Genome Browser 2022
Marie Saitou
4/23/2022
Last updated: 2022-05-26
Checks: 7 0
Knit directory: Bio326/
This reproducible R Markdown analysis was created with workflowr (version 1.7.0). The Checks tab describes the reproducibility checks that were applied when the results were created. The Past versions tab lists the development history.
Great! Since the R Markdown file has been committed to the Git repository, you know the exact version of the code that produced these results.
Great job! The global environment was empty. Objects defined in the global environment can affect the analysis in your R Markdown file in unknown ways. For reproduciblity it’s best to always run the code in an empty environment.
The command set.seed(20210128) was run prior to running the code in the R Markdown file. Setting a seed ensures that any results that rely on randomness, e.g. subsampling or permutations, are reproducible.
Great job! Recording the operating system, R version, and package versions is critical for reproducibility.
Nice! There were no cached chunks for this analysis, so you can be confident that you successfully produced the results during this run.
Great job! Using relative paths to the files within your workflowr project makes it easier to run your code on other machines.
Great! You are using Git for version control. Tracking code development and connecting the code version to the results is critical for reproducibility.
The results in this page were generated with repository version c3c2bc8. See the Past versions tab to see a history of the changes made to the R Markdown and HTML files.
Note that you need to be careful to ensure that all relevant files for the analysis have been committed to Git prior to generating the results (you can use wflow_publish or wflow_git_commit). workflowr only checks the R Markdown file, but you know if there are other scripts or data files that it depends on. Below is the status of the Git repository when the results were generated:
Ignored files:
Ignored: .DS_Store
Ignored: .RData
Ignored: .Rhistory
Ignored: analysis/.DS_Store
Ignored: analysis/popgen.simu.nb.html
Untracked files:
Untracked: BIO326 URL genome annotatin computer lab_24_MAR_2021.docx
Untracked: BIO326-121VGenomesequencingBIO326-121VGenomsekvensering;verktøyoganalyser-BIO326-121VGenomesequencing_PhillipByronPope.pdf
Untracked: BIO326-RNAseq.pptx
Untracked: BIO326-genome/
Untracked: BIO326.MS.10th_FEB_2021function.pptx
Untracked: BIO326_Introduction to sequence technology and protocols_3rd_FEB_2021.pdf
Untracked: BIO326_Introduction to sequence technology and protocols_3rd_FEB_2021.pptx
Untracked: BIO326_RNAseq_5th_FEB_2021.pptx
Untracked: BIO326_SQK-RAD004 DNA challenge.docx
Untracked: BIO326_visual_30_APR_2021.pptx
Untracked: Bio326.2022.1.Rmd
Untracked: Bio326.genome.html
Untracked: Nanopore_SumStatQC_Tutorial.Rmd
Untracked: PCRdemo.R
Untracked: Pig_mutation_hist.csv
Untracked: PopGenBio326.322/
Untracked: RNAseq.Rplot.pdf
Untracked: Untitled.R
Untracked: [eng]BIO326-121VGenomesequencingBIO326-121VGenomsekvensering;verktøyoganalyser-BIO326-121VGenomesequencing_PhillipByronPope.mht
Untracked: [eng]BIO326-121VGenomesequencingBIO326-121VGenomsekvensering;verktøyoganalyser-BIO326-121VGenomesequencing_PhillipByronPope.pdf
Untracked: analysis/AnimalGenomics.Rmd
Untracked: analysis/AnimalGenomicsVariant2022.Rmd
Untracked: prepare.txt
Untracked: samples.xlsx
Untracked: test/
Untracked: trial/
Untracked: vis.xlsx
Untracked: workflowR.bio326.R
Note that any generated files, e.g. HTML, png, CSS, etc., are not included in this status report because it is ok for generated content to have uncommitted changes.
These are the previous versions of the repository in which changes were made to the R Markdown (analysis/genomebrowser_for_lab.Rmd) and HTML (docs/genomebrowser_for_lab.html) files. If you’ve configured a remote Git repository (see ?wflow_git_remote), click on the hyperlinks in the table below to view the files as they were in that past version.
| File | Version | Author | Date | Message |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| html | 98de526 | mariesaitou | 2022-05-11 | Build site. |
| Rmd | a81045b | mariesaitou | 2022-05-11 | image data set |
| html | 41746eb | mariesaitou | 2022-04-26 | Build site. |
| Rmd | 18e099e | mariesaitou | 2022-04-26 | wflow_publish(c(“analysis/genomebrowser_for_lab.Rmd”)) |
| html | fdc68e7 | mariesaitou | 2022-04-25 | Build site. |
| Rmd | e529f09 | mariesaitou | 2022-04-25 | wflow_publish(c(“analysis/genomebrowser_for_lab.Rmd”)) |
| html | 4da5bf6 | mariesaitou | 2022-04-25 | Build site. |
| Rmd | e52e923 | mariesaitou | 2022-04-25 | image data set |
| html | 8ee71cb | mariesaitou | 2022-04-25 | Build site. |
| Rmd | 524afc1 | mariesaitou | 2022-04-25 | wflow_publish(c(“analysis/genomebrowser_for_lab.Rmd”)) |
| html | 0ce4c4c | mariesaitou | 2022-04-25 | Build site. |
| html | 6ee2cd1 | mariesaitou | 2022-04-25 | Build site. |
| Rmd | d01f497 | mariesaitou | 2022-04-25 | image data set |
| html | 45eea6a | mariesaitou | 2022-04-25 | Build site. |
| Rmd | 173a1b4 | mariesaitou | 2022-04-25 | wflow_publish(c(“analysis/genomebrowser_for_lab.Rmd”)) |
| html | 366d293 | mariesaitou | 2022-04-25 | Build site. |
| Rmd | 45cacf3 | mariesaitou | 2022-04-25 | wflow_publish(c(“analysis/genomebrowser_for_lab.Rmd”)) |
| html | f5f4065 | mariesaitou | 2022-04-25 | Build site. |
| Rmd | 8452478 | mariesaitou | 2022-04-25 | image data set |
| html | 8452478 | mariesaitou | 2022-04-25 | image data set |
| html | ef2a13c | mariesaitou | 2022-04-25 | Build site. |
| Rmd | 6f44b4b | mariesaitou | 2022-04-25 | wflow_publish(c(“analysis/genomebrowser_for_lab.Rmd”)) |
| html | f12c39f | mariesaitou | 2022-04-25 | Build site. |
| Rmd | c7517b0 | mariesaitou | 2022-04-25 | Add my first analysis |
0 Introduction - genome browsers
Aim: To get familiar with multiple genome browsers and explore potential use of their functions for your work.
National Center for Biotechnology Information. Good for primer design and litereture search.
The grafical use intereface is light and helpful. Most non-model species genomes are not up-to-date, but you can send them a request.
Most non-model species friendly. Good for evolutionary and functional genetics analysis.
1 Primer Design
Mission: You want to investigate if TP53 gene is expressed in a particular tissue of pig and want to design a primer set for its cDNA.
1-1 Search for gene info at NCBI
Go to:NCBI and search for “Sus scrofa TP53”.

Now you can see the gene information, exon-intron structure and gene/progein IDs. 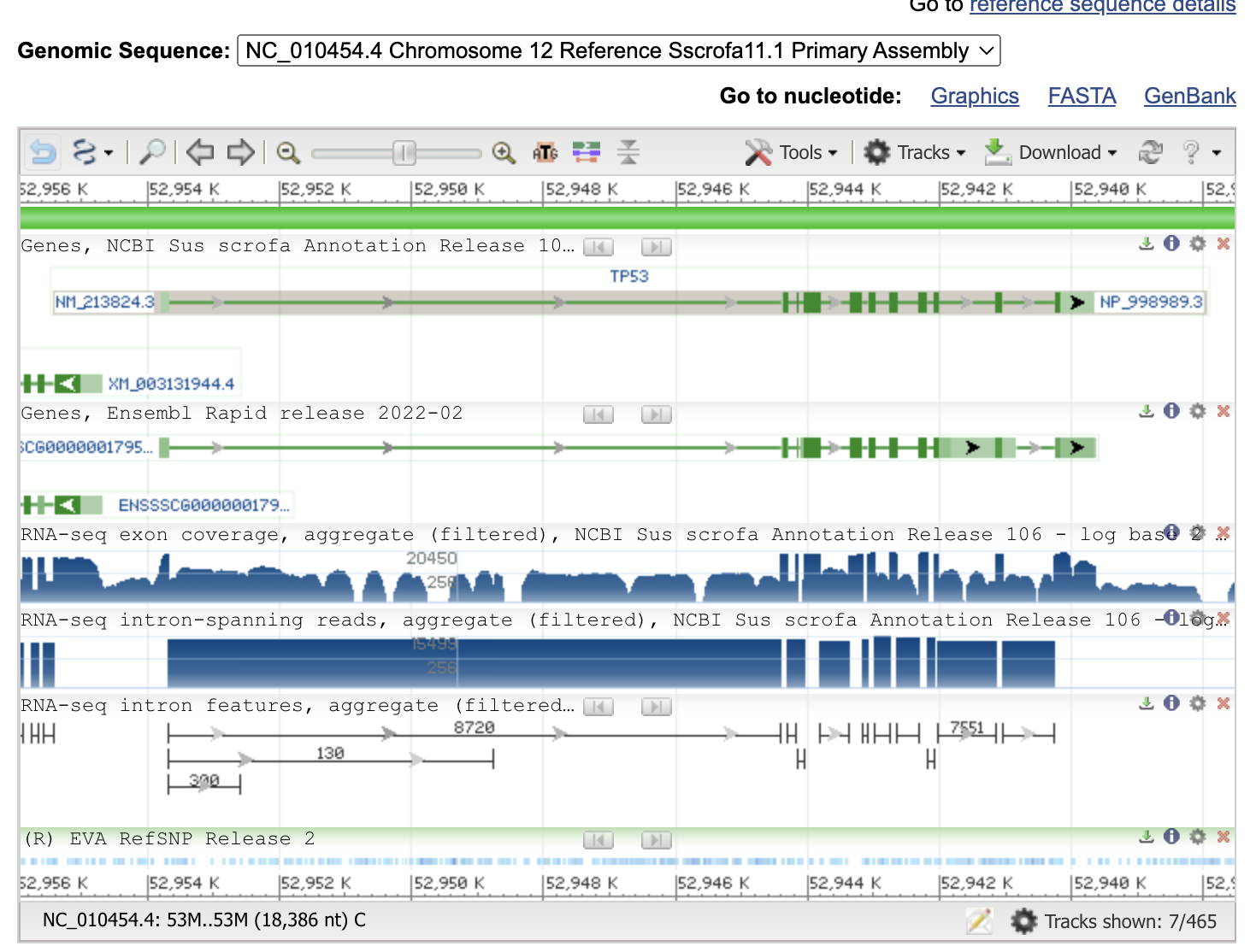
Thin green lines are the introns, thick green boxes are exons.
Also when you scroll it down, you can see the expression pattern of this gene in various tissues. 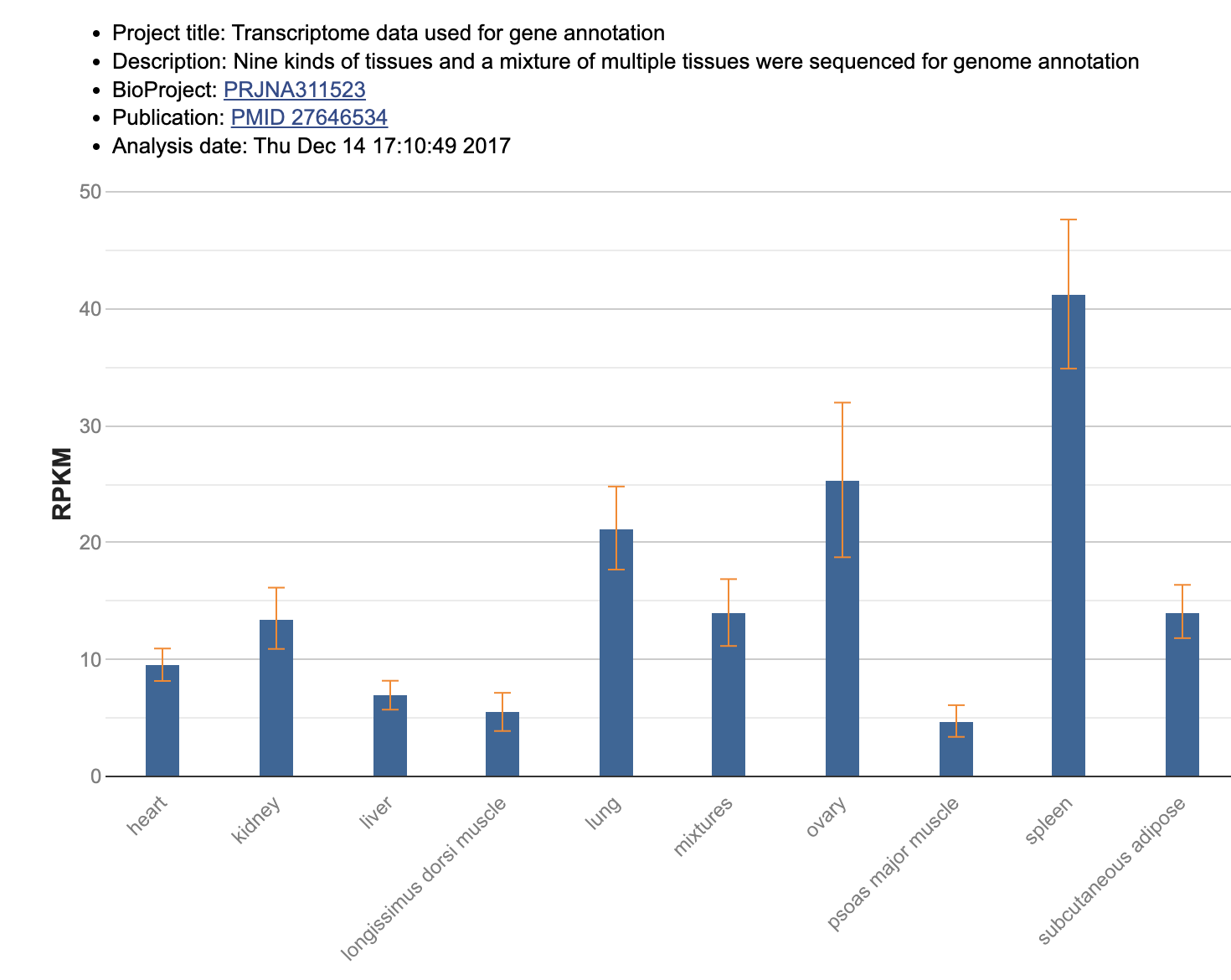
RPKM is a unit for gene expression
Furthere below, you can see relevant publications and expected function of this gene.
1-2 Primer blast - primer design
Now let’s design a primer set to amplify the cDNA. Put the mouse cursor on the gene image, and copy and note the refseq mRNA ID (NM_21824.3)
And go to:NCBI primer blast
Put the transcript ID “NM_21824.3” in the PCR template box.
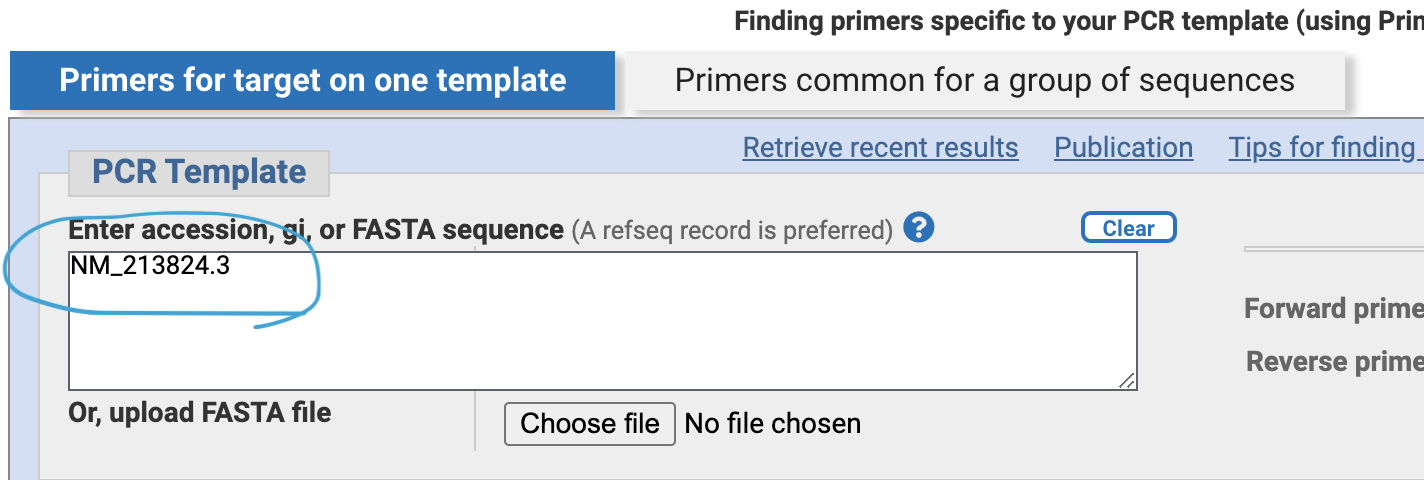
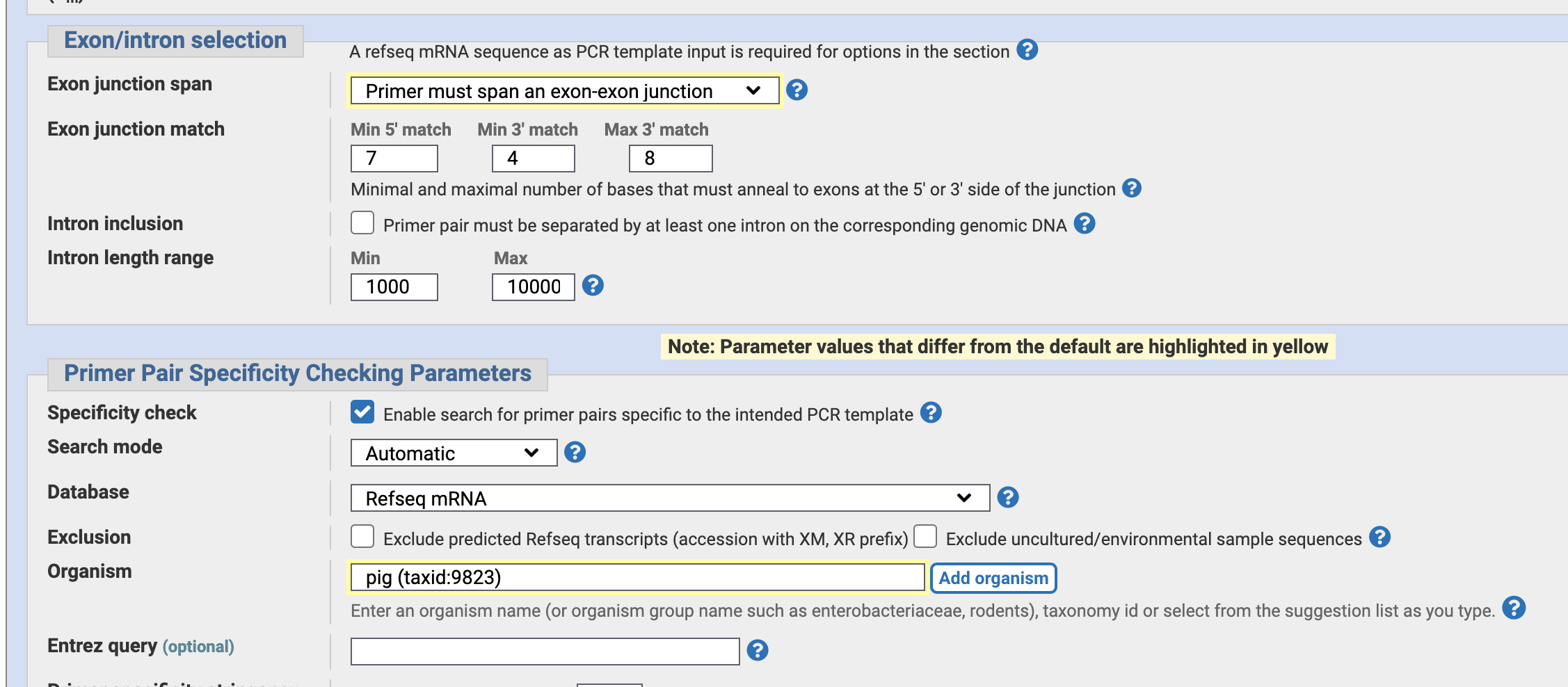
Specify “Primer mast span an exon-exon junction”. — to avoid false positive PCR amplification of genomic DNA and only observe mRNA by PCR.
Also, Specify tne organism “pig”.
Wait for a while…
Then the algorism gaves us the candidate primer sets. 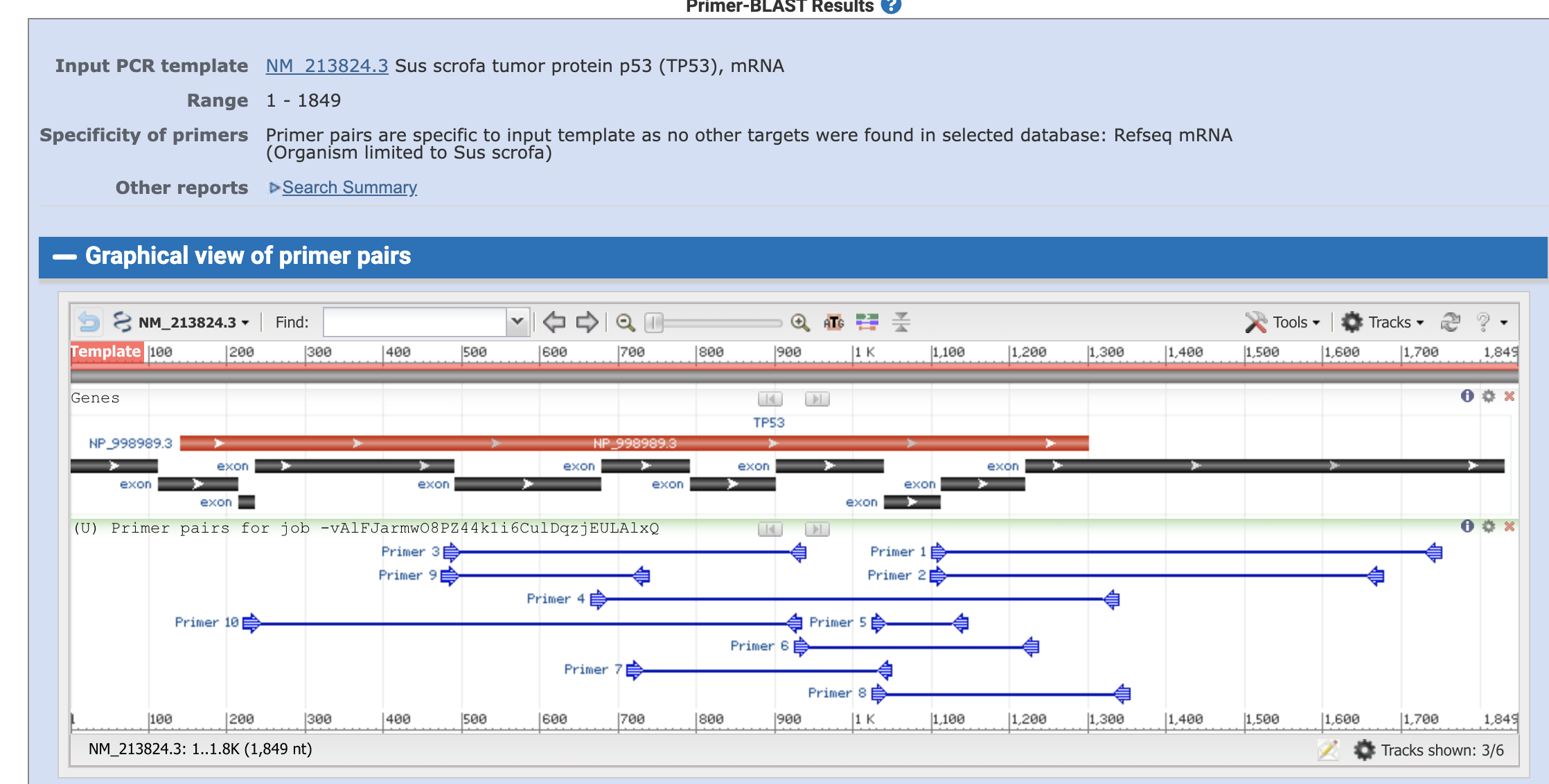
black bars are the exons and the blue thin lines are the primers and planned amplified region.
We can take a close look on each primer pair by clicking the primers.
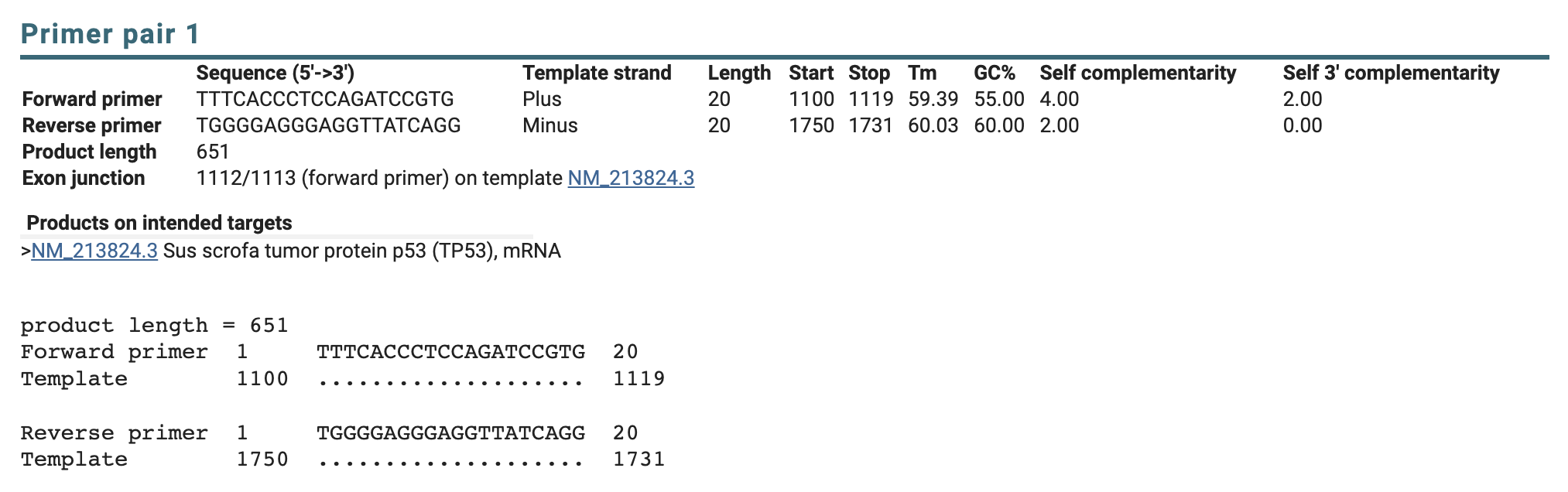
We can now see the primer sequences, locations, melting tempreture, GC content, self complementarity, and the product length. It also tells us that the forward primer spans a exon-exon junction (location 1112+1113 th of the nucleotide)
1-3 Primer blast - primer reuse
Now you want to know if the primer sets can be used for other species. To do so, we can extract the target template sequence from the pig transcriptome data and compare it for those of other species.
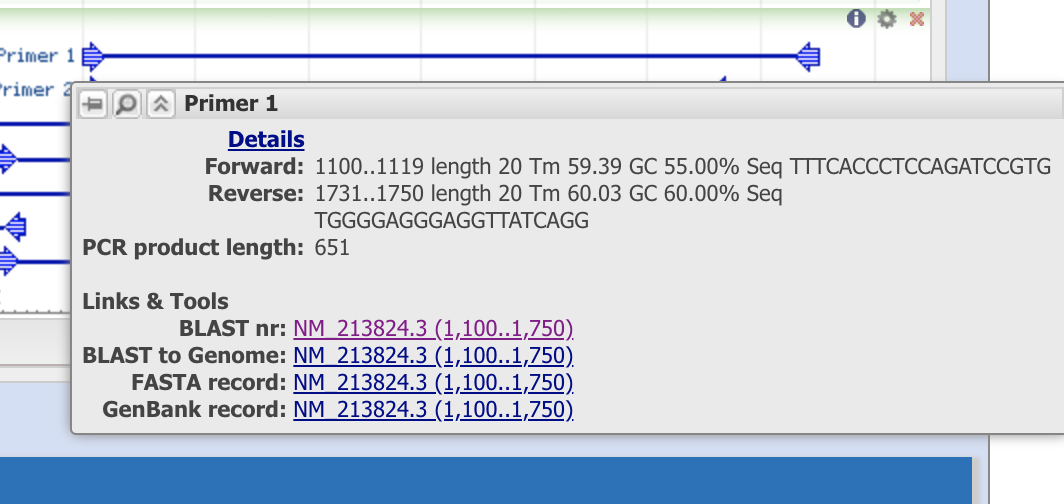
When you put the cursor on primer1, it shows that this primer set will amplity the “1,100 - 1,750 th nucleotide” of the sequence from mRNA, refseq ID (NM_21824.3). Note the info so see if the PCR template can be observed in other species.
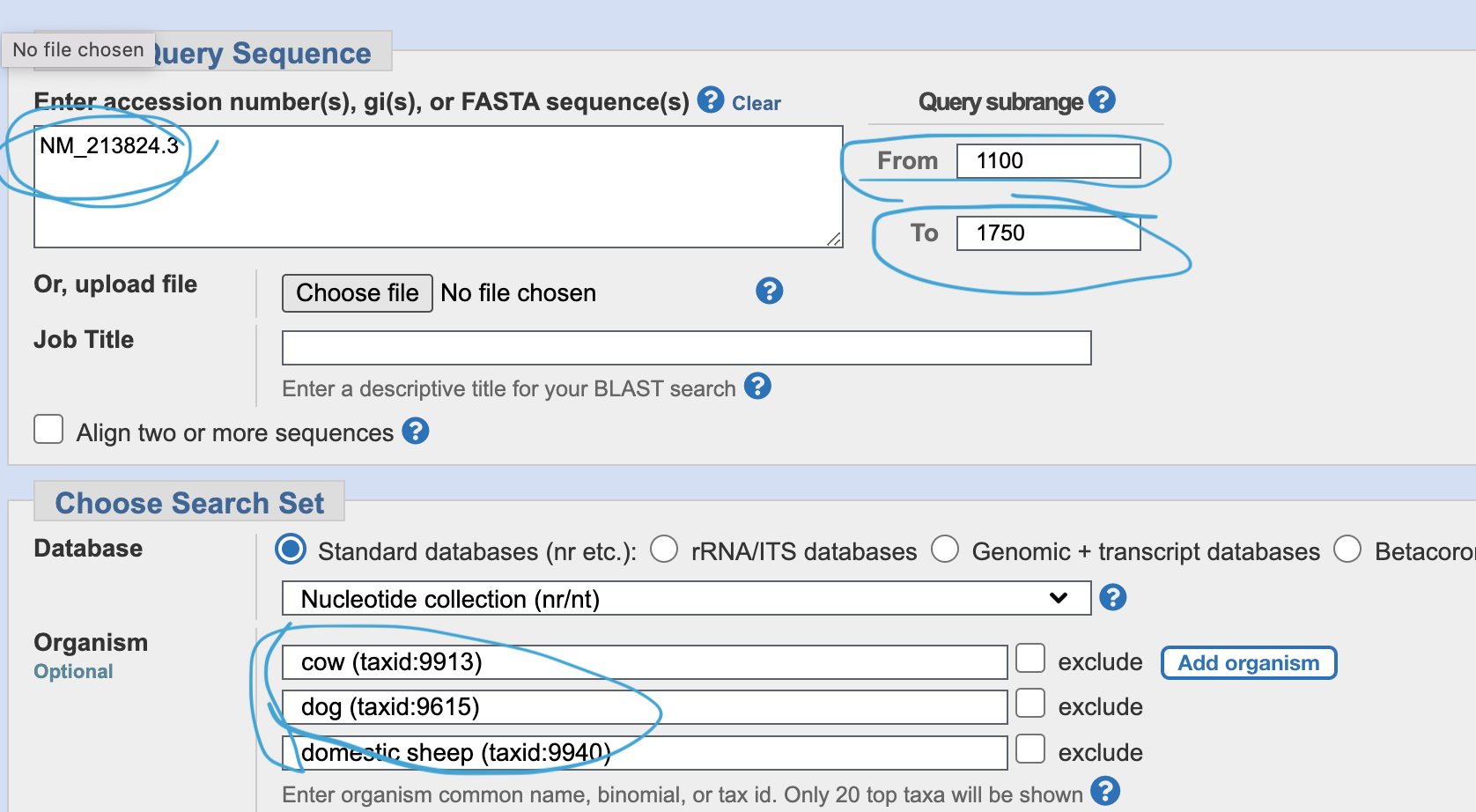
Go to primer blast, and input NM_21824.3, and range “from 1100 - to 1750”. Add your favorite species in the “organism” space.
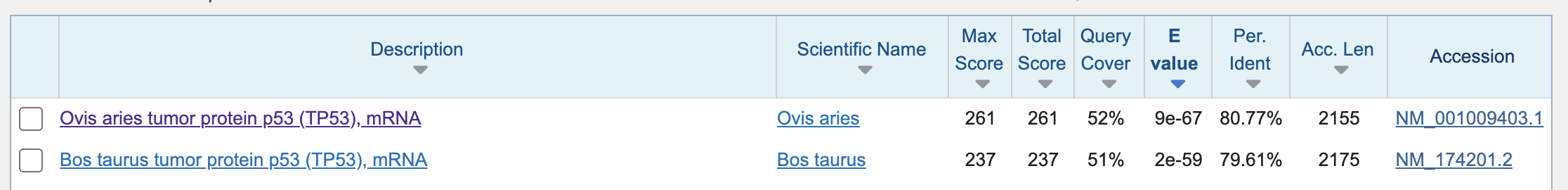
There are cattle and sheep mRNA found. Dog may not have highly similar mRNA.
Let’s look into the mRNA of sheep closely.

Query: 1100-1438 (pig TP53 mRNA) — the original region was 1100-1750, but of the sequence, only - 1438 showed the high similarity with the sheep mRNA.
Subject: 1074-1436 (sheep TP53 mRNA)
Bit score — can be used to compare alignment scores (similarity) from different searches. E-value (expect) — the number of different alignments expected to occur in a database search by chance. Identities — the number of identical nucleotids Gaps — the number of insertion/deletions in the alignment
The alignment indicates… the starting part is similar between sheep and pig mRNA, but 1439-1750 th bases of the pig mRNA did not show high similarity in sheep mRNA.
So probablly we have to design new primer sets for these species…
2 The effect of genetic variants
Mission: You found a genetic variant in your sequenced individual. You want to investigate the potential effect of the variants.
2-2 Variant effect predictor
Assume that you found the following deletion polymorphism at in a rabbit genome.
12: 107,236,296-107,236,969
Variant Effect Predictor Input the following information:
Species - rabbit (Oryctolagus_cuniculus)
Variant - 12 107236296 107236969 DEL + deletion1
the variant format, left to rignt … chromosome, starting point, ending point, kind, strand, variant ID (you can name it as you like) Variants.
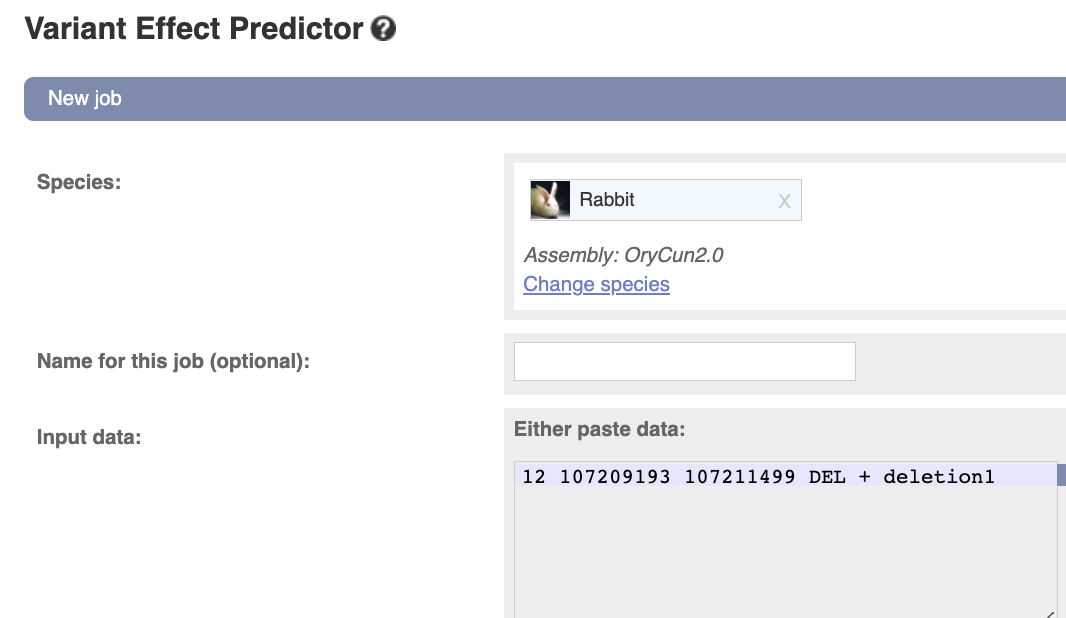
You can also find various acceptable input formats here
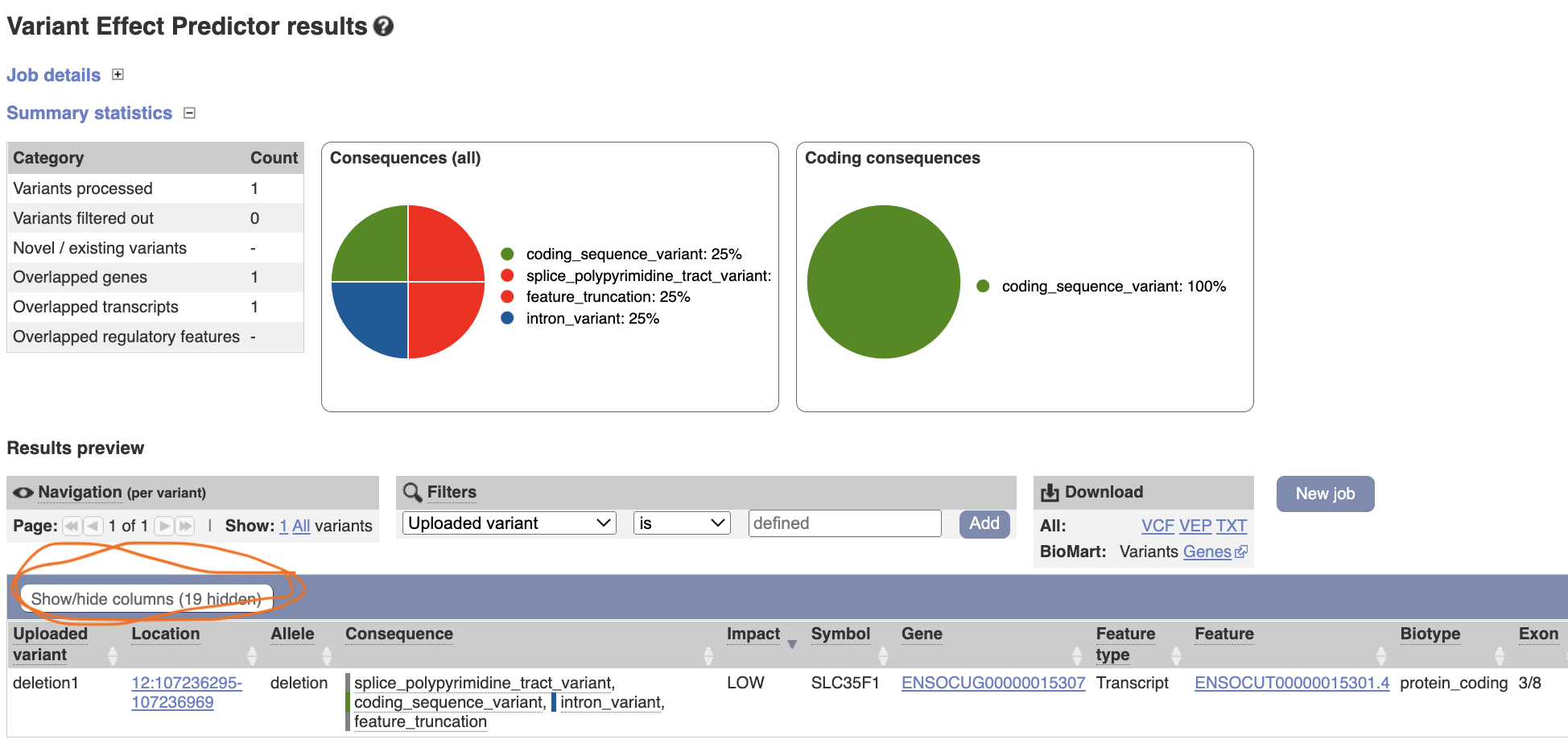
The result shows that the deletion is affecting a gene, SLC35F1, by causing coding sequence variant, splice variant, feature truncation and intron variant. You can modify the result table by clicking “show/hide columns”
2-2 What is this gene doing?
Click “ENSOCUG00000015307” to know more about this gene.
In the gene page, you can investigate its evolutionary history and potential function.
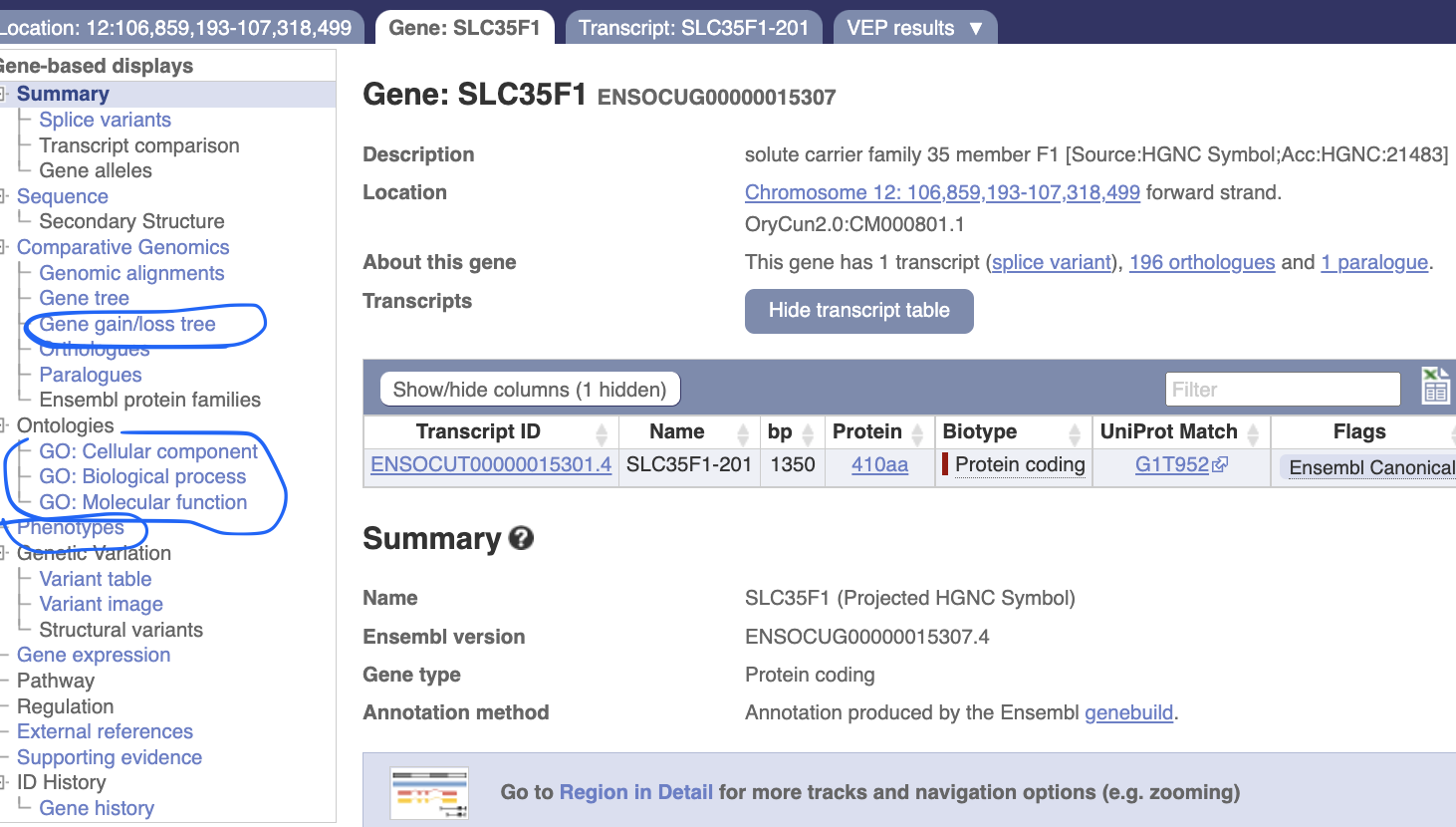
Let’s explore “gene gain/loss tree” “Ontologies” and “Phenotypes”
Gene gain/loss tree
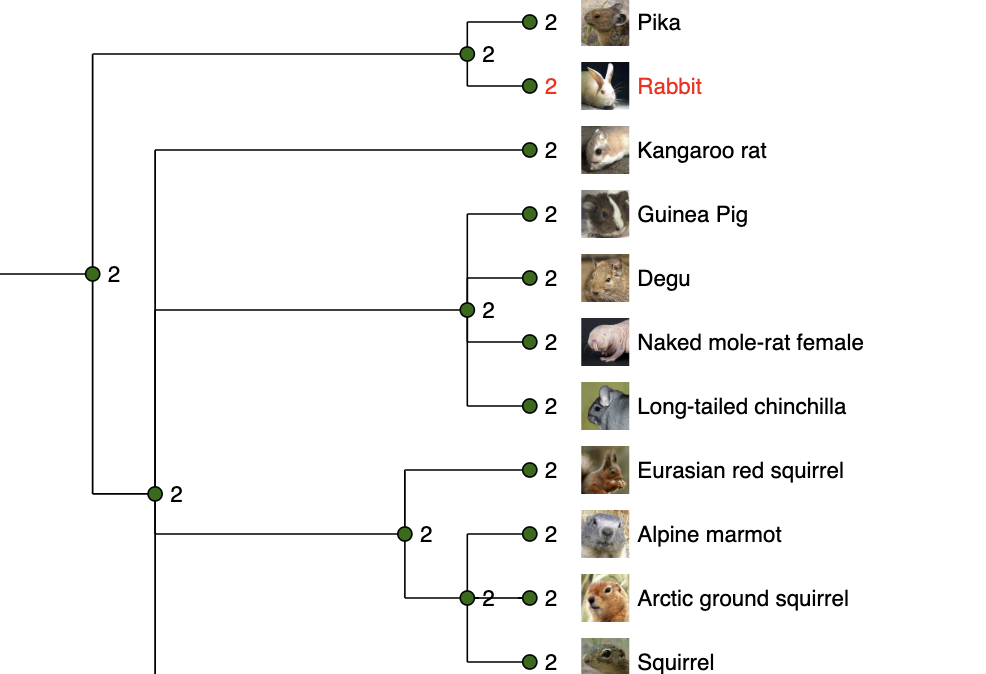
Most of mammalian species have two copies of this gene.
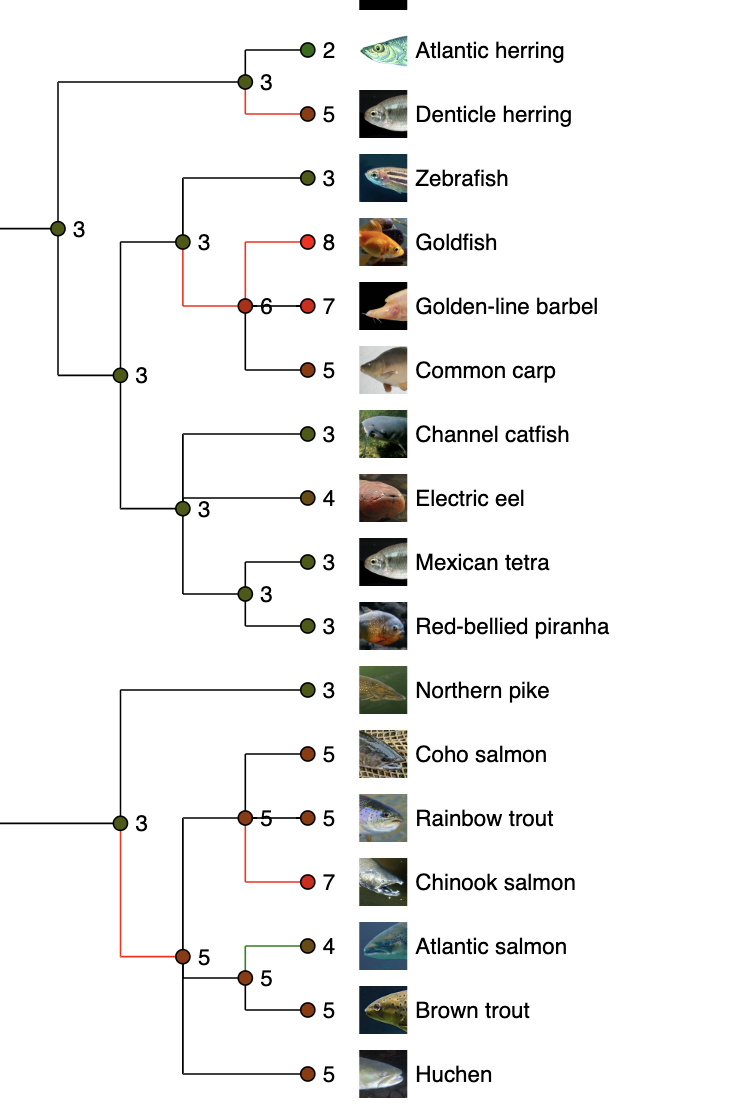
See what is happening in fish!
Gene Ontology 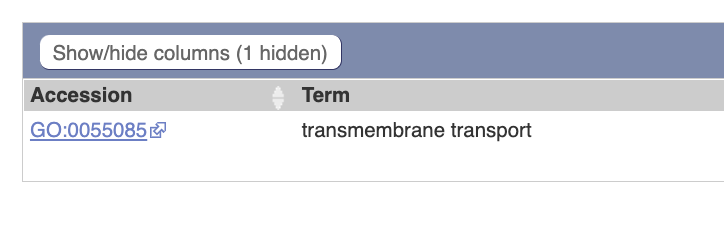 transmembrane transtport
transmembrane transtport
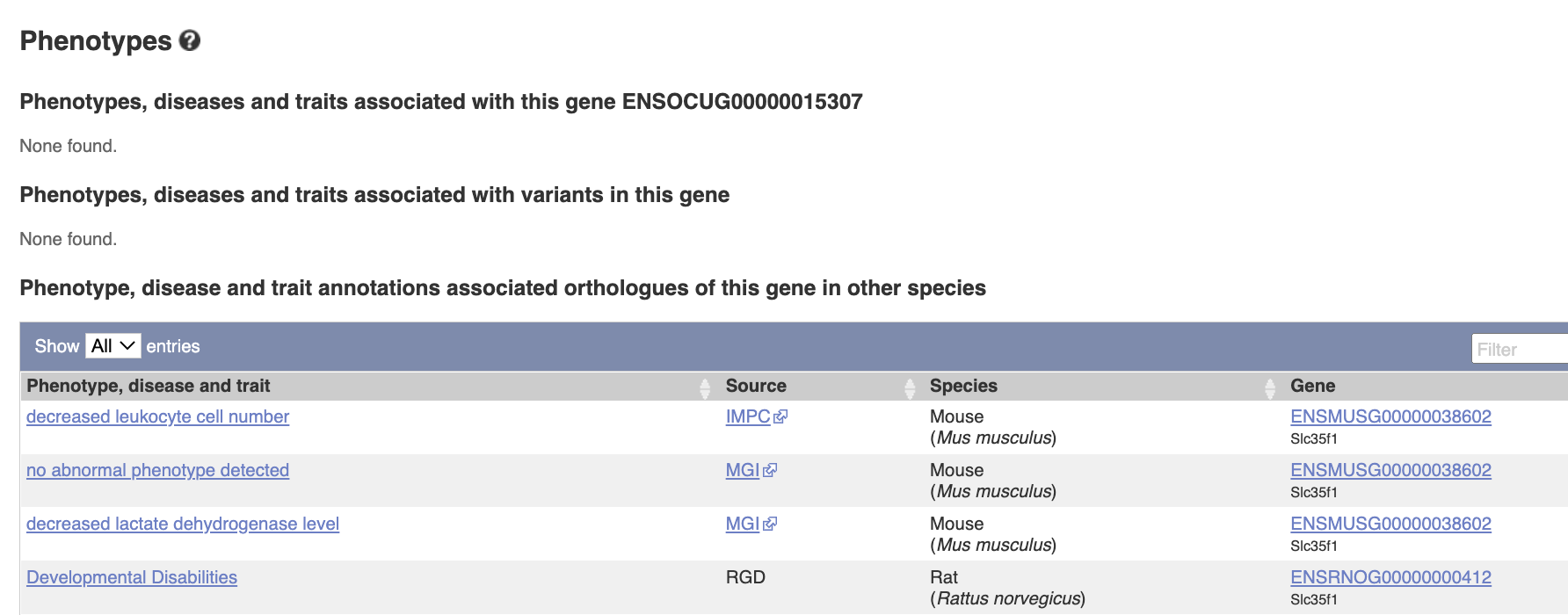
Phenotypes There is no phenotype information for this gene in rabbits, but there are some reports in mouse and rat, such as leukocyte cell number etc.
2-3 Comparative Analysis
Go back to the gene page, and click Orthologues in the left pane.
Find Alpaca… and let’s compare this gene in Rabbit and Alpaca.
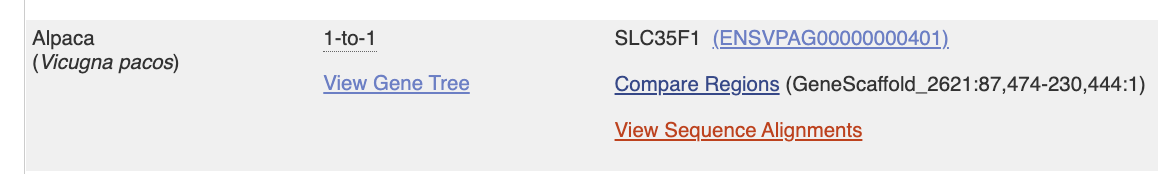 “Compare regions”
“Compare regions”
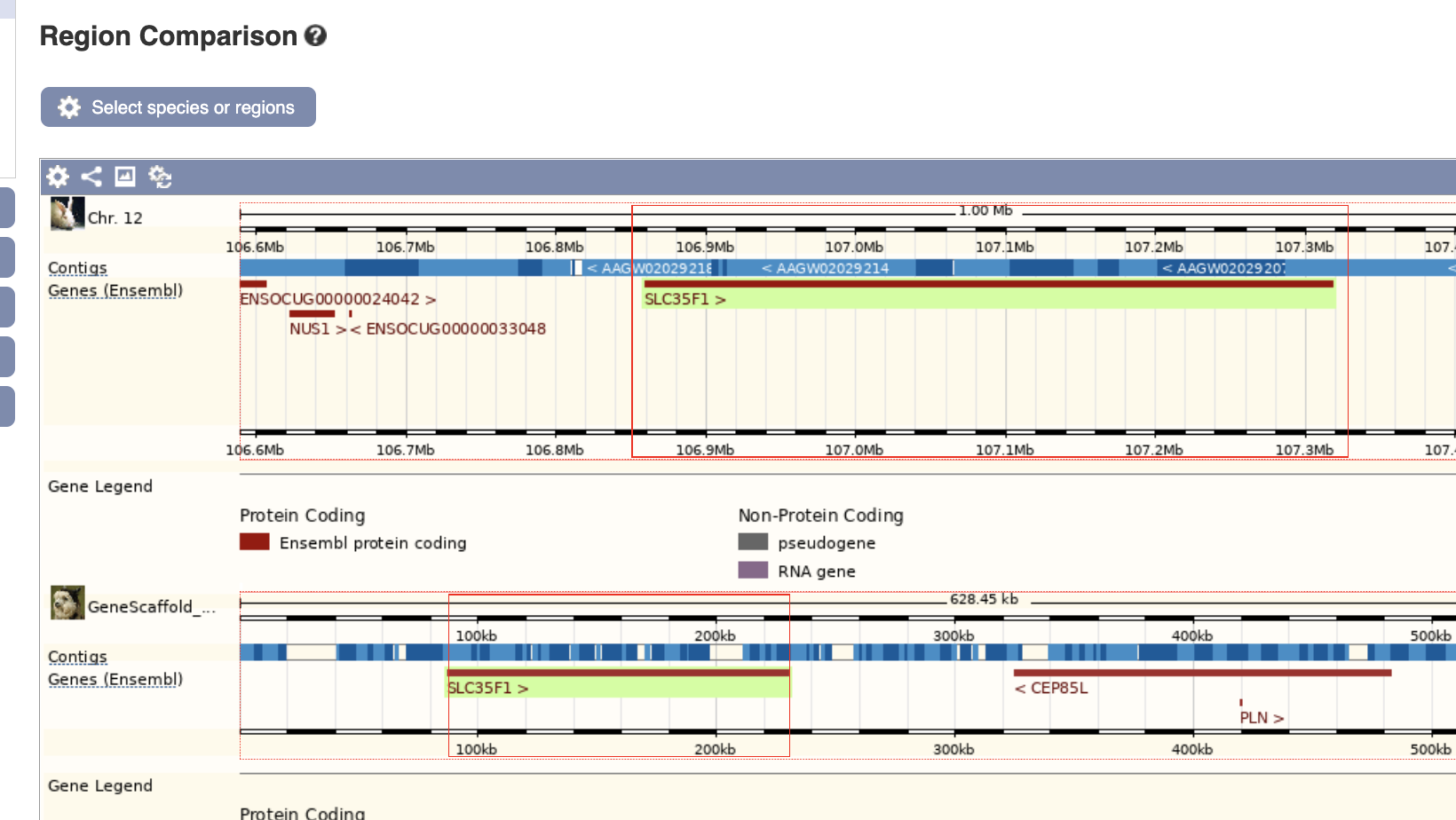 In both rabbit (top) and alpaca (bottom), seemingly, SLC35F1 is on the upstream of the CEF85L gene.
In both rabbit (top) and alpaca (bottom), seemingly, SLC35F1 is on the upstream of the CEF85L gene.

“View Sequence Alignments – Protein”

This is the protein alignment of this gene in the two species. Seemingly, these two sequences are very conserved (similar) except for the first 60 amino acids. * indicates the identical sequence.
3 The genomic architecture
Mission: Investigate the genomic arfhitecture of a particular region in the zebrafish genome
Go to UCSC Genome Browser
Select Zebrafish Genome, and search for “chr6:43,426,669-43,433,274”.
Now we see a gene structure at this region from multiple data sources - Thin lines are the introns, thick boxes are exons.
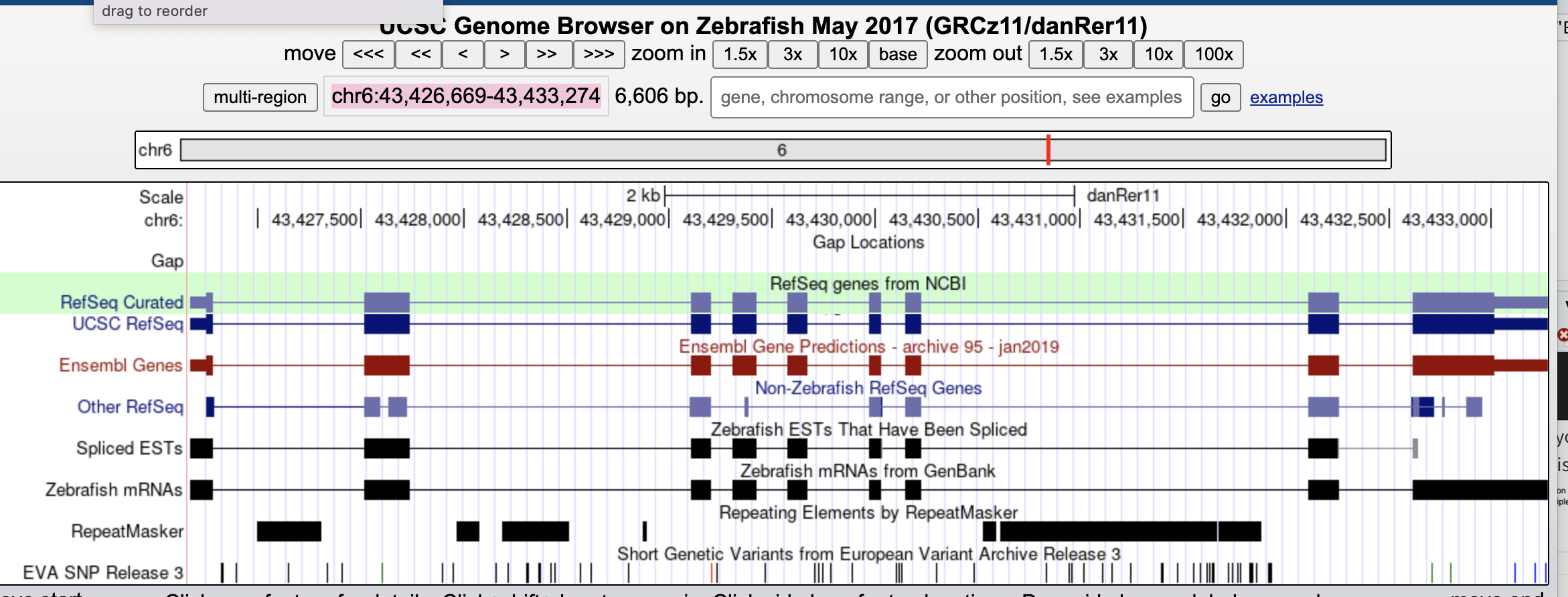

If you click RepeatMasker, you can see various different tipes of repeats in this reagion. What does it mean…? Click the left black part of “simple”.
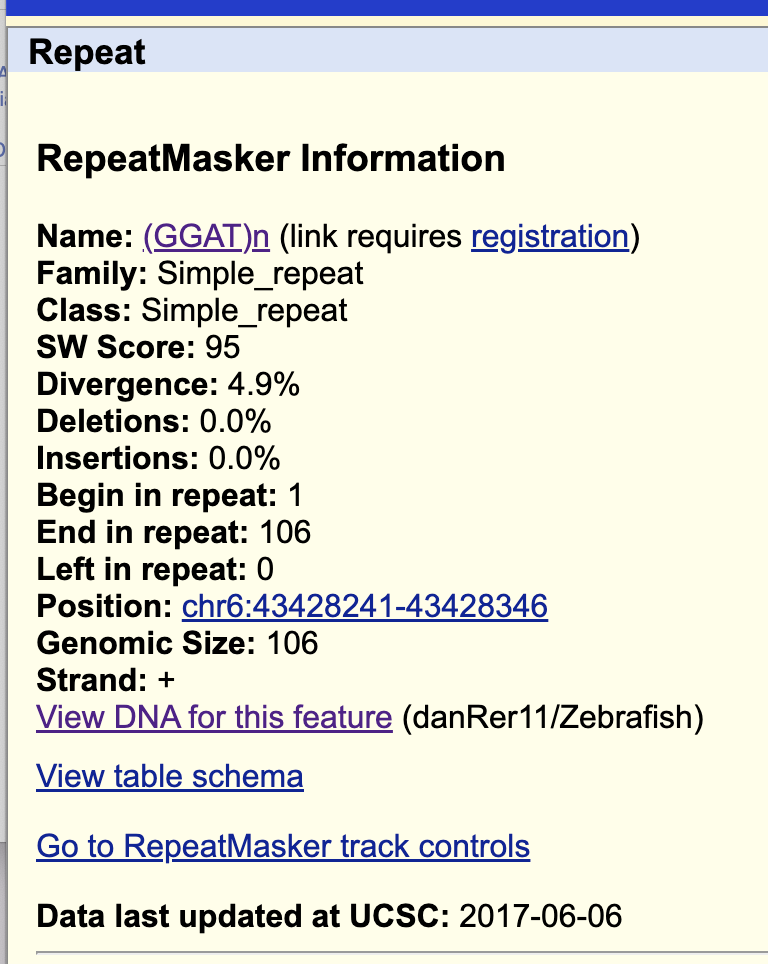
RepeatMasker Information
View table schema (<-click this in your browser)
>danRer11_rmsk_(GGAT)n range=chr6:43428241-43428346 5'pad=0 3'pad=0 strand=+ repeatMasking=none
GGATGGATGGATGGATGGATGGATGGATGGATGGATGGATGGATGGATGG
ATGGATGGATCGATGGAAGGATGGATGGATGGAAGGATGGATGGACAGAT
GGATGGSo, this means that in this region (chr6:43428241-43428346), there is repeats of “GGAT” sequences. This may happen during evolution - mostly by random or mechanistic mutations, and some are due to insertion og viral genetic sequences. Some of them could help a gene to gain a new function, and some can break a gene.
If you click EVA SNP Release3, you can see a lot of known variants in this region. rsXXX are the IDs of genetic variants.
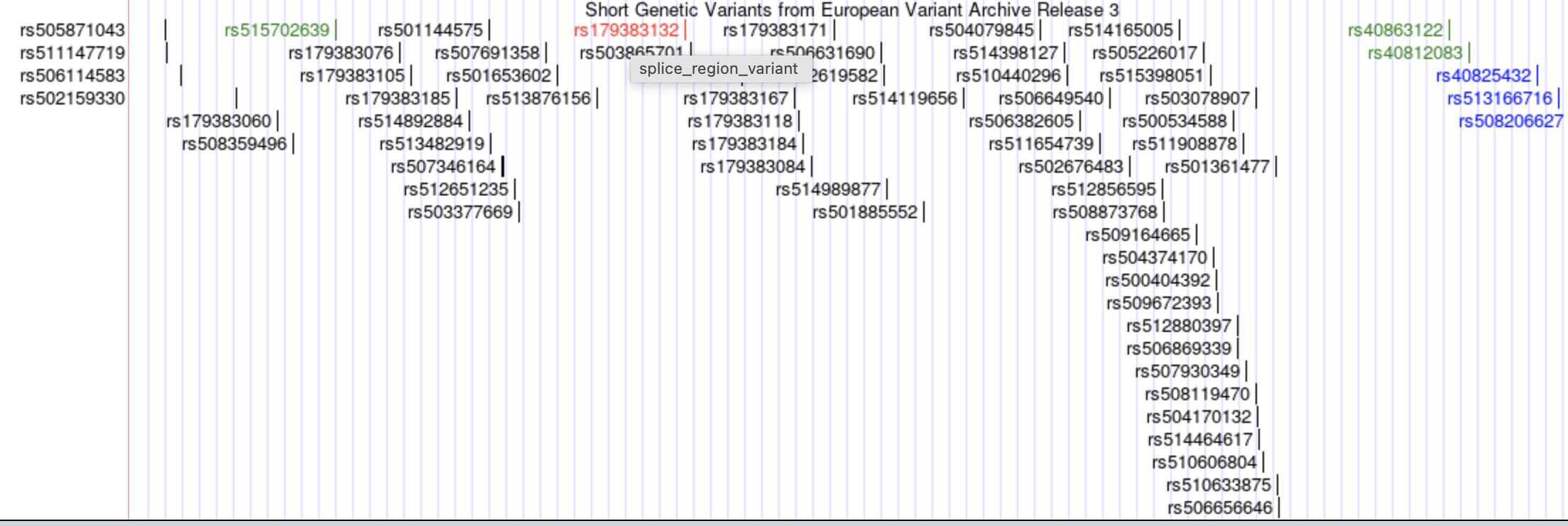
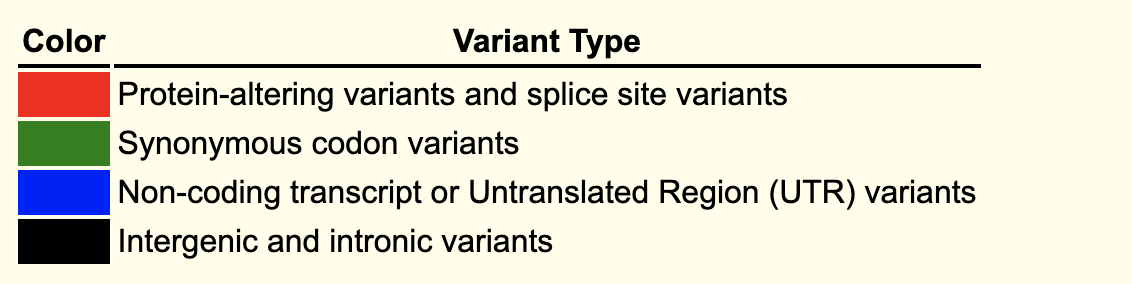
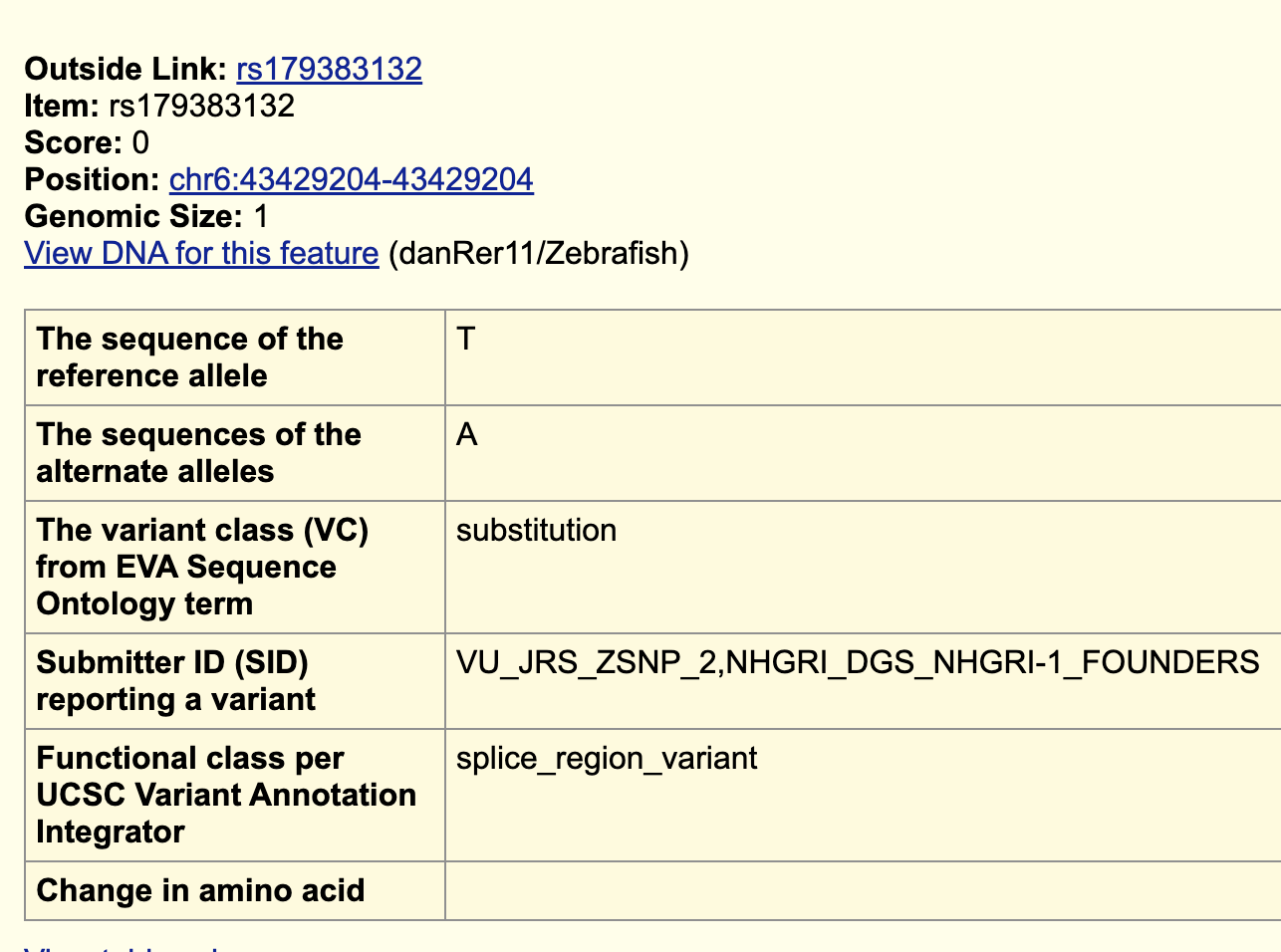
If you click “rs179383132”, you can see more information about this variant.
sessionInfo()R version 4.1.2 (2021-11-01)
Platform: x86_64-apple-darwin17.0 (64-bit)
Running under: macOS Big Sur 10.16
Matrix products: default
BLAS: /Library/Frameworks/R.framework/Versions/4.1/Resources/lib/libRblas.0.dylib
LAPACK: /Library/Frameworks/R.framework/Versions/4.1/Resources/lib/libRlapack.dylib
locale:
[1] en_US.UTF-8/en_US.UTF-8/en_US.UTF-8/C/en_US.UTF-8/en_US.UTF-8
attached base packages:
[1] stats graphics grDevices utils datasets methods base
other attached packages:
[1] workflowr_1.7.0
loaded via a namespace (and not attached):
[1] Rcpp_1.0.8.2 bslib_0.3.1 compiler_4.1.2 pillar_1.7.0
[5] later_1.3.0 git2r_0.29.0 jquerylib_0.1.4 tools_4.1.2
[9] getPass_0.2-2 digest_0.6.29 jsonlite_1.8.0 evaluate_0.15
[13] tibble_3.1.6 lifecycle_1.0.1 pkgconfig_2.0.3 rlang_1.0.2
[17] cli_3.2.0 rstudioapi_0.13 yaml_2.3.5 xfun_0.30
[21] fastmap_1.1.0 httr_1.4.2 stringr_1.4.0 knitr_1.37
[25] sass_0.4.0 fs_1.5.2 vctrs_0.3.8 rprojroot_2.0.2
[29] glue_1.6.2 R6_2.5.1 processx_3.5.2 fansi_1.0.2
[33] rmarkdown_2.13 callr_3.7.0 magrittr_2.0.2 whisker_0.4
[37] ps_1.6.0 promises_1.2.0.1 htmltools_0.5.2 ellipsis_0.3.2
[41] httpuv_1.6.5 utf8_1.2.2 stringi_1.7.6 crayon_1.5.0