Log
Last updated: 2020-11-03
Checks: 6 1
Knit directory: GradLog/
This reproducible R Markdown analysis was created with workflowr (version 1.6.2). The Checks tab describes the reproducibility checks that were applied when the results were created. The Past versions tab lists the development history.
The R Markdown is untracked by Git. To know which version of the R Markdown file created these results, you’ll want to first commit it to the Git repo. If you’re still working on the analysis, you can ignore this warning. When you’re finished, you can run wflow_publish to commit the R Markdown file and build the HTML.
Great job! The global environment was empty. Objects defined in the global environment can affect the analysis in your R Markdown file in unknown ways. For reproduciblity it’s best to always run the code in an empty environment.
The command set.seed(20201014) was run prior to running the code in the R Markdown file. Setting a seed ensures that any results that rely on randomness, e.g. subsampling or permutations, are reproducible.
Great job! Recording the operating system, R version, and package versions is critical for reproducibility.
Nice! There were no cached chunks for this analysis, so you can be confident that you successfully produced the results during this run.
Great job! Using relative paths to the files within your workflowr project makes it easier to run your code on other machines.
Great! You are using Git for version control. Tracking code development and connecting the code version to the results is critical for reproducibility.
The results in this page were generated with repository version a167ba4. See the Past versions tab to see a history of the changes made to the R Markdown and HTML files.
Note that you need to be careful to ensure that all relevant files for the analysis have been committed to Git prior to generating the results (you can use wflow_publish or wflow_git_commit). workflowr only checks the R Markdown file, but you know if there are other scripts or data files that it depends on. Below is the status of the Git repository when the results were generated:
Ignored files:
Ignored: .DS_Store
Ignored: .Rhistory
Ignored: .Rproj.user/
Ignored: analysis/.DS_Store
Ignored: code/.DS_Store
Ignored: data/.DS_Store
Ignored: output/.DS_Store
Untracked files:
Untracked: analysis/Log.Rmd
Untracked: data/GO.organizedResult.csv
Unstaged changes:
Modified: analysis/Trans.Rmd
Modified: analysis/_site.yml
Modified: analysis/index.Rmd
Note that any generated files, e.g. HTML, png, CSS, etc., are not included in this status report because it is ok for generated content to have uncommitted changes.
There are no past versions. Publish this analysis with wflow_publish() to start tracking its development.
Nov 01
Why use minModuleSize=30 in WGCNA for TCGA?
There are three reasons why I set the minimum number of genes in modules to be 30.
1. DGN used this setting.
At first, we looked at the variance explained by the top three PC of each modules under different settings, i.e. minModuleSize=100, 50, 30. We found that under setting of 30, the top three PC’s explained more variance, so we tended to use 30.
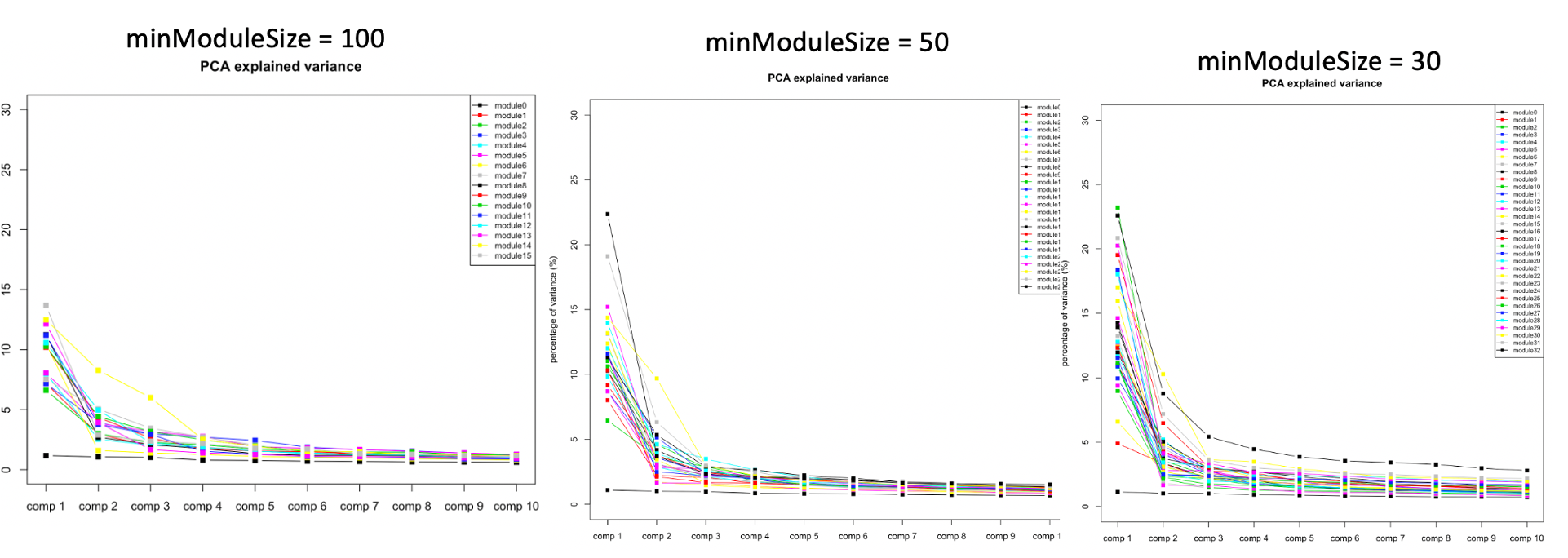
The above plots used all 13634 genes without removing any poorly mapped genes. Next, I removed the poorly mapped genes, with 5258 genes left. I used 30 to cluster these 5258 genes and resulted in 18 modules. We then looked at the explained variance and found nothing seemed wrong. So we decided to use 30 for WGCNA and these 18 modules for downstream analysis.

2. 30 is the default module size in WGCNA tutorial, and also used by the elife paper.
WGCNA tutorial used 30 as default. The elife method also used the default parameters.
3. I tried other parameters, e.g. 100. 50, which both increase the unclassified genes.
| minModuleSize | Num.unclassified.geens | Num.modules |
|---|---|---|
| 100 | 5247 | 4 |
| 50 | 3251 | 59 |
| 30 | 2908 | 57 |
Look into enrichment of TCGA modules.
Here is the complete enrichment result.
KEGG pathway enrichment
| source | term_name | sig_module | p_adjusted |
|---|---|---|---|
| KEGG | ErbB signaling pathway | 21 | 0.008964903 |
| KEGG | Neuroactive ligand-receptor interaction | 3 | 0.015524997 |
| KEGG | Mucin type O-glycan biosynthesis | 20 | 0.016931426 |
| KEGG | Human papillomavirus infection | 2 | 0.019400355 |
| KEGG | Prolactin signaling pathway | 2 | 0.041320205 |
| KEGG | Cocaine addiction | 2;26 | 0.04269822;0.049447144 |
| KEGG | PI3K-Akt signaling pathway | 21 | 0.048894331 |
ErbB signaling pathway: "ErbB family members and some of their ligands are often over-expressed, amplified, or mutated in many forms of cancer, making them important therapeutic targets. For example, researchers have found EGFR to be amplified and/or mutated in gliomas and NSCLC while ErbB2 amplifications are seen in breast, ovarian, bladder, NSCLC, as well as several other tumor types. [source]
Neuroactive ligand-receptor interaction:
Mucin type O-glycan biosynthesis: “Changes in mucin-type O-linked glycosylation are seen in over 90% of breast cancers” [source] [source]
Human papillomavirus infection: “We demonstrated that HPV is associated with breast cancer development, although the role of HPV in breast cancers is still questionable and further research is required to investigate, in more detail, the role of HPV infection in breast cancer.” [source]
Prolactin signaling pathway: “elevated PRL levels are correlated with increased breast cancer risk and metastasis” “In vitro studies have indicated a role for PRL in breast cancer proliferation and survival.” [source]
Cocaine addiction: ???
PI3K-Akt signaling pathway: “PI3K/Akt signaling pathway is key in the development of BC” (breast cancer) [source]
Nov 06
R version 3.6.3 (2020-02-29)
Platform: x86_64-apple-darwin15.6.0 (64-bit)
Running under: macOS Catalina 10.15.6
Matrix products: default
BLAS: /Library/Frameworks/R.framework/Versions/3.6/Resources/lib/libRblas.0.dylib
LAPACK: /Library/Frameworks/R.framework/Versions/3.6/Resources/lib/libRlapack.dylib
locale:
[1] en_US.UTF-8/en_US.UTF-8/en_US.UTF-8/C/en_US.UTF-8/en_US.UTF-8
attached base packages:
[1] stats graphics grDevices utils datasets methods base
loaded via a namespace (and not attached):
[1] workflowr_1.6.2 Rcpp_1.0.4 rprojroot_1.3-2 digest_0.6.25
[5] later_1.0.0 R6_2.4.1 backports_1.1.5 git2r_0.27.1
[9] magrittr_1.5 evaluate_0.14 highr_0.8 stringi_1.4.6
[13] rlang_0.4.7 fs_1.3.2 promises_1.1.0 rmarkdown_2.1
[17] tools_3.6.3 stringr_1.4.0 glue_1.3.2 httpuv_1.5.2
[21] xfun_0.12 yaml_2.2.1 compiler_3.6.3 htmltools_0.4.0
[25] knitr_1.28