_",
unique(tref$year[2]),
".csv",
sep = ""
))
cant_tref_2 <- cant_tref_2 %>%
rename(cant_tref_2 = cant_total) %>%
select(-year)cant_M <- left_join(cant_tref_1, cant_tref_2) %>%
mutate(cant = cant_tref_2 - cant_tref_1)
cant_M <- cant_M %>%
mutate(cant_pos = if_else(cant <= 0, 0, cant))
cant_M <- cant_M %>%
mutate(eras = "JGOFS/WOCE")
rm(cant_cant_tref_1, cant_cant_tref_2)cant_zonal_M <- m_zonal_mean_section(cant_M)
cant_zonal_M <- cant_zonal_M %>%
select(lat,
depth,
basin_AIP,
cant_mean,
cant_pos_mean,
cant_sd,
cant_pos_sd)cant_inv_M <- m_cant_inv(cant_M)
cant_inv_M <- cant_inv_M %>%
select(-eras)1.3 Join data sets
Inventories and zonal sections are merged, and differences calculate per grid cell.
# add estimate label
cant_inv_long <- bind_rows(
cant_inv_JDM %>% mutate(estimate = "JDM"),
cant_inv_M %>% mutate(estimate = "M")
)
# pivot to wide format
cant_inv_wide <- cant_inv_long %>%
pivot_wider(names_from = estimate, values_from = cant_pos_inv:cant_inv) %>%
drop_na()
# calculate offset
cant_inv_wide <- cant_inv_wide %>%
mutate(cant_pos_inv_offset = cant_pos_inv_JDM - cant_pos_inv_M,
cant_inv_offset = cant_inv_JDM - cant_inv_M,
estimate = "JDM - M")# add estimate label
cant_zonal_long <- bind_rows(
cant_zonal_JDM %>% mutate(estimate = "JDM"),
cant_zonal_M %>% mutate(estimate = "M")
)
# pivot to wide format
cant_zonal_wide <- cant_zonal_long %>%
pivot_wider(names_from = estimate, values_from = cant_mean:cant_pos_sd) %>%
drop_na()
# calculate offset
cant_zonal_wide <- cant_zonal_wide %>%
mutate(cant_pos_mean_offset = cant_pos_mean_JDM - cant_pos_mean_M,
cant_mean_offset = cant_mean_JDM - cant_mean_M,
estimate = "JDM - M")2 Cant budgets
Global Cant inventories budget were estimated for different ocean basins in units of Pg C, based on all vs positive only Cant estimates. Please note that here we only added Cant values for the standard inventory depth (3000 m) and do not apply additional corrections for areas not covered.
# calculate budgets
cant_inv_budget <- cant_inv_long %>%
mutate(surface_area = earth_surf(lat, lon),
cant_inv_grid = cant_inv*surface_area,
cant_pos_inv_grid = cant_pos_inv*surface_area) %>%
group_by(basin_AIP, estimate) %>%
summarise(cant_total = sum(cant_inv_grid)*12*1e-15,
cant_total = round(cant_total,1),
cant_pos_total = sum(cant_pos_inv_grid)*12*1e-15,
cant_pos_total = round(cant_pos_total,1)) %>%
ungroup()
# print budget table
cant_inv_budget %>%
gt(rowname_col = "basin_AIP",
groupname_col = c("estimate")) %>%
summary_rows(
groups = TRUE,
fns = list(total = "sum")
)| cant_total | cant_pos_total | |
|---|---|---|
| JDM | ||
| Atlantic | 7.3 | 7.7 |
| Indian | 4.9 | 6.4 |
| Pacific | 17.1 | 18.4 |
| total | 29.30 | 32.50 |
| M | ||
| Atlantic | 20.7 | 20.8 |
| Indian | 21.6 | 21.6 |
| Pacific | 41.4 | 41.6 |
| total | 83.70 | 84.00 |
rm(cant_inv_budget)3 Cant - positive only
In a first series of plots we explore the distribution of Cant, taking only positive estimates into account (positive here refers to the mean cant estimate across the MLR model predictions available for each grid cell). Negative values were set to zero before calculating mean sections and inventories.
3.1 Inventory maps
3.1.1 Absolute values
Column inventory of positive Cant between the surface and 3000m water depth per horizontal grid cell (lat x lon).
# i_estimate <- unique(cant_inv_long$estimate)[1]
for (i_estimate in unique(cant_inv_long$estimate)) {
print(
p_map_cant_inv(
cant_inv_long %>% filter(estimate == i_estimate),
subtitle_text = paste("Estimate:", i_estimate))
)
}

3.1.2 Offset
Column inventory of positive cant between the surface and 3000m water depth per horizontal grid cell (lat x lon).
p_map_cant_inv_offset(cant_inv_wide,
"cant_pos_inv_offset",
subtitle_text = "Estimate JDM - M")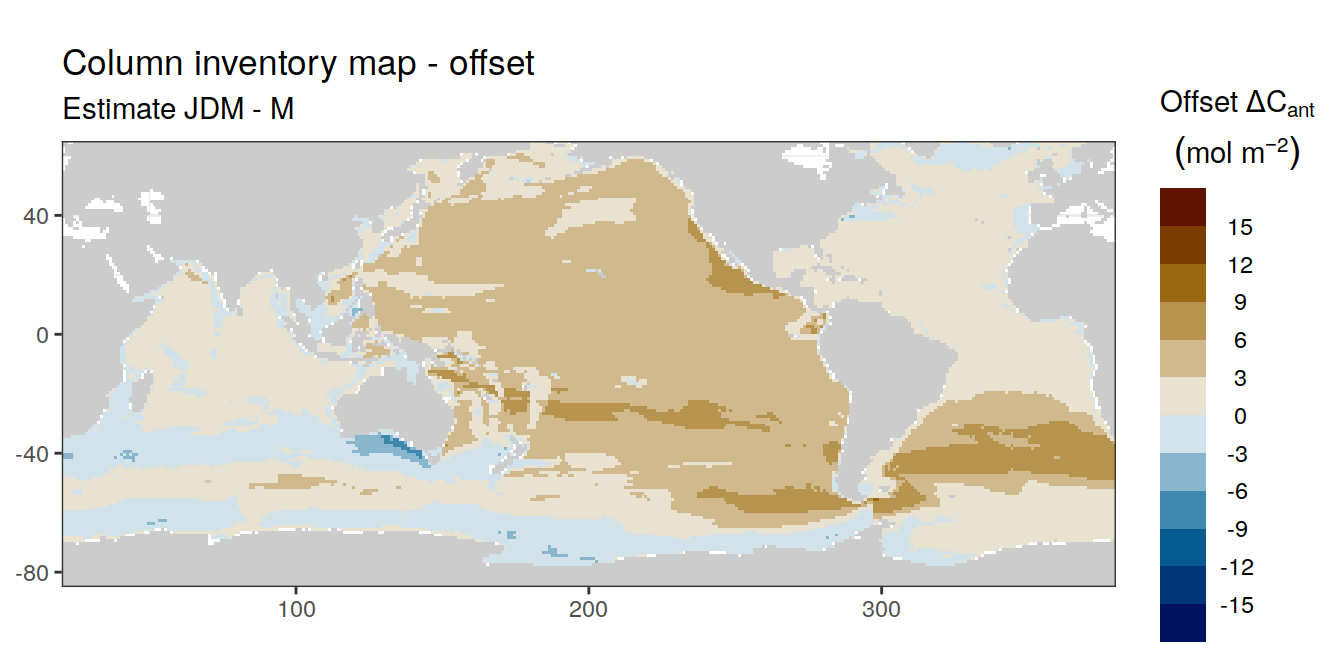
3.2 Zonal mean sections
3.2.1 Absolute values
# i_basin_AIP <- unique(cant_zonal_long$basin_AIP)[1]
# i_estimate <- unique(cant_zonal_long$estimate)[1]
for (i_basin_AIP in unique(cant_zonal_long$basin_AIP)) {
for (i_estimate in unique(cant_zonal_long$estimate)) {
print(
p_section_zonal(
df = cant_zonal_long %>%
filter(basin_AIP == i_basin_AIP,
estimate == i_estimate),
var = "cant_pos_mean",
plot_slabs = "n",
subtitle_text =
paste("Basin:", i_basin_AIP, "| estimate:", i_estimate)
)
)
}
}





3.2.2 Offset
# i_basin_AIP <- unique(cant_zonal_wide$basin_AIP)[1]
for (i_basin_AIP in unique(cant_zonal_wide$basin_AIP)) {
print(
p_section_zonal(
df = cant_zonal_wide %>%
filter(basin_AIP == i_basin_AIP),
var = "cant_pos_mean_offset",
breaks = params_global$breaks_cant_offset,
plot_slabs = "n",
col = "divergent",
subtitle_text =
paste("Basin:", i_basin_AIP, "| estimate: JDM-M")
)
)
}


4 Cant - all
In a second series of plots we explore the distribution of Cant, taking positive and negative estimates into account (positive here refers to the mean cant estimate across MLR model predictions available for each grid cell).
4.1 Inventory maps
4.1.1 Absolute values
Column inventory of Cant (including positive and negative values) between the surface and 3000m water depth per horizontal grid cell (lat x lon).
# i_estimate <- unique(cant_inv_long$estimate)[1]
for (i_estimate in unique(cant_inv_long$estimate)) {
print(
p_map_cant_inv(
cant_inv_long %>% filter(estimate == i_estimate),
subtitle_text = paste("Estimate:", i_estimate),
col = "divergent")
)
}

4.2 Zonal mean sections
4.2.1 Absolute values
# i_basin_AIP <- unique(df$basin_AIP)[1]
# i_estimate <- unique(df$estimate)[1]
for (i_basin_AIP in unique(cant_zonal_long$basin_AIP)) {
for (i_estimate in unique(cant_zonal_long$estimate)) {
print(
p_section_zonal(
df = cant_zonal_long %>%
filter(basin_AIP == i_basin_AIP,
estimate == i_estimate),
var = "cant_mean",
col = "divergent",
breaks = params_global$breaks_cant,
plot_slabs = "n",
legend_title = expression(atop(Delta * C[ant],
(mu * mol ~ kg ^ {-1}))),
subtitle_text =
paste("Basin:", i_basin_AIP, "| estimate:", i_estimate)
)
)
}
}





4.2.2 Offset
# i_basin_AIP <- unique(cant_zonal_wide$basin_AIP)[1]
for (i_basin_AIP in unique(cant_zonal_wide$basin_AIP)) {
print(
p_section_zonal(
df = cant_zonal_wide %>%
filter(basin_AIP == i_basin_AIP),
var = "cant_mean_offset",
plot_slabs = "n",
col = "divergent",
breaks = params_global$breaks_cant_offset,
subtitle_text =
paste("Basin:", i_basin_AIP, "| estimate: JDM - M")
)
)
}


sessionInfo()R version 4.0.3 (2020-10-10)
Platform: x86_64-pc-linux-gnu (64-bit)
Running under: openSUSE Leap 15.2
Matrix products: default
BLAS: /usr/local/R-4.0.3/lib64/R/lib/libRblas.so
LAPACK: /usr/local/R-4.0.3/lib64/R/lib/libRlapack.so
locale:
[1] LC_CTYPE=en_US.UTF-8 LC_NUMERIC=C
[3] LC_TIME=en_US.UTF-8 LC_COLLATE=en_US.UTF-8
[5] LC_MONETARY=en_US.UTF-8 LC_MESSAGES=en_US.UTF-8
[7] LC_PAPER=en_US.UTF-8 LC_NAME=C
[9] LC_ADDRESS=C LC_TELEPHONE=C
[11] LC_MEASUREMENT=en_US.UTF-8 LC_IDENTIFICATION=C
attached base packages:
[1] stats graphics grDevices utils datasets methods base
other attached packages:
[1] gt_0.2.2 marelac_2.1.10 shape_1.4.5 scales_1.1.1
[5] metR_0.9.0 scico_1.2.0 patchwork_1.1.1 collapse_1.5.0
[9] forcats_0.5.0 stringr_1.4.0 dplyr_1.0.2 purrr_0.3.4
[13] readr_1.4.0 tidyr_1.1.2 tibble_3.0.4 ggplot2_3.3.2
[17] tidyverse_1.3.0 workflowr_1.6.2
loaded via a namespace (and not attached):
[1] httr_1.4.2 sass_0.2.0 jsonlite_1.7.1
[4] here_0.1 modelr_0.1.8 assertthat_0.2.1
[7] blob_1.2.1 cellranger_1.1.0 yaml_2.2.1
[10] pillar_1.4.7 backports_1.1.10 lattice_0.20-41
[13] glue_1.4.2 RcppEigen_0.3.3.7.0 digest_0.6.27
[16] promises_1.1.1 checkmate_2.0.0 rvest_0.3.6
[19] colorspace_1.4-1 htmltools_0.5.0 httpuv_1.5.4
[22] Matrix_1.2-18 pkgconfig_2.0.3 broom_0.7.2
[25] seacarb_3.2.14 haven_2.3.1 whisker_0.4
[28] later_1.1.0.1 git2r_0.27.1 farver_2.0.3
[31] generics_0.0.2 ellipsis_0.3.1 withr_2.3.0
[34] cli_2.1.0 magrittr_1.5 crayon_1.3.4
[37] readxl_1.3.1 evaluate_0.14 fs_1.5.0
[40] fansi_0.4.1 xml2_1.3.2 RcppArmadillo_0.10.1.2.0
[43] oce_1.2-0 tools_4.0.3 data.table_1.13.2
[46] hms_0.5.3 lifecycle_0.2.0 munsell_0.5.0
[49] reprex_0.3.0 gsw_1.0-5 isoband_0.2.2
[52] compiler_4.0.3 rlang_0.4.9 grid_4.0.3
[55] rstudioapi_0.13 labeling_0.4.2 rmarkdown_2.5
[58] testthat_2.3.2 gtable_0.3.0 DBI_1.1.0
[61] R6_2.5.0 lubridate_1.7.9 knitr_1.30
[64] rprojroot_2.0.2 stringi_1.5.3 parallel_4.0.3
[67] Rcpp_1.0.5 vctrs_0.3.5 dbplyr_1.4.4
[70] tidyselect_1.1.0 xfun_0.18 