Polygon preparation
Robert Schlegel
2019-07-24
Last updated: 2019-08-11
workflowr checks: (Click a bullet for more information)-
✔ R Markdown file: up-to-date
Great! Since the R Markdown file has been committed to the Git repository, you know the exact version of the code that produced these results.
-
✔ Environment: empty
Great job! The global environment was empty. Objects defined in the global environment can affect the analysis in your R Markdown file in unknown ways. For reproduciblity it’s best to always run the code in an empty environment.
-
✔ Seed:
set.seed(20190513)The command
set.seed(20190513)was run prior to running the code in the R Markdown file. Setting a seed ensures that any results that rely on randomness, e.g. subsampling or permutations, are reproducible. -
✔ Session information: recorded
Great job! Recording the operating system, R version, and package versions is critical for reproducibility.
-
Great! You are using Git for version control. Tracking code development and connecting the code version to the results is critical for reproducibility. The version displayed above was the version of the Git repository at the time these results were generated.✔ Repository version: b6e2cd9
Note that you need to be careful to ensure that all relevant files for the analysis have been committed to Git prior to generating the results (you can usewflow_publishorwflow_git_commit). workflowr only checks the R Markdown file, but you know if there are other scripts or data files that it depends on. Below is the status of the Git repository when the results were generated:
Note that any generated files, e.g. HTML, png, CSS, etc., are not included in this status report because it is ok for generated content to have uncommitted changes.Ignored files: Ignored: .Rhistory Ignored: .Rproj.user/ Ignored: data/ALL_anom.Rda Ignored: data/ALL_clim.Rda Ignored: data/ERA5_lhf.Rda Ignored: data/ERA5_lwr.Rda Ignored: data/ERA5_qnet.Rda Ignored: data/ERA5_qnet_anom.Rda Ignored: data/ERA5_qnet_clim.Rda Ignored: data/ERA5_shf.Rda Ignored: data/ERA5_swr.Rda Ignored: data/ERA5_t2m.Rda Ignored: data/ERA5_t2m_anom.Rda Ignored: data/ERA5_t2m_clim.Rda Ignored: data/ERA5_u.Rda Ignored: data/ERA5_u_anom.Rda Ignored: data/ERA5_u_clim.Rda Ignored: data/ERA5_v.Rda Ignored: data/ERA5_v_anom.Rda Ignored: data/ERA5_v_clim.Rda Ignored: data/GLORYS_mld.Rda Ignored: data/GLORYS_mld_anom.Rda Ignored: data/GLORYS_mld_clim.Rda Ignored: data/GLORYS_u.Rda Ignored: data/GLORYS_u_anom.Rda Ignored: data/GLORYS_u_clim.Rda Ignored: data/GLORYS_v.Rda Ignored: data/GLORYS_v_anom.Rda Ignored: data/GLORYS_v_clim.Rda Ignored: data/NAPA_clim_U.Rda Ignored: data/NAPA_clim_V.Rda Ignored: data/NAPA_clim_W.Rda Ignored: data/NAPA_clim_emp_ice.Rda Ignored: data/NAPA_clim_emp_oce.Rda Ignored: data/NAPA_clim_fmmflx.Rda Ignored: data/NAPA_clim_mldkz5.Rda Ignored: data/NAPA_clim_mldr10_1.Rda Ignored: data/NAPA_clim_qemp_oce.Rda Ignored: data/NAPA_clim_qla_oce.Rda Ignored: data/NAPA_clim_qns.Rda Ignored: data/NAPA_clim_qsb_oce.Rda Ignored: data/NAPA_clim_qt.Rda Ignored: data/NAPA_clim_runoffs.Rda Ignored: data/NAPA_clim_ssh.Rda Ignored: data/NAPA_clim_sss.Rda Ignored: data/NAPA_clim_sst.Rda Ignored: data/NAPA_clim_taum.Rda Ignored: data/NAPA_clim_vars.Rda Ignored: data/NAPA_clim_vecs.Rda Ignored: data/OAFlux.Rda Ignored: data/OISST_sst.Rda Ignored: data/OISST_sst_anom.Rda Ignored: data/OISST_sst_clim.Rda Ignored: data/node_mean_all_anom.Rda Ignored: data/packet_all.Rda Ignored: data/packet_all_anom.Rda Ignored: data/packet_nolab.Rda Ignored: data/packet_nolab14.Rda Ignored: data/packet_nolabgsl.Rda Ignored: data/packet_nolabmod.Rda Ignored: data/som_all.Rda Ignored: data/som_all_anom.Rda Ignored: data/som_nolab.Rda Ignored: data/som_nolab14.Rda Ignored: data/som_nolab_16.Rda Ignored: data/som_nolab_9.Rda Ignored: data/som_nolabgsl.Rda Ignored: data/som_nolabmod.Rda Ignored: data/synoptic_states.Rda Ignored: data/synoptic_vec_states.Rda Untracked files: Untracked: docs/assets/NAPA/ Untracked: docs/assets/no_ls/ Untracked: docs/assets/no_ls_14/ Untracked: docs/assets/no_ls_3x3/ Unstaged changes: Modified: analysis/_site.yml Modified: code/workflow.R
Expand here to see past versions:
| File | Version | Author | Date | Message |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| html | 2652a3a | robwschlegel | 2019-08-11 | Build site. |
| html | f0d2efb | robwschlegel | 2019-08-07 | Build site. |
| html | aa82e6e | robwschlegel | 2019-07-31 | Build site. |
| Rmd | 498909b | robwschlegel | 2019-07-31 | Re-publish entire site. |
| Rmd | 51ed681 | robwschlegel | 2019-07-25 | Completed anoms for OISST |
| Rmd | 0b6f065 | robwschlegel | 2019-07-25 | Push before beginning to write code for loading entire obs/reanalysis products into memory for clim calculations |
| html | 7792f24 | robwschlegel | 2019-07-24 | Build site. |
| html | 7cc8ec3 | robwschlegel | 2019-07-24 | Build site. |
| Rmd | 463b89a | robwschlegel | 2019-07-24 | Edited the polygon and sst prep vignettes while redoing methodology. |
| html | 81e961d | robwschlegel | 2019-07-09 | Build site. |
| Rmd | b25762e | robwschlegel | 2019-06-12 | More work on figures |
| html | c23c50b | robwschlegel | 2019-06-10 | Build site. |
| html | 028d3cc | robwschlegel | 2019-06-10 | Build site. |
| html | c61a15f | robwschlegel | 2019-06-06 | Build site. |
| Rmd | 44ac335 | robwschlegel | 2019-06-06 | Working on inclusion of vectors into SOM pipeline |
| html | 6dd6da8 | robwschlegel | 2019-06-06 | Build site. |
| Rmd | 94ce8f6 | robwschlegel | 2019-06-04 | Functions for creating data packets are up and running |
| html | 5cb8e8f | robwschlegel | 2019-05-28 | Build site. |
| Rmd | 3cdb0aa | robwschlegel | 2019-05-28 | Extended the corners of the study region. |
| html | def6979 | robwschlegel | 2019-05-24 | Build site. |
| Rmd | 4144097 | robwschlegel | 2019-05-24 | Minor edit to polygon prep vignette. |
| html | c09b4f7 | robwschlegel | 2019-05-24 | Build site. |
| Rmd | 5dc8bd9 | robwschlegel | 2019-05-24 | Finished initial creation of SST prep vignette. |
| Rmd | 5c2b406 | robwschlegel | 2019-05-23 | Commit before changes |
| html | d544295 | robwschlegel | 2019-05-23 | Build site. |
| Rmd | 9cb3efa | robwschlegel | 2019-05-23 | Updating work done on the polygon prep vignette. |
| Rmd | d8f2b99 | robwschlegel | 2019-05-23 | Working on polygon vignette |
Introduction
This markdown file contains all of the code that prepares the polygons used to define the different regions in the Northwest Atlantic. These different regions then have their SST pixels spatially averaged to create a single time series per region. This is done so that the MHW detection algorithm may then be run on these individual time series as a general representation of the SST in those regions, rather than running the algorithm on each pixel individually, which would introduce a host of problems.
# Packages used in this vignette
library(jsonlite, lib.loc = "../R-packages/")
library(tidyverse) # Base suite of functions
library(R.matlab) # For dealing with MATLAB files
# library(marmap) # For bathymetry
# library(maptools) # Contour tools
# library(rgeos) # For intersectionsCoastal region polygons
The first step in this analysis is to broadly define the coastal regions based on previous research into thermally relevant boundaries. We have chosen to use a paper by Richaud et al. (2016) to do this (https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0278434316303181#f0010). Being the kind-hearted man that he is, Benjamin forwarded us the polygons [Richaud et al. (2016); Figure 2] from this work as a MATLAB file. In order to use this here we must first open the file and convert it to an R format. It should be noted that these areas were designed to not encompass depths deeper than 600 m as the investigators were interested in characterising the climatologies for the shelf and upper slope regions of the north east coast of North America.
# Load the file
NWA_polygons <- readMat("data/boundaries.mat")
# Remove index list items and attributes
NWA_polygons[grepl("[.]",names(NWA_polygons))] <- NULL
# attributes(NWA_polygons) <- NULL
# Function for neatly converting list items into a dataframe
# vec <- NWA_polygons[1]
mat_col <- function(vec){
df <- as.data.frame(vec)
df$region <- substr(colnames(df)[1], 2, nchar(colnames(df)[1]))
colnames(df)[1] <- strtrim(colnames(df)[1], 1)
df <- df[c(2,1)]
return(df)
}
# Create multiple smaller data.frames
coords_1 <- cbind(mat_col(NWA_polygons[1]), mat_col(NWA_polygons[2])[2])
coords_2 <- cbind(mat_col(NWA_polygons[3]), mat_col(NWA_polygons[4])[2])
coords_3 <- cbind(mat_col(NWA_polygons[5]), mat_col(NWA_polygons[6])[2])
coords_4 <- cbind(mat_col(NWA_polygons[7]), mat_col(NWA_polygons[8])[2])
coords_5 <- cbind(mat_col(NWA_polygons[9]), mat_col(NWA_polygons[10])[2])
coords_6 <- cbind(mat_col(NWA_polygons[11]), mat_col(NWA_polygons[12])[2])
# Combine them into one full dataframe and save
NWA_coords <- rbind(coords_1, coords_2, coords_3, coords_4, coords_5, coords_6)
colnames(NWA_coords) <- c("region", "lon", "lat")
# saveRDS(NWA_coords, "data/NWA_coords.Rda")With our polygons switched over from MATLAB to R we now want to visualise them to ensure that everything has gone smoothly.
# Load polygon coordinates
NWA_coords <- readRDS("data/NWA_coords.Rda")
# The base map
map_base <- ggplot2::fortify(maps::map(fill = TRUE, col = "grey80", plot = FALSE)) %>%
dplyr::rename(lon = long) %>%
mutate(group = ifelse(lon > 180, group+9999, group),
lon = ifelse(lon > 180, lon-360, lon)) %>%
select(-region, -subregion)
# Quick map
NWA_coords_plot <- ggplot(data = NWA_coords, aes(x = lon, y = lat)) +
geom_polygon(aes(colour = region, fill = region), size = 1.5, alpha = 0.2) +
geom_polygon(data = map_base, aes(group = group), show.legend = F) +
coord_cartesian(xlim = c(min(NWA_coords$lon)-2, max(NWA_coords$lon)+2),
ylim = c(min(NWA_coords$lat)-2, max(NWA_coords$lat)+2)) +
labs(x = NULL, y = NULL, colour = "Region", fill = "Region") +
theme(legend.position = "bottom")
# ggsave(NWA_coords_plot, filename = "output/NWA_coords_plot.pdf", height = 5, width = 6)
# Visualise
NWA_coords_plot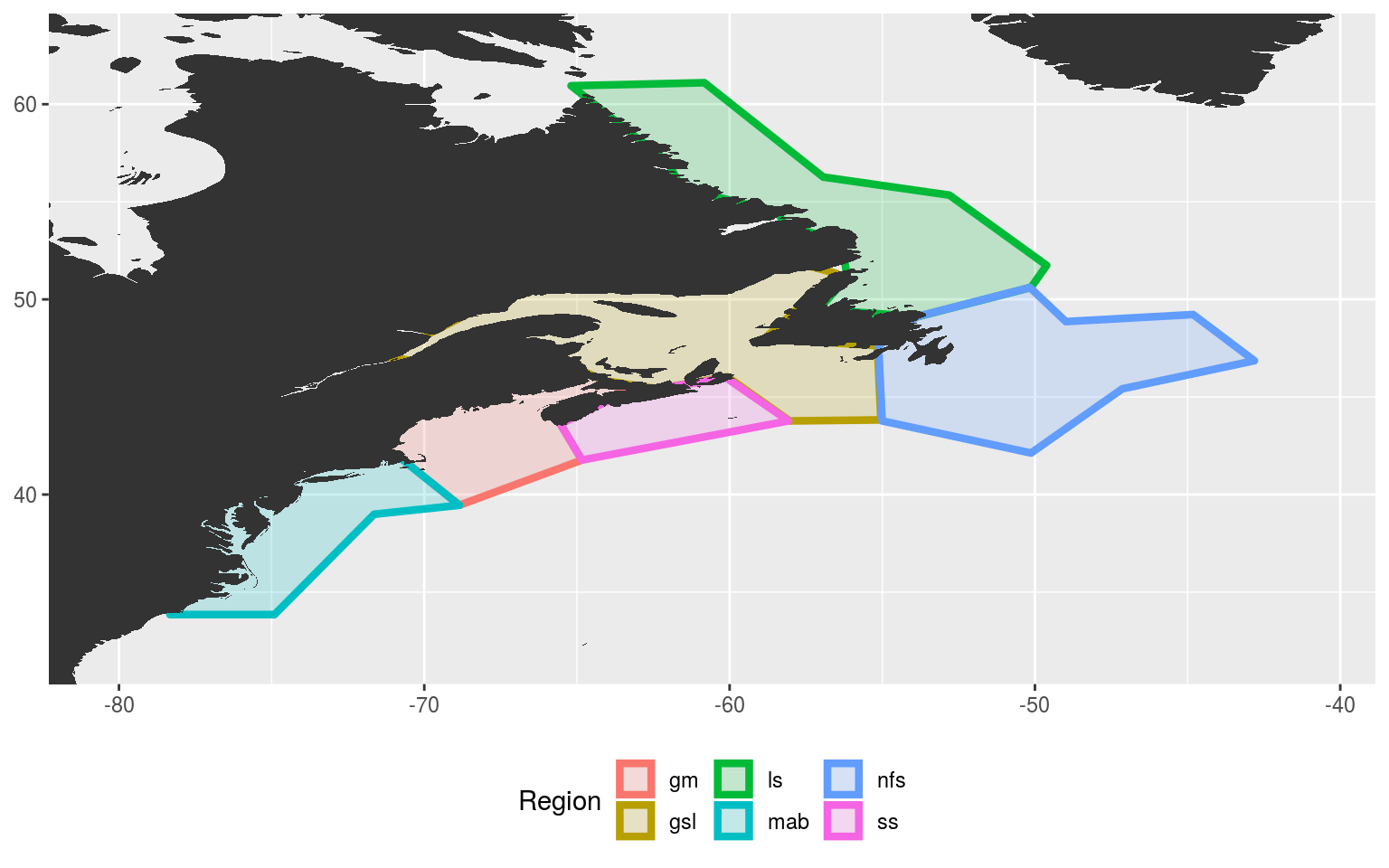
Expand here to see past versions of poly-vis-1.png:
| Version | Author | Date |
|---|---|---|
| 7cc8ec3 | robwschlegel | 2019-07-24 |
| 5cb8e8f | robwschlegel | 2019-05-28 |
| c09b4f7 | robwschlegel | 2019-05-24 |
| d544295 | robwschlegel | 2019-05-23 |
The region abbreviations are: “gm” for Gulf of Maine, “gls” for Gulf of St. Lawrence, “ls” for Labrador Shelf, “mab” for Mid-Atlantic Bight, “nfs” for Newfoundland Shelf and “ss” for Scotian Shelf.
Before we move on, we’ll do a bit of house keeping to establish a consistent study area for this project based on our polygons. We’ll simply extend the study area by the nearest 2 whole degrees of longitude and latitude from the furthest edges of the polygons, as seen in the figure above. This will encompass broad synoptic scale variables that may be driving MHWs in our study regions, but should not be so broad as to begin to account for teleconnections, which are currently beyond the scope of this project.
# Set the max/min lon/at values
lon_min <- round(min(NWA_coords$lon)-2)
lon_max <- round(max(NWA_coords$lon)+2)
lat_min <- round(min(NWA_coords$lat)-2)
lat_max <- round(max(NWA_coords$lat)+2)
# Combine and save
NWA_corners <- c(lon_min, lon_max, lat_min, lat_max)
# saveRDS(NWA_corners, file = "data/NWA_corners.Rda")Cabot Strait
It was decided that because we are interested in the geography of the regions, and not just their temperature regimes, the Cabot Strait needed to be defined apart from the Gulf of St. Lawrence region. To do this we will simply snip the “gsl” polygon into two pieces at its narrowest point.
# Extract the gsl region only
gsl_sub <- NWA_coords[NWA_coords$region == "gsl",]
# Add a simple integer column for ease of plotting
gsl_sub$row_count <- 1:nrow(gsl_sub)
ggplot(data = gsl_sub, aes(x = lon, y = lat)) +
geom_polygon(aes(fill = region)) +
geom_label(aes(label = row_count)) +
labs(x = NULL, y = NULL)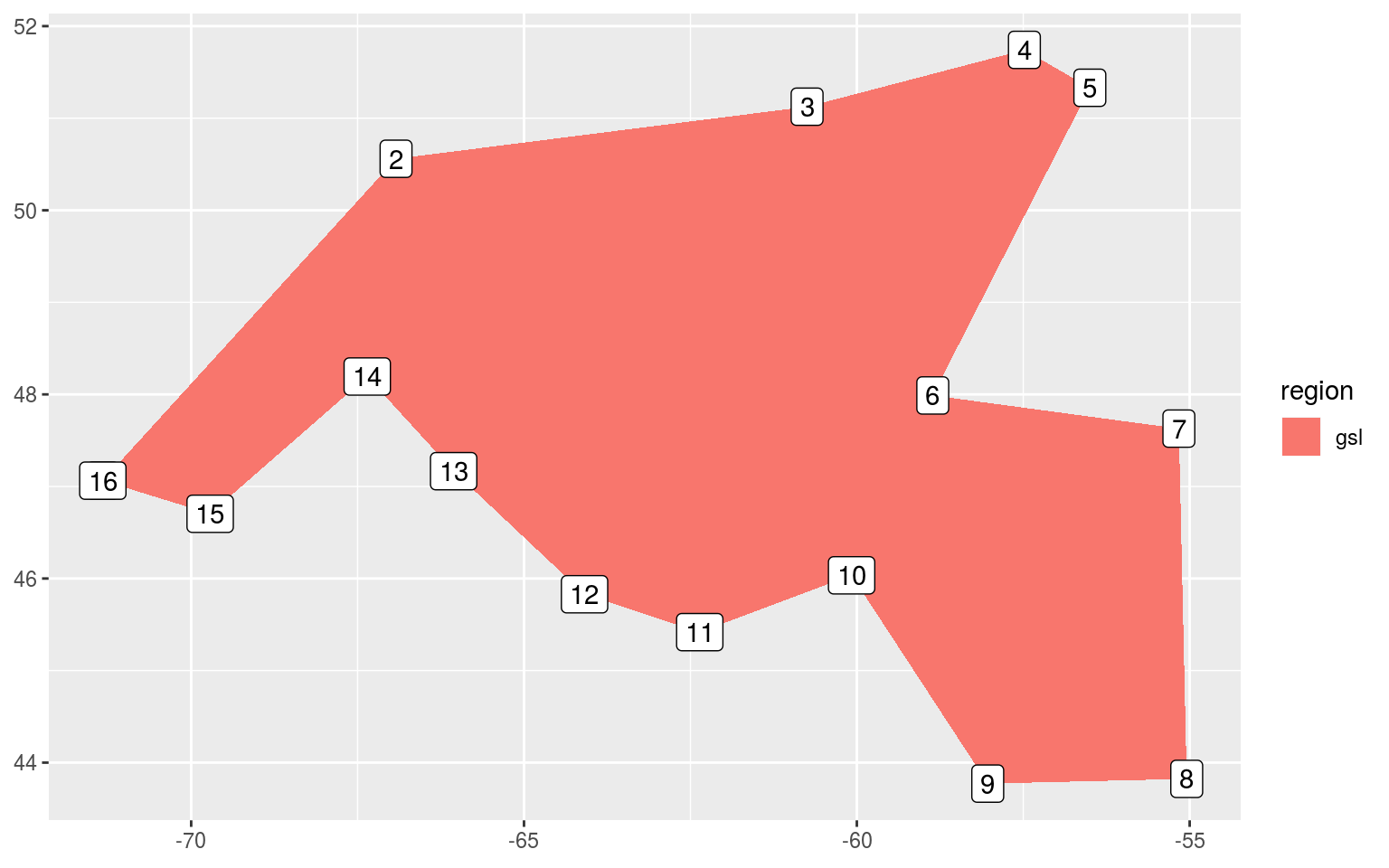
Expand here to see past versions of cabot-strait-1-1.png:
| Version | Author | Date |
|---|---|---|
| 5cb8e8f | robwschlegel | 2019-05-28 |
| c09b4f7 | robwschlegel | 2019-05-24 |
| d544295 | robwschlegel | 2019-05-23 |
It appears from the crude figure above that we should pinch the polygon off into two separate shapes at row 6 and 10.
# Create smaller gsl polygon
gsl_new <- NWA_coords[NWA_coords$region == "gsl",] %>%
slice(-c(7:9))
# Create new cbs (Cabot Strait) polygon
cbs <- NWA_coords[NWA_coords$region == "gsl",] %>%
slice(6:10) %>%
mutate(region = "cbs")
# Attach the new polygons to the original polygons
NWA_coords_cabot <- NWA_coords %>%
filter(region != "gsl") %>%
rbind(., gsl_new, cbs)
# saveRDS(NWA_coords_cabot, "data/NWA_coords_cabot.Rda")
# Plot the new areas to ensure everything worked
NWA_coords_cabot_plot <- ggplot(data = NWA_coords_cabot, aes(x = lon, y = lat)) +
geom_polygon(aes(colour = region, fill = region), size = 1.5, alpha = 0.2) +
geom_polygon(data = map_base, aes(group = group), show.legend = F) +
coord_cartesian(xlim = NWA_corners[1:2],
ylim = NWA_corners[3:4]) +
labs(x = NULL, y = NULL, colour = "Region", fill = "Region") +
theme(legend.position = "bottom")
# ggsave(NWA_coords_cabot_plot, filename = "output/NWA_coords_cabot_plot.pdf", height = 5, width = 6)
# Visualise
NWA_coords_cabot_plot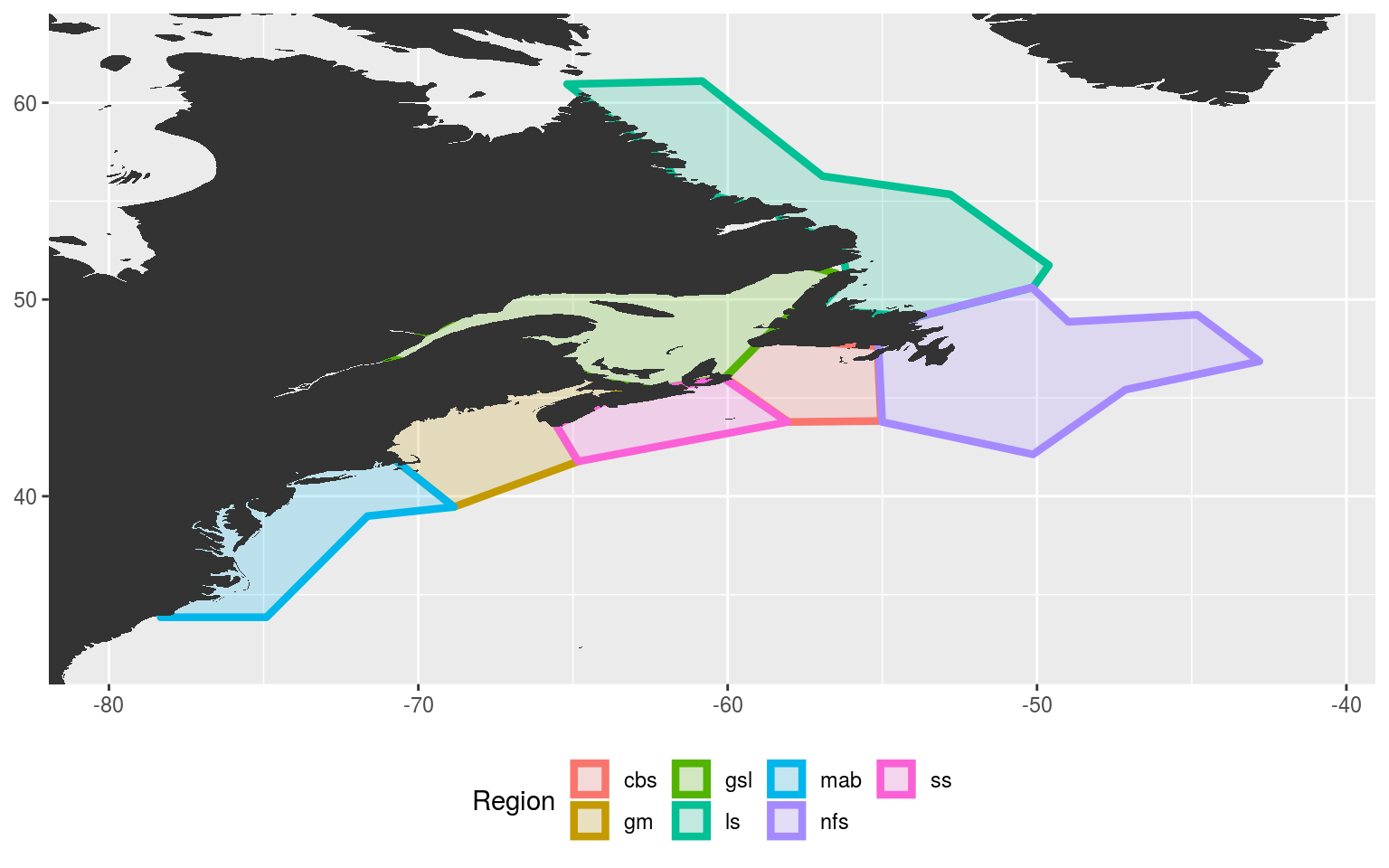
Expand here to see past versions of cabot-strait-2-1.png:
| Version | Author | Date |
|---|---|---|
| aa82e6e | robwschlegel | 2019-07-31 |
| 7cc8ec3 | robwschlegel | 2019-07-24 |
| 5cb8e8f | robwschlegel | 2019-05-28 |
| c09b4f7 | robwschlegel | 2019-05-24 |
| d544295 | robwschlegel | 2019-05-23 |
Everything is looking good, but we may want to divide the Gulf of Maine (gm) into two polygons as well. This would make the Bay of Fundy in it’s own region. For now however we will move on to the next step, which is dividing the current polygons by bathymetry.
We will now go about creating SST time series for each of the regions. This work is continued in the SST preparation vignette.
References
Richaud, B., Kwon, Y.-O., Joyce, T. M., Fratantoni, P. S., and Lentz, S. J. (2016). Surface and bottom temperature and salinity climatology along the continental shelf off the canadian and us east coasts. Continental Shelf Research 124, 165–181.
Session information
sessionInfo()R version 3.6.1 (2019-07-05)
Platform: x86_64-pc-linux-gnu (64-bit)
Running under: Ubuntu 16.04.5 LTS
Matrix products: default
BLAS: /usr/lib/openblas-base/libblas.so.3
LAPACK: /usr/lib/libopenblasp-r0.2.18.so
locale:
[1] LC_CTYPE=en_CA.UTF-8 LC_NUMERIC=C
[3] LC_TIME=en_CA.UTF-8 LC_COLLATE=en_CA.UTF-8
[5] LC_MONETARY=en_CA.UTF-8 LC_MESSAGES=en_CA.UTF-8
[7] LC_PAPER=en_CA.UTF-8 LC_NAME=C
[9] LC_ADDRESS=C LC_TELEPHONE=C
[11] LC_MEASUREMENT=en_CA.UTF-8 LC_IDENTIFICATION=C
attached base packages:
[1] stats graphics grDevices utils datasets methods base
other attached packages:
[1] bindrcpp_0.2.2 R.matlab_3.6.1 forcats_0.3.0 stringr_1.3.1
[5] dplyr_0.7.6 purrr_0.2.5 readr_1.1.1 tidyr_0.8.1
[9] tibble_1.4.2 ggplot2_3.0.0 tidyverse_1.2.1 jsonlite_1.6
loaded via a namespace (and not attached):
[1] tidyselect_0.2.4 haven_1.1.2 lattice_0.20-35
[4] colorspace_1.3-2 htmltools_0.3.6 yaml_2.2.0
[7] rlang_0.2.2 R.oo_1.22.0 pillar_1.3.0
[10] glue_1.3.0 withr_2.1.2 R.utils_2.7.0
[13] modelr_0.1.2 readxl_1.1.0 bindr_0.1.1
[16] plyr_1.8.4 munsell_0.5.0 gtable_0.2.0
[19] workflowr_1.1.1 cellranger_1.1.0 rvest_0.3.2
[22] R.methodsS3_1.7.1 evaluate_0.11 labeling_0.3
[25] knitr_1.20 broom_0.5.0 Rcpp_0.12.18
[28] backports_1.1.2 scales_1.0.0 hms_0.4.2
[31] digest_0.6.16 stringi_1.2.4 grid_3.6.1
[34] rprojroot_1.3-2 cli_1.0.0 tools_3.6.1
[37] maps_3.3.0 magrittr_1.5 lazyeval_0.2.1
[40] crayon_1.3.4 whisker_0.3-2 pkgconfig_2.0.2
[43] xml2_1.2.0 lubridate_1.7.4 assertthat_0.2.0
[46] rmarkdown_1.10 httr_1.3.1 rstudioapi_0.7
[49] R6_2.2.2 nlme_3.1-137 git2r_0.23.0
[52] compiler_3.6.1 This reproducible R Markdown analysis was created with workflowr 1.1.1