Tr1: Differential Gene Expression
Stephen Pederson & Caitlin Abbott
25 October, 2022
Last updated: 2022-10-25
Checks: 6 1
Knit directory: Tr1-RNA-Sequencing-/
This reproducible R Markdown analysis was created with workflowr (version 1.7.0). The Checks tab describes the reproducibility checks that were applied when the results were created. The Past versions tab lists the development history.
The R Markdown file has unstaged changes. To know which version of
the R Markdown file created these results, you’ll want to first commit
it to the Git repo. If you’re still working on the analysis, you can
ignore this warning. When you’re finished, you can run
wflow_publish to commit the R Markdown file and build the
HTML.
Great job! The global environment was empty. Objects defined in the global environment can affect the analysis in your R Markdown file in unknown ways. For reproduciblity it’s best to always run the code in an empty environment.
The command set.seed(20221025) was run prior to running
the code in the R Markdown file. Setting a seed ensures that any results
that rely on randomness, e.g. subsampling or permutations, are
reproducible.
Great job! Recording the operating system, R version, and package versions is critical for reproducibility.
Nice! There were no cached chunks for this analysis, so you can be confident that you successfully produced the results during this run.
Great job! Using relative paths to the files within your workflowr project makes it easier to run your code on other machines.
Great! You are using Git for version control. Tracking code development and connecting the code version to the results is critical for reproducibility.
The results in this page were generated with repository version 173bae6. See the Past versions tab to see a history of the changes made to the R Markdown and HTML files.
Note that you need to be careful to ensure that all relevant files for
the analysis have been committed to Git prior to generating the results
(you can use wflow_publish or
wflow_git_commit). workflowr only checks the R Markdown
file, but you know if there are other scripts or data files that it
depends on. Below is the status of the Git repository when the results
were generated:
Ignored files:
Ignored: .Rhistory
Ignored: .Rproj.user/
Untracked files:
Untracked: output/fit.rds
Unstaged changes:
Modified: analysis/_site.yml
Modified: analysis/dge.Rmd
Modified: analysis/enrichment.Rmd
Modified: code/analysis with DN.R
Note that any generated files, e.g. HTML, png, CSS, etc., are not included in this status report because it is ok for generated content to have uncommitted changes.
These are the previous versions of the repository in which changes were
made to the R Markdown (analysis/dge.Rmd) and HTML
(docs/dge.html) files. If you’ve configured a remote Git
repository (see ?wflow_git_remote), click on the hyperlinks
in the table below to view the files as they were in that past version.
| File | Version | Author | Date | Message |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rmd | 8745ba2 | Steve Pederson | 2022-10-25 | Shifted to workflowr |
| html | 8745ba2 | Steve Pederson | 2022-10-25 | Shifted to workflowr |
knitr::opts_chunk$set(
warning = FALSE, message = FALSE,
fig.width = 10, fig.height = 8,
dev = c("png", "pdf")
)library(tidyverse)
library(magrittr)
library(limma)
library(edgeR)
library(ggrepel)
library(ggplot2)
library(pheatmap)
library(AnnotationHub)
library(ensembldb)
library(scales)
library(broom)
library(glue)
library(pander)
library(grid)
theme_set(
theme_bw() +
theme(plot.title = element_text(hjust = 0.5))
)Data Preparation & Inspection
counts <- here::here("data", "genes.out.gz") %>%
read_tsv() %>%
rename_all(basename) %>%
rename_all(str_remove_all, pattern = "Aligned.sortedByCoord.out.bam")
samples <- tibble(
sample = setdiff(colnames(counts), "Geneid"),
condition = gsub("M2_|M3_|M5_|M6_", "", sample) %>%
factor(levels = c("DN", "DP", "LAG_3", "CD49b")),
mouse = str_extract(sample, "M[0-9]"),
label = glue("{condition} ({mouse})")
)
dgeList <- counts %>%
as.data.frame() %>%
column_to_rownames("Geneid") %>%
as.matrix() %>%
DGEList(
samples = samples
) %>%
calcNormFactors(method = "TMM")ah <- AnnotationHub()
#Find which genome did we use
# unique(ah$dataprovider)
# subset(ah, dataprovider == "Ensembl") %>% #In Ensembl databse
# subset(species == "Mus musculus") %>% #under Mouse
# subset(rdataclass == "EnsDb")
ensDb <- ah[["AH69210"]] #This is the genome used for assigning reads to genes
genes <- genes(ensDb) %>% #extract the genes
subset(seqnames %in% c(1:19, "MT", "X", "Y")) %>%
keepStandardChromosomes() %>%
sortSeqlevels()
dgeList$genes <- data.frame(gene_id = rownames(dgeList)) %>%
left_join(
mcols(genes) %>%
as.data.frame() %>%
dplyr::select(gene_id, gene_name, gene_biotype, description, entrezid),
by = "gene_id"
)
id2gene <- setNames(genes$gene_name, genes$gene_id)genes2keep <- dgeList %>%
cpm(log = TRUE) %>%
is_greater_than(1) %>%
rowSums() %>%
is_greater_than(4)
dgeFilt <- dgeList[genes2keep,, keep.lib.sizes = FALSE]Genes were only retained in the final dataset if \(> 4\) samples returned \(>1\) log2 Counts per Million (logCPM). The gave a dataset of 11,117 of the initial 55,450 genes which were retained for downstream analysis.
Library Sizes
dgeList$samples %>%
mutate(CellType = dgeList$samples$condition) %>%
ggplot(aes(x = label, y = lib.size / 1e6, fill = CellType)) +
geom_col() +
geom_hline(
yintercept = mean(dgeList$samples$lib.size / 1e6),
linetype = 2, colour = "grey30"
) +
labs(x = "Sample", y = "Library Size (millions)") +
facet_wrap(~mouse, scales = "free_x", nrow = 1) +
scale_x_discrete(labels = label_wrap(5)) +
scale_y_continuous(expand = expansion(c(0, 0.05))) 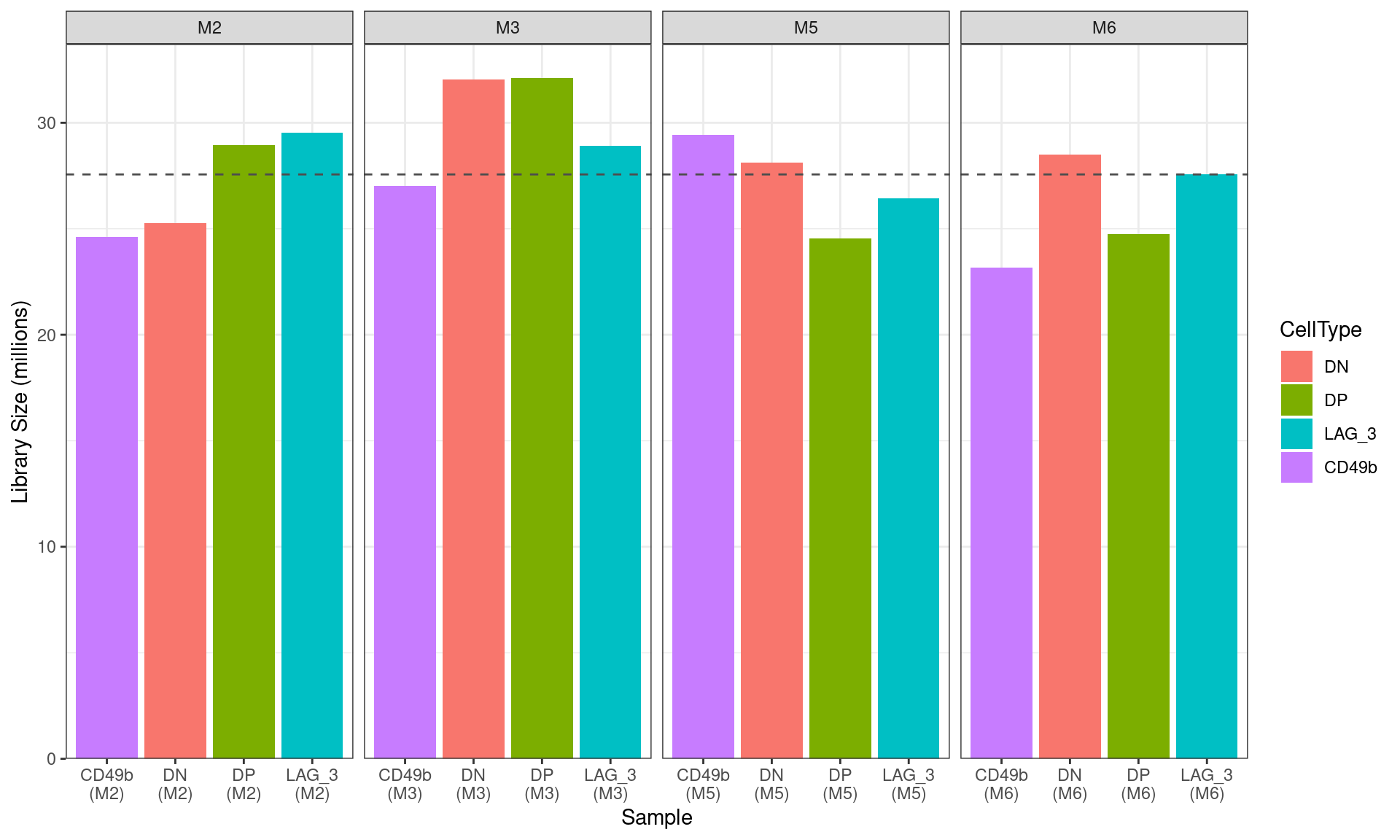
Figure S7a Library sizes for all libraries after summarisation to gene-level counts. The mean library size across all libraries is shown as a dashed horizontal line.
| Version | Author | Date |
|---|---|---|
| 8745ba2 | Steve Pederson | 2022-10-25 |
Count Densities
dgeFilt %>%
cpm(log = TRUE) %>%
as_tibble(rownames = "gene_id") %>%
pivot_longer(cols = all_of(colnames(dgeFilt)), names_to = "sample", values_to = "logCPM") %>%
left_join(dgeFilt$samples, by = "sample") %>%
ggplot(aes(logCPM, y = stat(density), colour = condition, group = sample)) +
geom_density() +
facet_wrap(~mouse) +
scale_y_continuous(expand = expansion(c(0.01, 0.05)))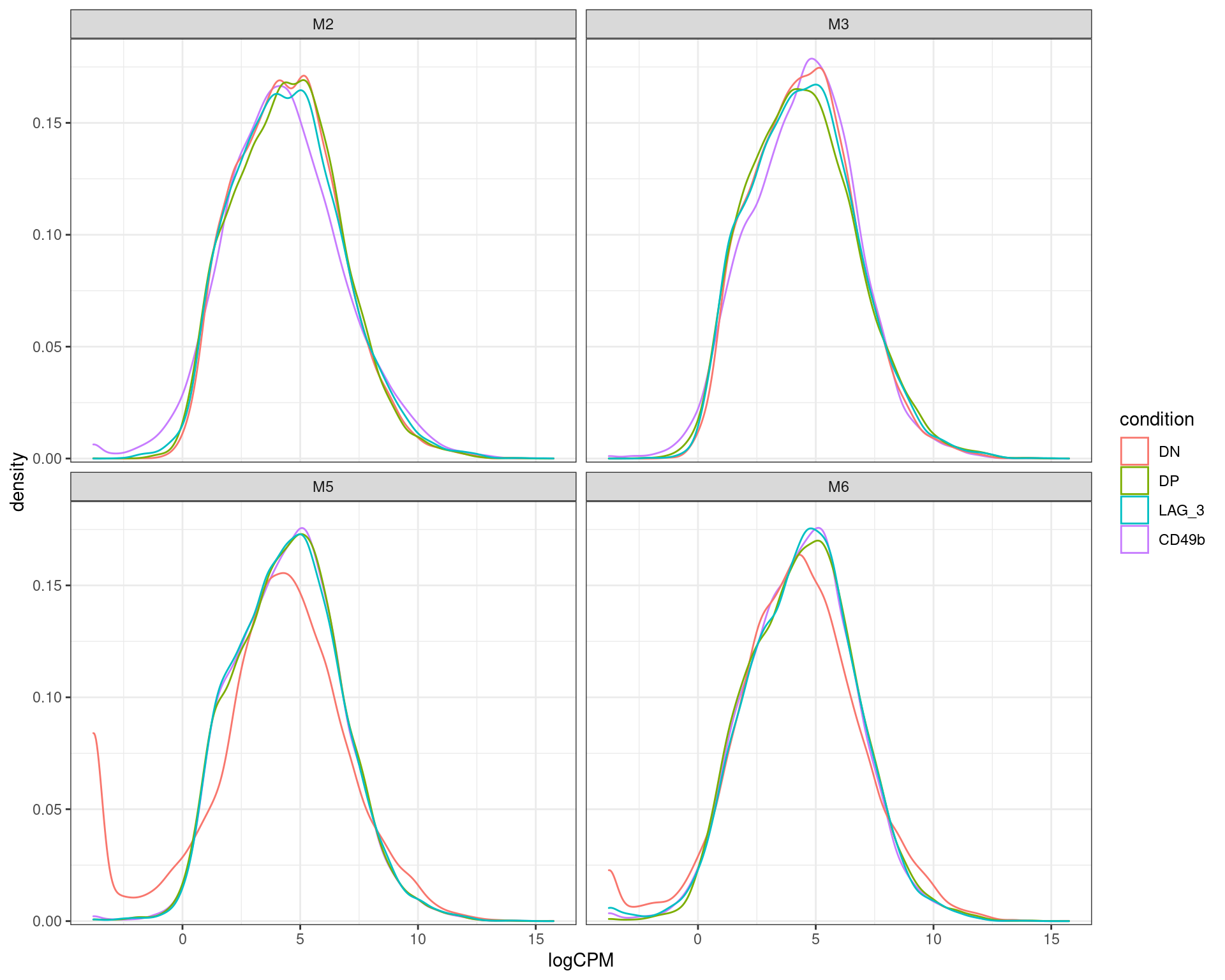
logCPM densisties after removal of undetectable genes. The double negative (DN) samples for both m% and M6 appear to skew to lower overall counts compared to all other samples, with a handful of highly expressed genes likely to dominate the sample.
| Version | Author | Date |
|---|---|---|
| 8745ba2 | Steve Pederson | 2022-10-25 |
PCA
pca <- dgeFilt %>%
cpm(log = TRUE) %>%
t() %>%
prcomp()
pca %>%
broom::tidy() %>%
dplyr::rename(sample = row) %>%
dplyr::filter(PC %in% c(1, 2)) %>%
pivot_wider(names_from = "PC", names_prefix = "PC", values_from = "value") %>%
left_join(dgeFilt$samples, by = "sample") %>%
ggplot(aes(PC1, PC2, colour = condition)) +
geom_point(size = 3) +
geom_text_repel(
aes(label = label),#str_replace_all(label, " ", "\n")),
max.overlaps = Inf
) +
labs(
x = glue("PC1 ({percent(summary(pca)$importance[2, 'PC1'])})"),
y = glue("PC2 ({percent(summary(pca)$importance[2, 'PC2'])})"),
colour = "Cell Type"
)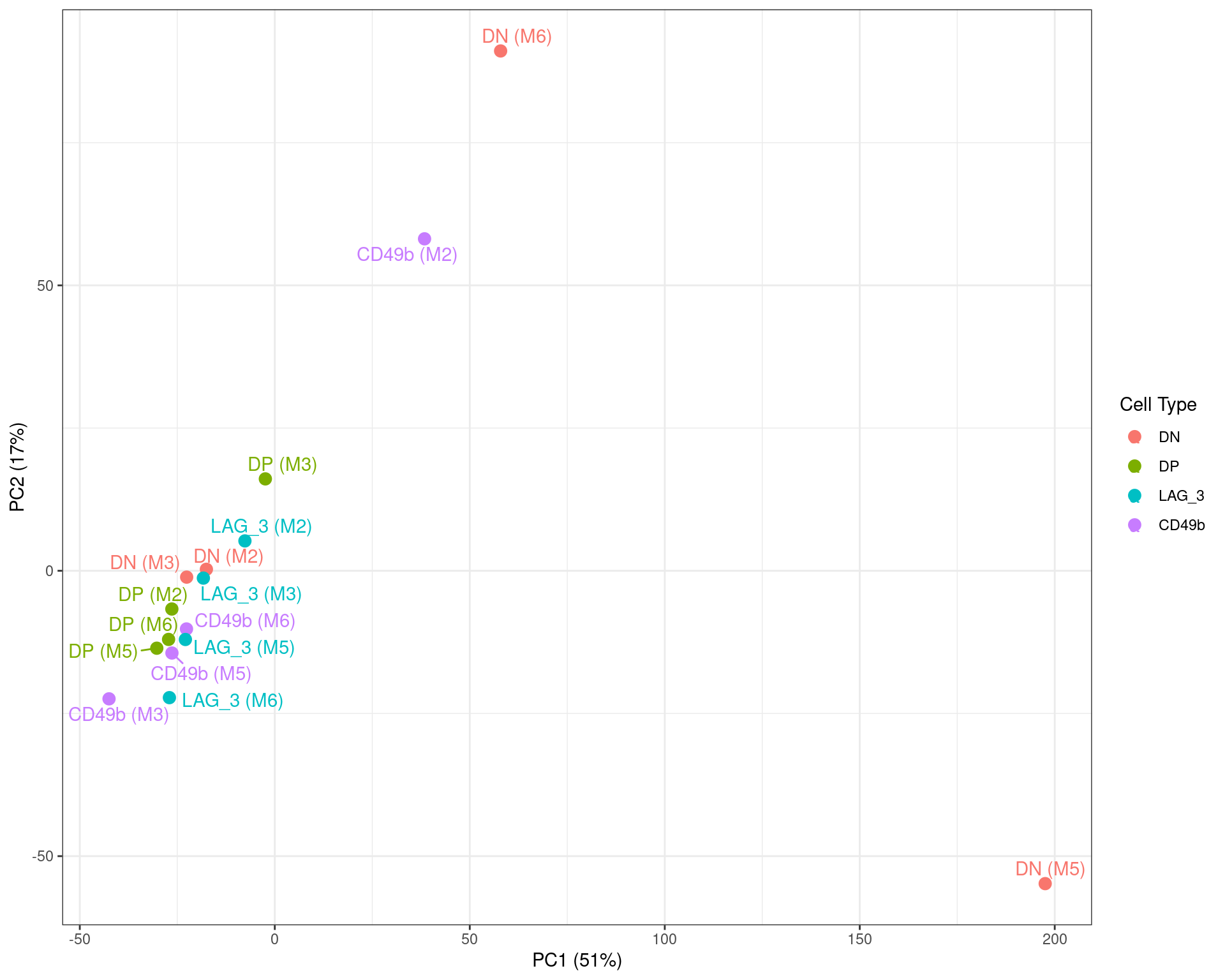
Figure S7b PCA on logCPM values, with the two DN samples identified above clearly showing strong divergence from the remainder of the dataset. The CD49b sample fro M2 also appeared slightly divergent, with the previous density plot also showing a slght skew towards lower overall counts.
| Version | Author | Date |
|---|---|---|
| 8745ba2 | Steve Pederson | 2022-10-25 |
The above PCA revealed some potential problems with two of the four DN samples. Exclusion of the clear outliers will reduce the number of viable samples within the DN group to 2 and as an alternative, a weighting strategy was instead sought for all samples.
Model Fitting
U <- matrix(1, nrow = ncol(dgeFilt)) %>%
set_colnames("Intercept")
v <- voomWithQualityWeights(dgeFilt, design = U)
X <- model.matrix(~0 + condition, data = dgeFilt$samples) %>%
set_colnames(str_remove(colnames(.), "condition"))
rho <- duplicateCorrelation(v, X, block=dgeFilt$samples$mouse)$consensus.correlation
v <- voomWithQualityWeights(
counts = dgeFilt, design = U, block=dgeFilt$samples$mouse, correlation=rho
)
v$design <- XSample-level weights were estimated by assuming all samples were
drawn from the same group and running
voomWithQualityWeights(). After running this, samples were
compared within each mouse-of-origin and correlations within mice were
estimated using duplicateCorrelation() (\(\rho=\) 0.118).
voomWithQualityWeights() was then run again setting mouse
as the blocking variable and including the consensus correlations
v$targets %>%
ggplot(aes(label, sample.weights, fill = condition)) +
geom_col() +
geom_hline(yintercept = 1, linetype = 2, col = "grey30") +
facet_wrap(~mouse, nrow = 1, scales = "free_x") +
scale_x_discrete(labels = scales::label_wrap(5)) +
scale_y_continuous(expand = expansion(c(0, 0.05))) +
labs(
x = "Sample", y = "Sample Weights", fill = "Cell Type"
)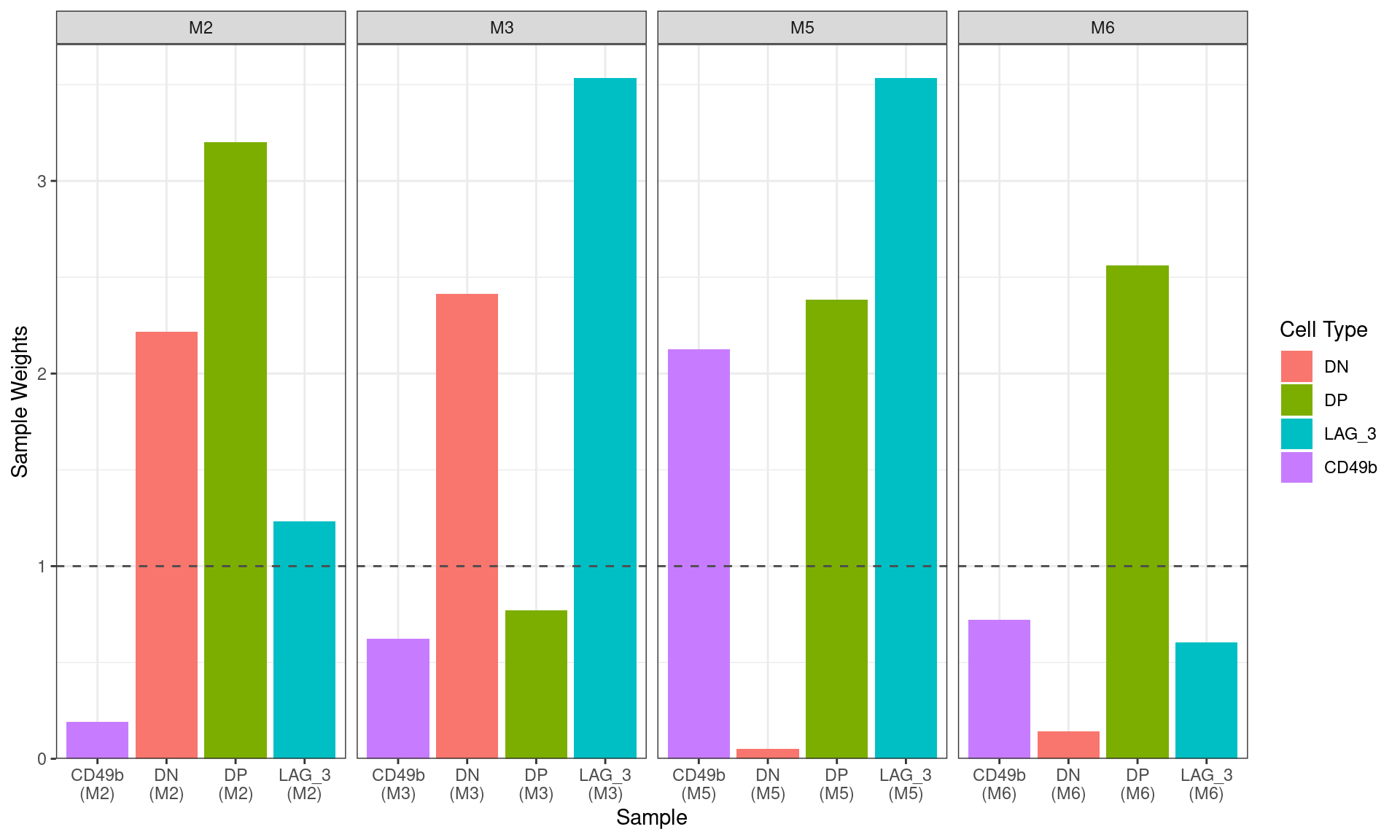
Sample-level weights after running
voomWithQualityWeights setting all samples as being drawn
from the same condition. The ideal equal wweighting of 1 is shown as the
dashed horizontal line, with those samples below this being assumed to
be of lower quality than those above the line. Thw two previously
identified DN samples were strongly down-weighted, as was the CD49b
sample from M2
| Version | Author | Date |
|---|---|---|
| 8745ba2 | Steve Pederson | 2022-10-25 |
cont.matrix <- makeContrasts(
DNvLAG3 = DN - LAG_3,
DNvDP = DN - DP,
DNvCD49b = DN - CD49b,
LAG3vCD49b = LAG_3 - CD49b,
CD49bvDP = CD49b - DP,
LAG3vDP = LAG_3 - DP,
levels = X
)
fit <- lmFit(v, design = X, block = v$targets$mouse, correlation = rho) %>%
contrasts.fit(cont.matrix) %>%
# treat()
eBayes()Summary Table
top_tables <- colnames(cont.matrix) %>%
lapply(function(x) topTable(fit, coef = x, number = Inf)) %>%
# lapply(function(x) topTreat(fit, coef = x, number = Inf)) %>%
lapply(as_tibble) %>%
lapply(mutate, DE = adj.P.Val < 0.05 & abs(logFC) > 1) %>%
setNames(colnames(cont.matrix))
top_tables %>%
lapply(
function(x){
df <- dplyr::filter(x,DE)
tibble(
Up = sum(df$logFC > 0),
Down = sum(df$logFC < 0),
`Total DE` = Up + Down
)
}
) %>%
bind_rows(.id = "Comparison") %>%
pander(
justify = "lrrr",
caption = glue(
"
Results from each comparison, where genes are considered DE using an FDR
< 0.05 along with an estimated logFC beyond $\\pm1$. In total,
{length(unique(dplyr::filter(bind_rows(top_tables), DE)$gene_id))}
unique genes were considered to be DE in at least one comparison.
"
)
)| Comparison | Up | Down | Total DE |
|---|---|---|---|
| DNvLAG3 | 46 | 31 | 77 |
| DNvDP | 27 | 34 | 61 |
| DNvCD49b | 16 | 2 | 18 |
| LAG3vCD49b | 111 | 56 | 167 |
| CD49bvDP | 6 | 32 | 38 |
| LAG3vDP | 16 | 17 | 33 |
MA Plots
DN Vs. LAG3
top_tables$DNvLAG3 %>%
ggplot(aes(AveExpr, logFC)) +
geom_point(aes(colour = DE), alpha = 0.6) +
geom_smooth(se = FALSE) +
geom_label_repel(
aes(label = gene_name, colour = DE),
data = . %>%
dplyr::filter(DE, logFC > 0) %>%
arrange(desc(logFC)) %>%
dplyr::slice(1:5),
max.overlaps = Inf,
fontface = "italic",
show.legend = FALSE
) +
geom_label_repel(
aes(label = gene_name, colour = DE),
data = . %>%
dplyr::filter(DE, logFC < 0) %>%
arrange(logFC) %>%
dplyr::slice(1:5),
max.overlaps = Inf,
fontface = "italic",
show.legend = FALSE
) +
ggtitle("DN Vs. LAG3") +
scale_colour_manual(values = c("grey30", "red"))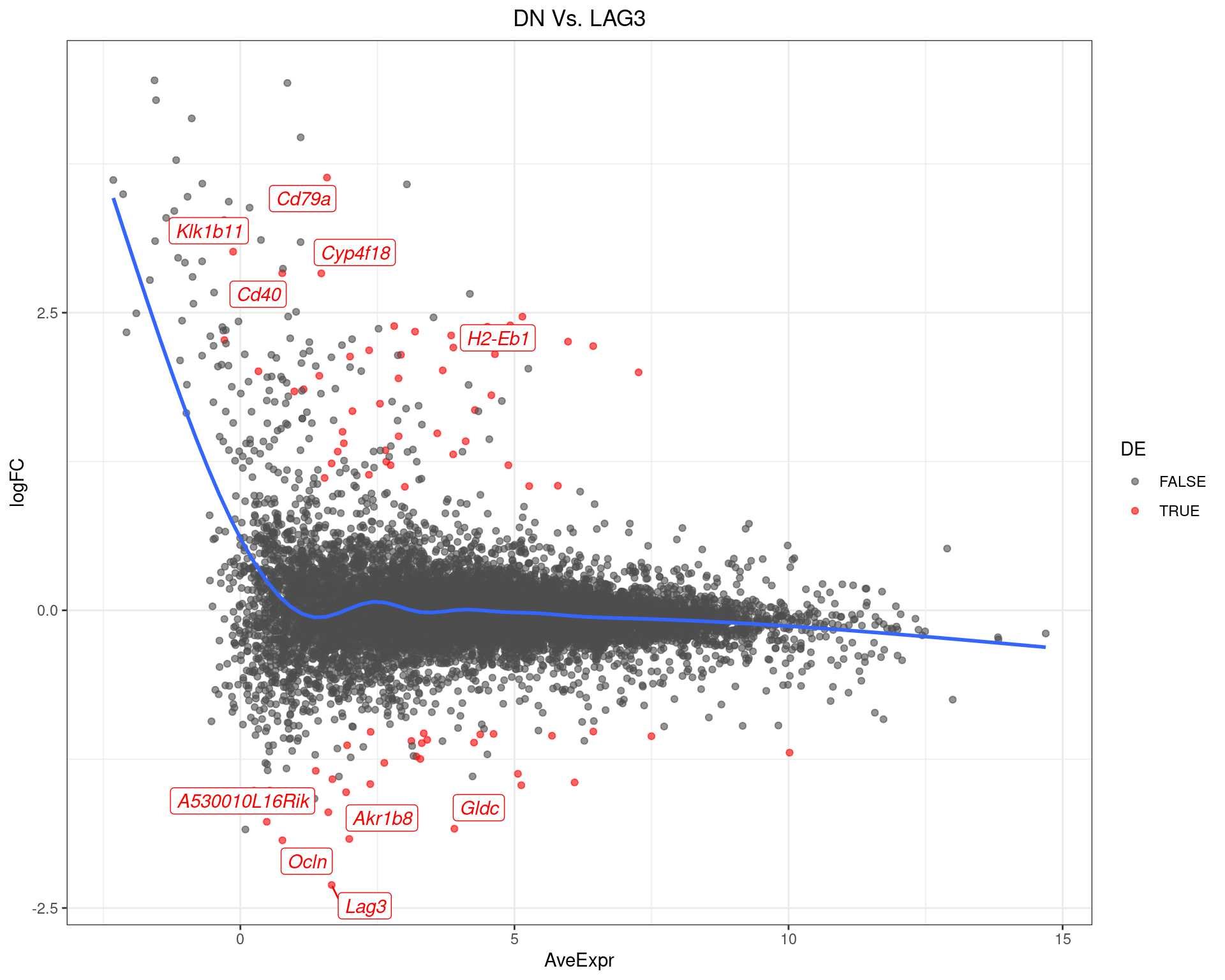
MA-Plot for DN Vs. LAG3. The 5 most up/down-regulated genes are labelled, with the blue line representing a spline through the data.
| Version | Author | Date |
|---|---|---|
| 8745ba2 | Steve Pederson | 2022-10-25 |
DN Vs. DP
top_tables$DNvDP %>%
ggplot(aes(AveExpr, logFC)) +
geom_point(aes(colour = DE), alpha = 0.6) +
geom_smooth(se = FALSE) +
geom_label_repel(
aes(label = gene_name, colour = DE),
data = . %>%
dplyr::filter(DE, logFC > 0) %>%
arrange(desc(logFC)) %>%
dplyr::slice(1:5),
max.overlaps = Inf,
fontface = "italic",
show.legend = FALSE
) +
geom_label_repel(
aes(label = gene_name, colour = DE),
data = . %>%
dplyr::filter(DE, logFC < 0) %>%
arrange(logFC) %>%
dplyr::slice(1:5),
max.overlaps = Inf,
fontface = "italic",
show.legend = FALSE
) +
ggtitle("DN Vs. DP") +
scale_colour_manual(values = c("grey30", "red"))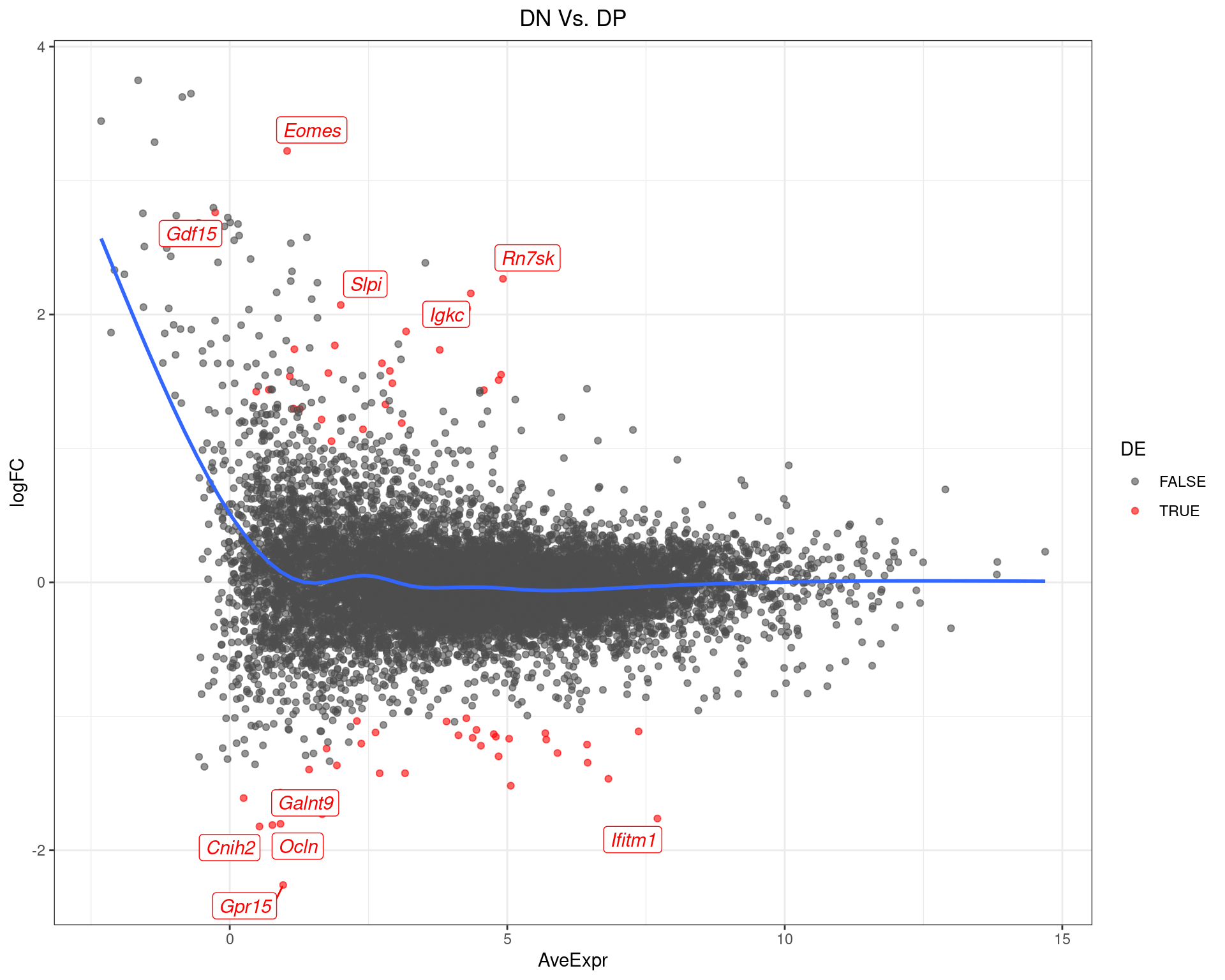
MA-Plot for DN Vs. DP. The 5 most up/down-regulated genes are labelled, with the blue line representing a spline through the data.
| Version | Author | Date |
|---|---|---|
| 8745ba2 | Steve Pederson | 2022-10-25 |
DN Vs. CD49b
top_tables$DNvCD49b %>%
ggplot(aes(AveExpr, logFC)) +
geom_point(aes(colour = DE), alpha = 0.6) +
geom_smooth(se = FALSE) +
geom_label_repel(
aes(label = gene_name, colour = DE),
data = . %>%
dplyr::filter(DE, logFC > 0) %>%
arrange(desc(logFC)) %>%
dplyr::slice(1:5),
max.overlaps = Inf,
fontface = "italic",
show.legend = FALSE
) +
geom_label_repel(
aes(label = gene_name, colour = DE),
data = . %>%
dplyr::filter(DE, logFC < 0) %>%
arrange(logFC) %>%
dplyr::slice(1:5),
max.overlaps = Inf,
fontface = "italic",
show.legend = FALSE
) +
ggtitle("DN Vs. CD49b") +
scale_colour_manual(values = c("grey30", "red"))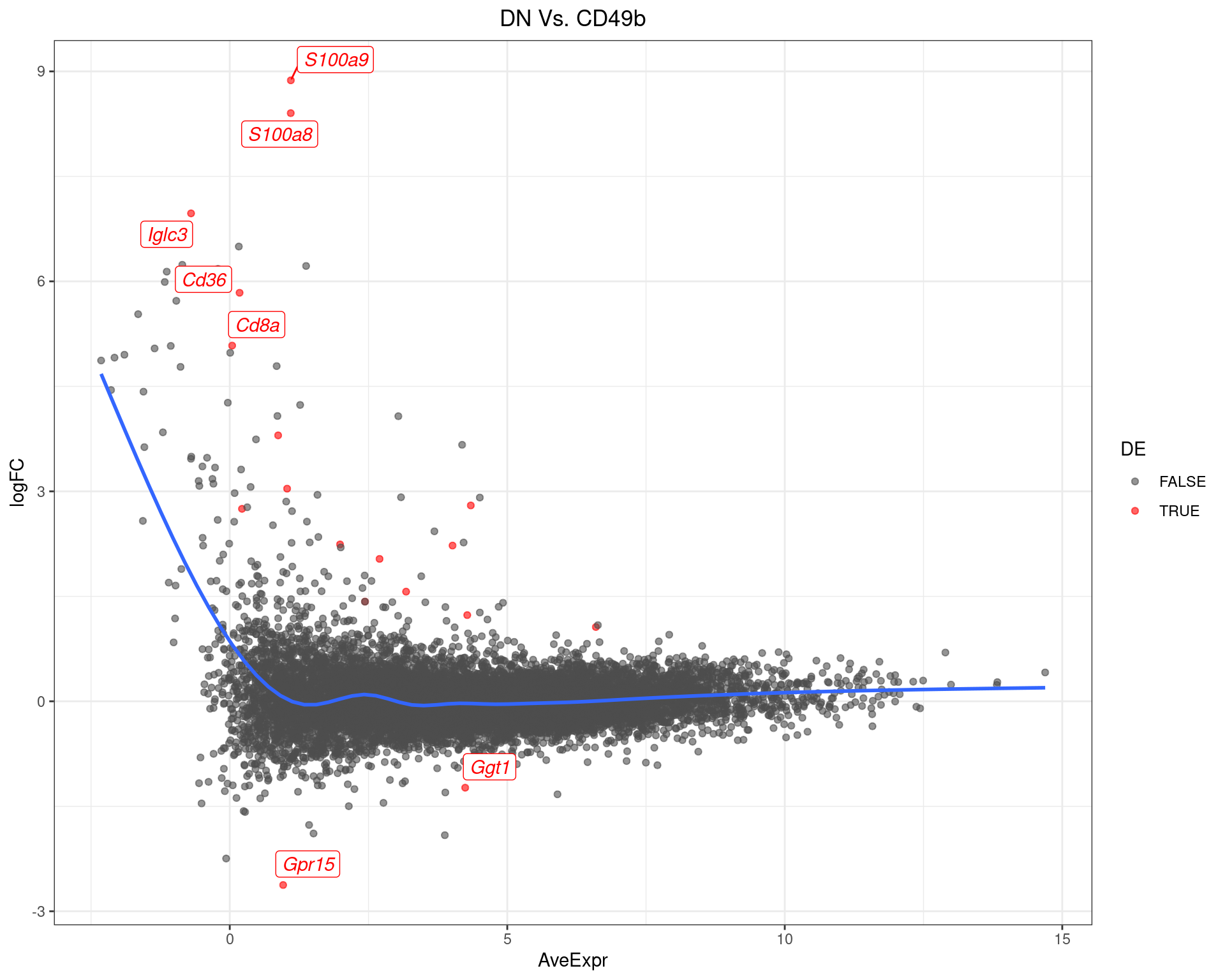
MA-Plot for DN Vs. CD49b The most up/down-regulated genes are labelled, with the blue line representing a spline through the data.
| Version | Author | Date |
|---|---|---|
| 8745ba2 | Steve Pederson | 2022-10-25 |
LAG3 Vs. CD49b
top_tables$LAG3vCD49b %>%
ggplot(aes(AveExpr, logFC)) +
geom_point(aes(colour = DE), alpha = 0.6) +
geom_smooth(se = FALSE) +
geom_label_repel(
aes(label = gene_name, colour = DE),
data = . %>%
dplyr::filter(DE, logFC > 0) %>%
arrange(desc(logFC)) %>%
dplyr::slice(1:5),
max.overlaps = Inf,
fontface = "italic",
show.legend = FALSE
) +
geom_label_repel(
aes(label = gene_name, colour = DE),
data = . %>%
dplyr::filter(DE, logFC < 0) %>%
arrange(logFC) %>%
dplyr::slice(1:5),
max.overlaps = Inf,
fontface = "italic",
show.legend = FALSE
) +
ggtitle("LAG3 Vs. CD49b") +
scale_colour_manual(values = c("grey30", "red"))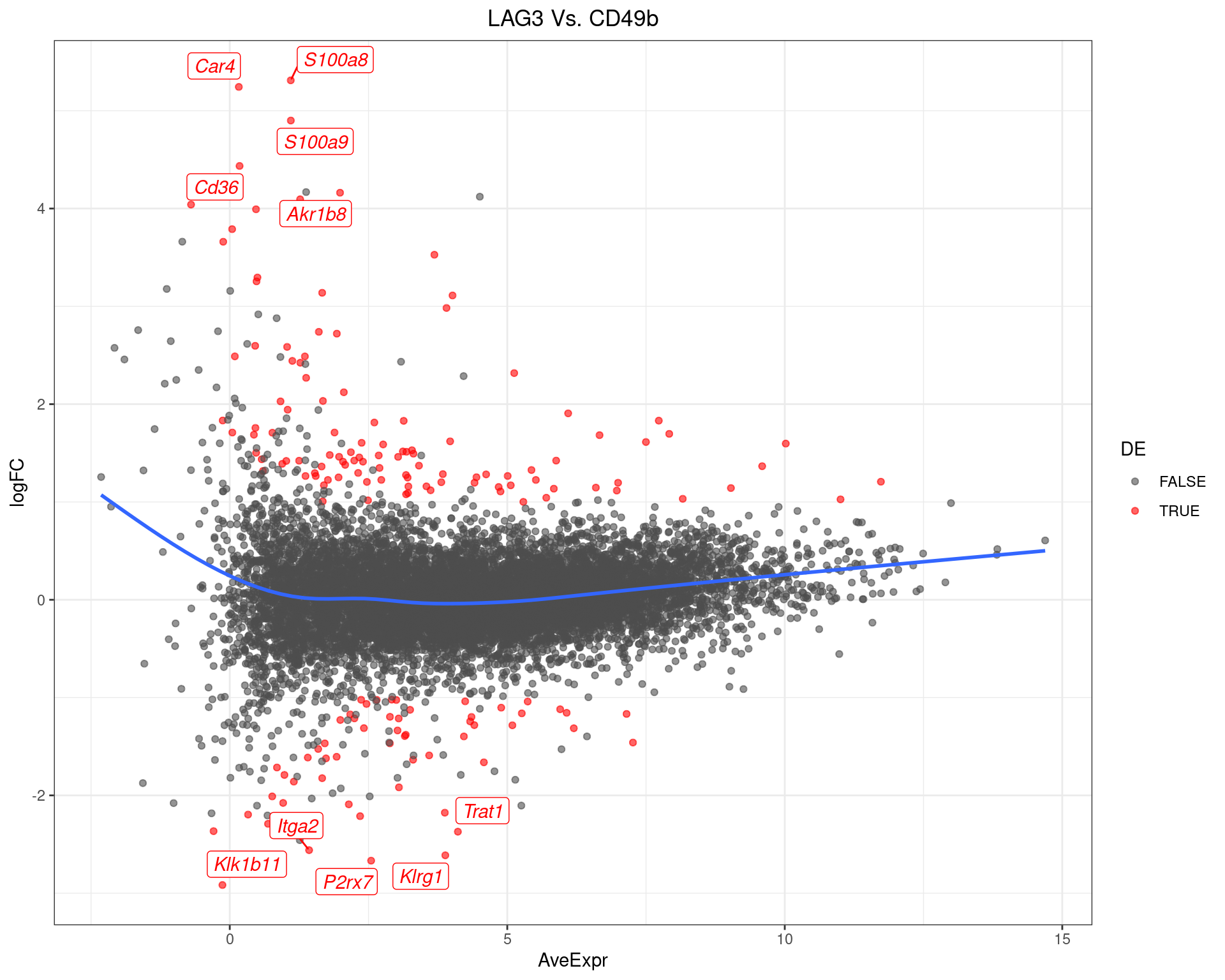
MA-Plot for LAG3 Vs. CD49b. The 5 most up/down-regulated genes are labelled, with the blue line representing a spline through the data.
| Version | Author | Date |
|---|---|---|
| 8745ba2 | Steve Pederson | 2022-10-25 |
LAG3 Vs. DP
top_tables$LAG3vDP %>%
ggplot(aes(AveExpr, logFC)) +
geom_point(aes(colour = DE), alpha = 0.6) +
geom_smooth(se = FALSE) +
geom_label_repel(
aes(label = gene_name, colour = DE),
data = . %>%
dplyr::filter(DE, logFC > 0) %>%
arrange(desc(logFC)) %>%
dplyr::slice(1:5),
max.overlaps = Inf,
fontface = "italic",
show.legend = FALSE
) +
geom_label_repel(
aes(label = gene_name, colour = DE),
data = . %>%
dplyr::filter(DE, logFC < 0) %>%
arrange(logFC) %>%
dplyr::slice(1:5),
max.overlaps = Inf,
fontface = "italic",
show.legend = FALSE
) +
ggtitle("LAG3 Vs. DP") +
scale_colour_manual(values = c("grey30", "red"))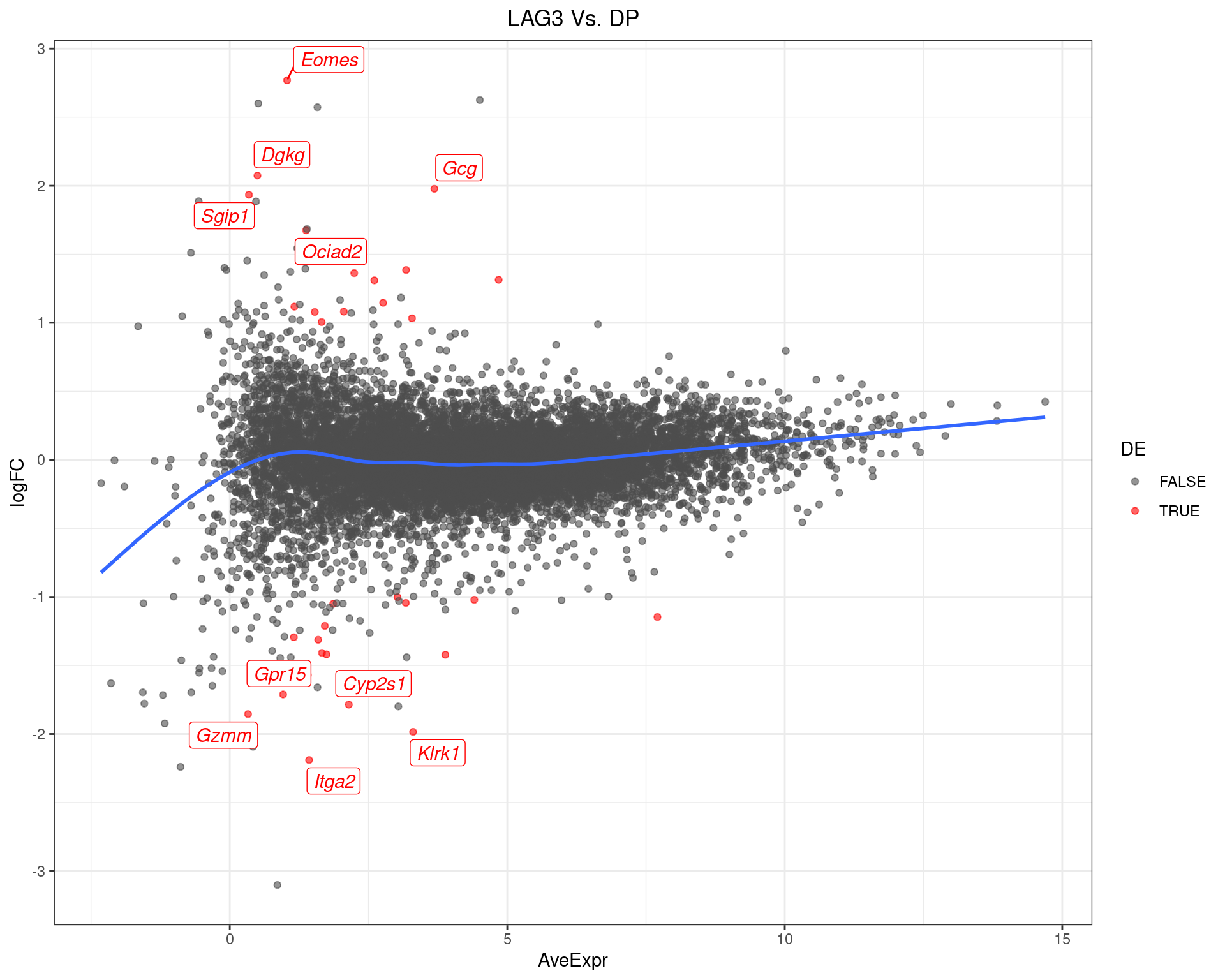
MA-Plot for LAG3 Vs. DP The 5 most up/down-regulated genes are labelled, with the blue line representing a spline through the data.
| Version | Author | Date |
|---|---|---|
| 8745ba2 | Steve Pederson | 2022-10-25 |
CD49b Vs. DP
top_tables$CD49bvDP %>%
ggplot(aes(AveExpr, logFC)) +
geom_point(aes(colour = DE), alpha = 0.6) +
geom_smooth(se = FALSE) +
geom_label_repel(
aes(label = gene_name, colour = DE),
data = . %>%
dplyr::filter(DE, logFC > 0) %>%
arrange(desc(logFC)) %>%
dplyr::slice(1:5),
max.overlaps = Inf,
fontface = "italic",
show.legend = FALSE
) +
geom_label_repel(
aes(label = gene_name, colour = DE),
data = . %>%
dplyr::filter(DE, logFC < 0) %>%
arrange(logFC) %>%
dplyr::slice(1:5),
max.overlaps = Inf,
fontface = "italic",
show.legend = FALSE
) +
ggtitle("CD49b Vs. DP") +
scale_colour_manual(values = c("grey30", "red"))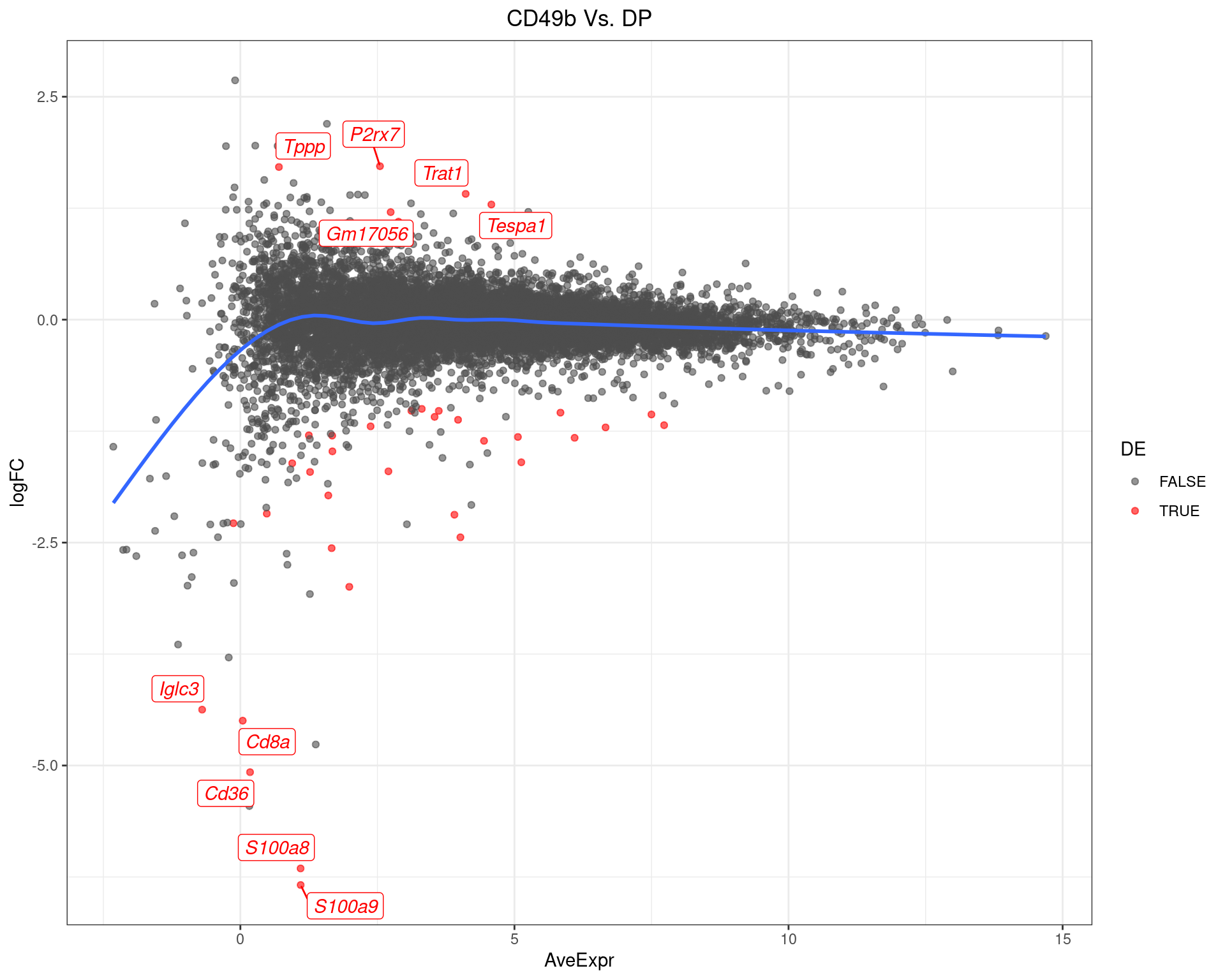
MA-Plot for CD49b Vs. DP. The 5 most up/down-regulated genes are labelled, with the blue line representing a spline through the data.
| Version | Author | Date |
|---|---|---|
| 8745ba2 | Steve Pederson | 2022-10-25 |
Volcano Plots
DN Vs. LAG3
top_tables$DNvLAG3 %>%
ggplot(aes(logFC, -log10(P.Value))) +
geom_point(aes(colour = DE), alpha = 0.6) +
geom_label_repel(
aes(label = gene_name, colour = DE),
data = . %>%
dplyr::filter(DE) %>%
arrange(P.Value) %>%
dplyr::slice(1:10),
max.overlaps = Inf,
fontface = "italic",
show.legend = FALSE
) +
ggtitle("DN Vs. LAG3") +
scale_colour_manual(values = c("grey30", "red"))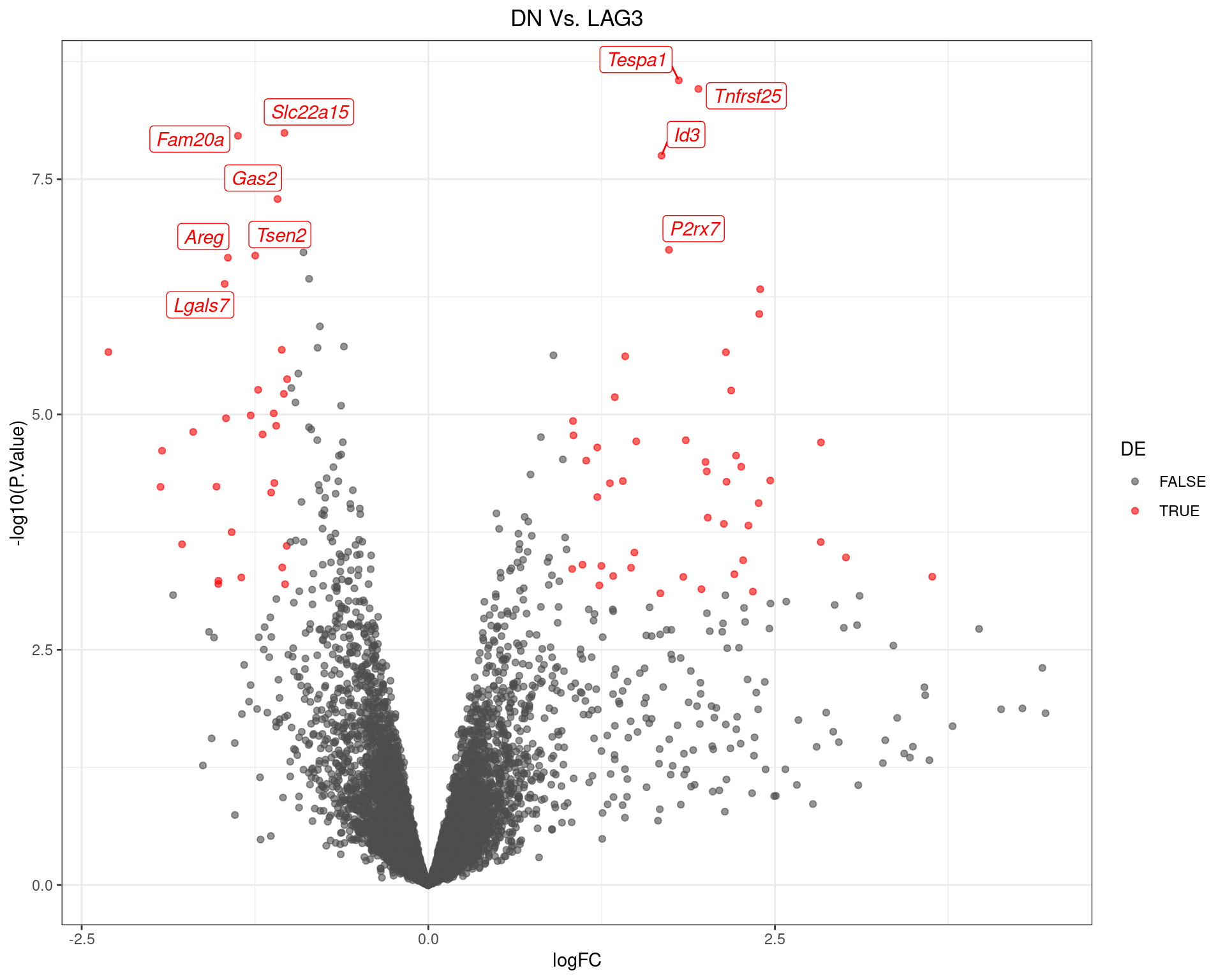
Volcano Plot for DN Vs. LAG3. The 10 most highly-ranked genes are labelled, with the blue line representing a spline through the data.
| Version | Author | Date |
|---|---|---|
| 8745ba2 | Steve Pederson | 2022-10-25 |
DN Vs. DP
top_tables$DNvDP %>%
ggplot(aes(logFC, -log10(P.Value))) +
geom_point(aes(colour = DE), alpha = 0.6) +
geom_label_repel(
aes(label = gene_name, colour = DE),
data = . %>%
dplyr::filter(DE) %>%
arrange(P.Value) %>%
dplyr::slice(1:10),
max.overlaps = Inf,
fontface = "italic",
show.legend = FALSE
) +
ggtitle("DN Vs. DP") +
scale_colour_manual(values = c("grey30", "red"))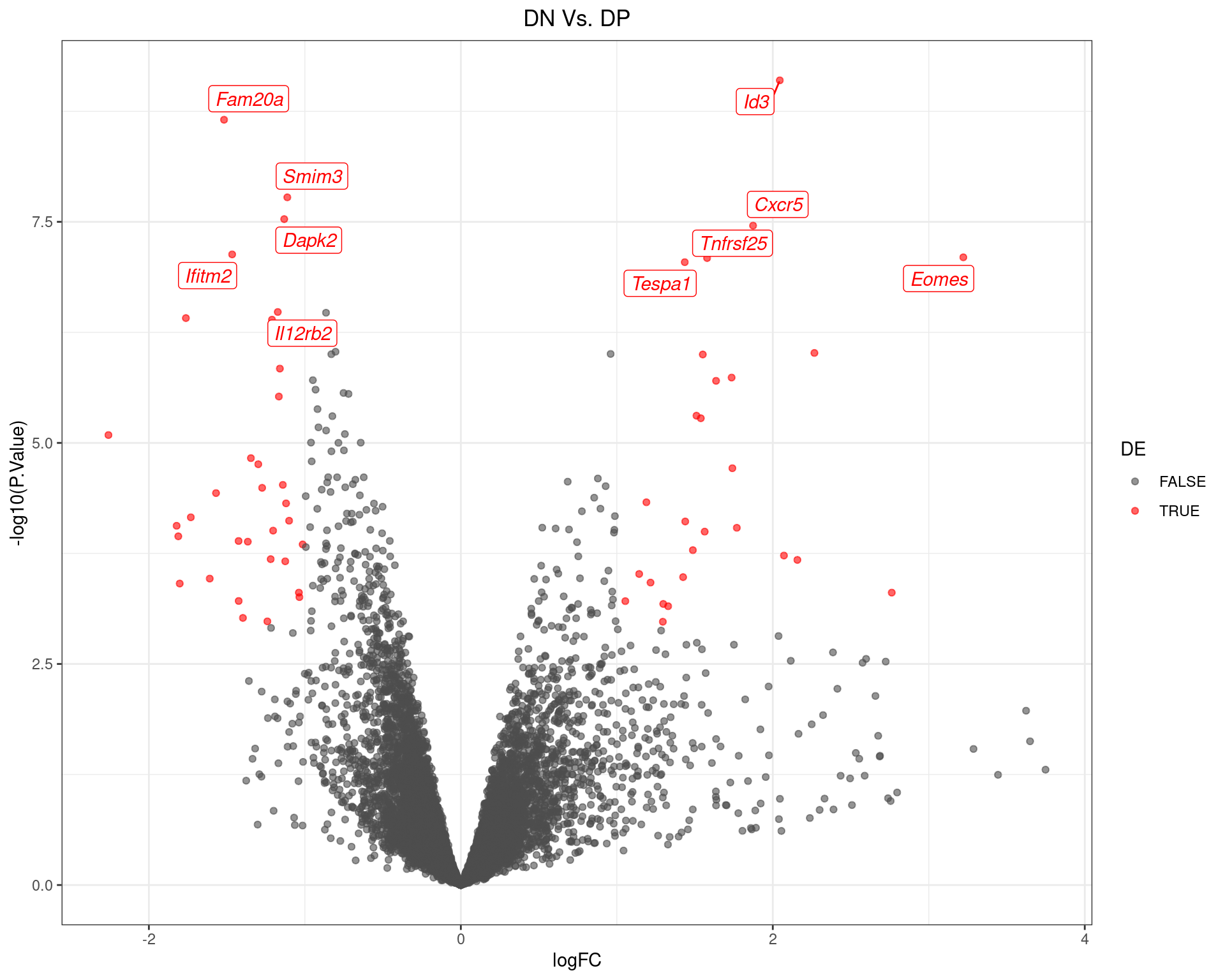
Volcano Plot for DN Vs. DP. The 10 most highly-ranked genes are labelled, with the blue line representing a spline through the data.
| Version | Author | Date |
|---|---|---|
| 8745ba2 | Steve Pederson | 2022-10-25 |
DN Vs. CD49b
top_tables$DNvCD49b %>%
ggplot(aes(logFC, -log10(P.Value))) +
geom_point(aes(colour = DE), alpha = 0.6) +
geom_label_repel(
aes(label = gene_name, colour = DE),
data = . %>%
dplyr::filter(DE) %>%
arrange(P.Value) %>%
dplyr::slice(1:10),
max.overlaps = Inf,
fontface = "italic",
show.legend = FALSE
) +
ggtitle("DN Vs. CD49b") +
scale_colour_manual(values = c("grey30", "red"))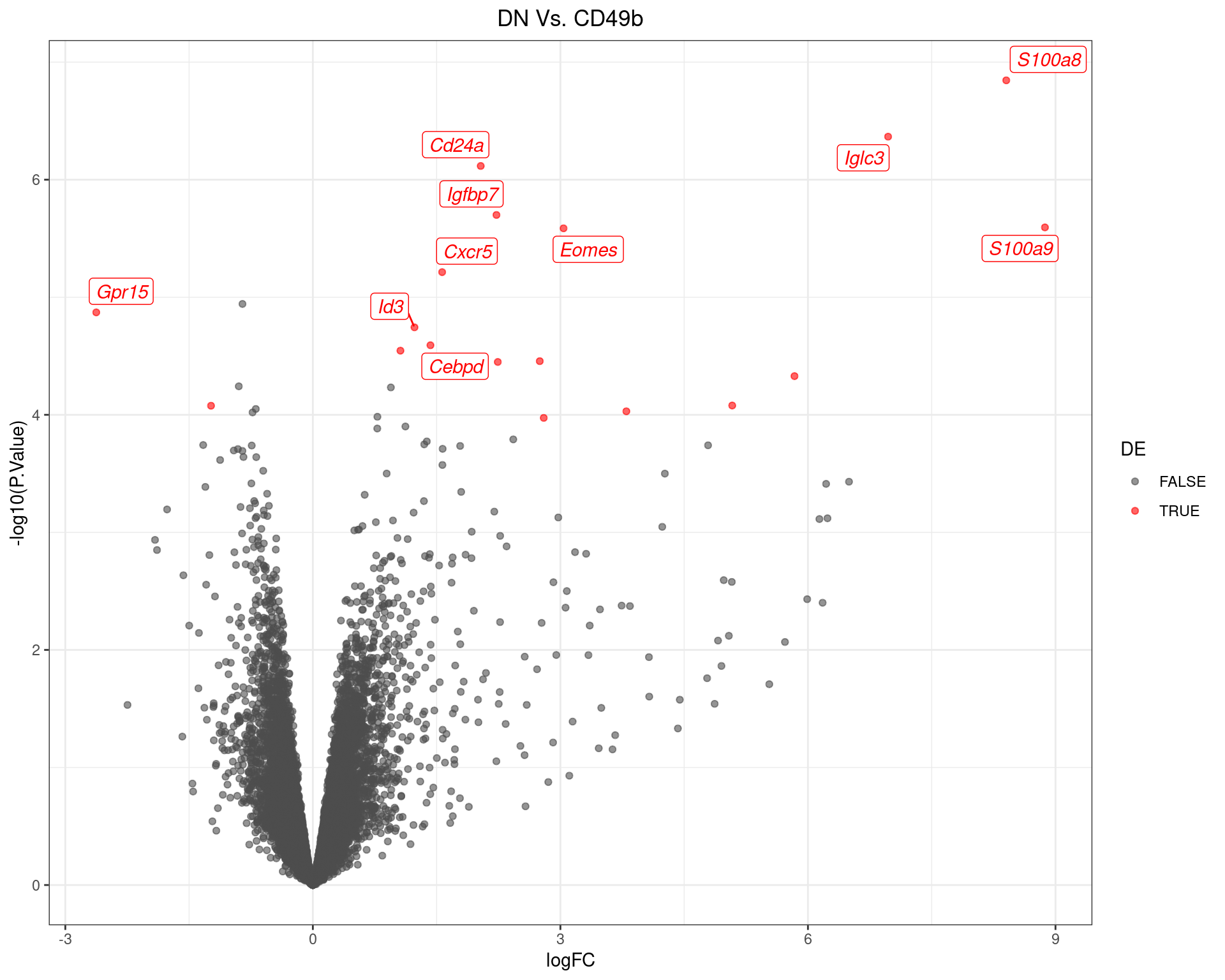
Volcano Plot for DN Vs. CD49b The most up/down-regulated genes are labelled, with the blue line representing a spline through the data.
| Version | Author | Date |
|---|---|---|
| 8745ba2 | Steve Pederson | 2022-10-25 |
LAG3 Vs. CD49b
top_tables$LAG3vCD49b %>%
ggplot(aes(logFC, -log10(P.Value))) +
geom_point(aes(colour = DE), alpha = 0.6) +
geom_label_repel(
aes(label = gene_name, colour = DE),
data = . %>%
dplyr::filter(DE) %>%
arrange(P.Value) %>%
dplyr::slice(1:10),
max.overlaps = Inf,
fontface = "italic",
show.legend = FALSE
) +
ggtitle("LAG3 Vs. CD49b") +
scale_colour_manual(values = c("grey30", "red"))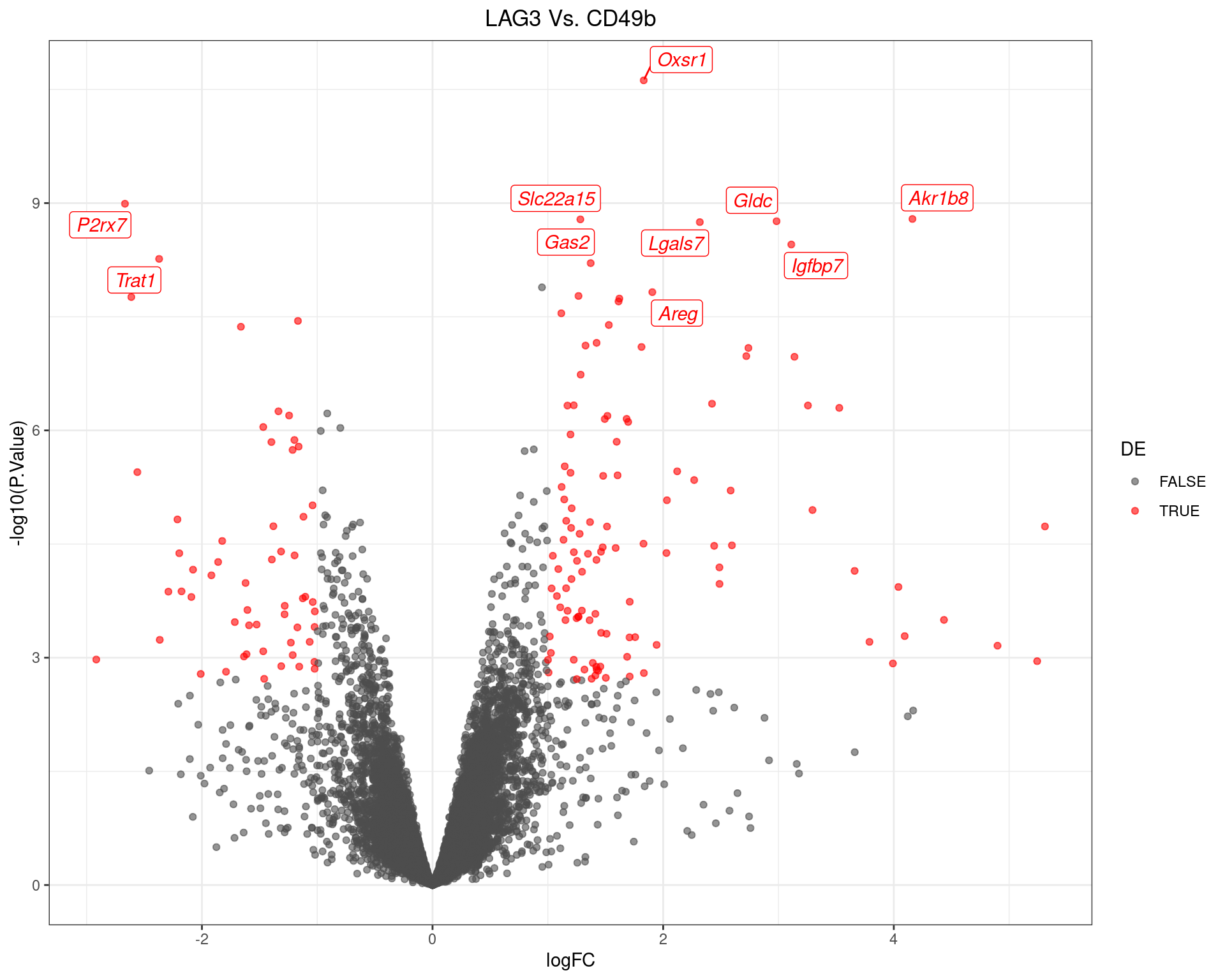
Volcano Plot for LAG3 Vs. CD49b. The 10 most highly-ranked genes are labelled, with the blue line representing a spline through the data.
| Version | Author | Date |
|---|---|---|
| 8745ba2 | Steve Pederson | 2022-10-25 |
LAG3 Vs. DP
top_tables$LAG3vDP %>%
ggplot(aes(logFC, -log10(P.Value))) +
geom_point(aes(colour = DE), alpha = 0.6) +
geom_label_repel(
aes(label = gene_name, colour = DE),
data = . %>%
dplyr::filter(DE) %>%
arrange(P.Value) %>%
dplyr::slice(1:10),
max.overlaps = Inf,
fontface = "italic",
show.legend = FALSE
) +
ggtitle("LAG3 Vs. DP") +
scale_colour_manual(values = c("grey30", "red"))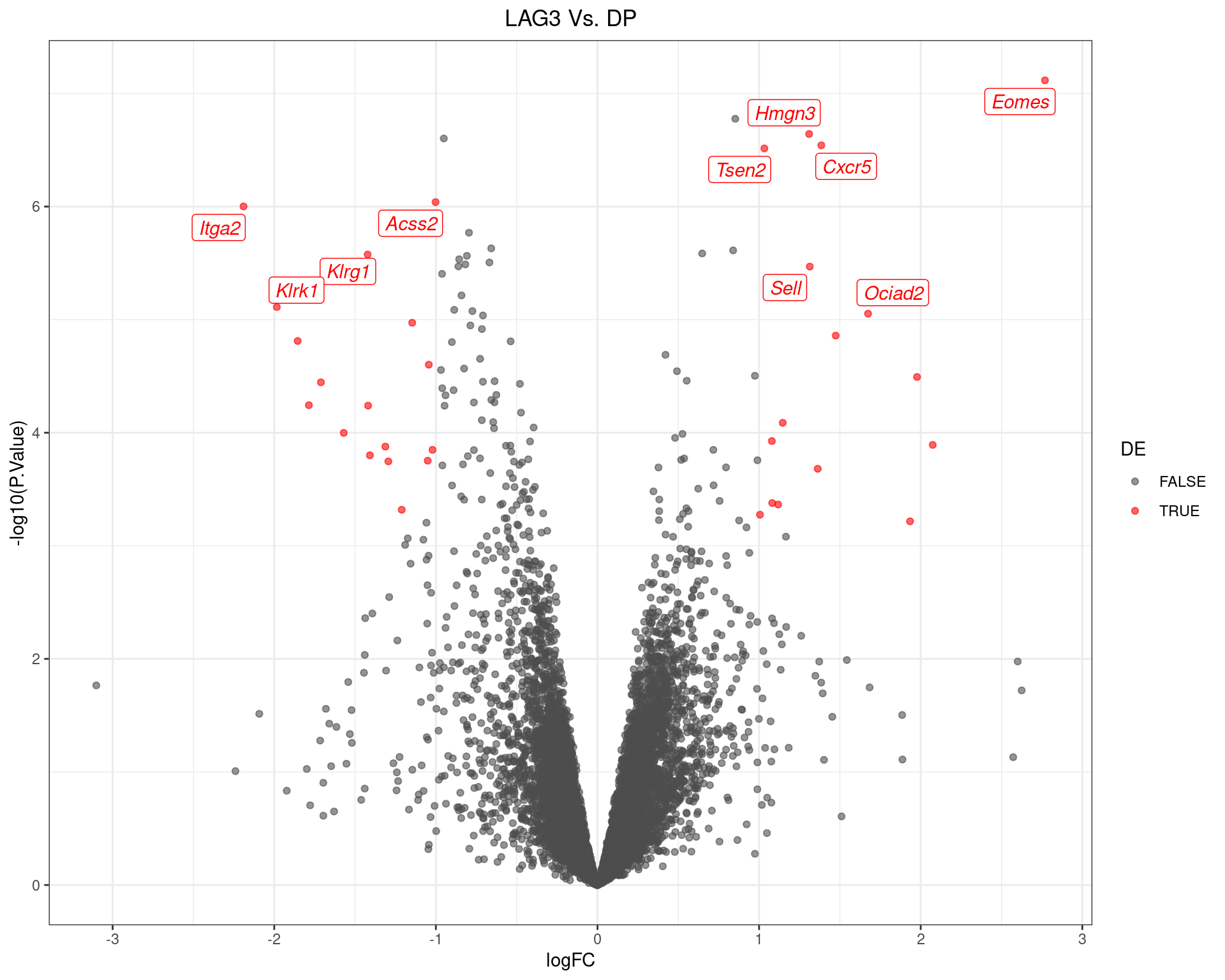
Volcano Plot for LAG3 Vs. DP The 10 most highly-ranked genes are labelled, with the blue line representing a spline through the data.
| Version | Author | Date |
|---|---|---|
| 8745ba2 | Steve Pederson | 2022-10-25 |
CD49b Vs. DP
top_tables$CD49bvDP %>%
ggplot(aes(logFC, -log10(P.Value))) +
geom_point(aes(colour = DE), alpha = 0.6) +
geom_label_repel(
aes(label = gene_name, colour = DE),
data = . %>%
dplyr::filter(DE) %>%
arrange(P.Value) %>%
dplyr::slice(1:10),
max.overlaps = Inf,
fontface = "italic",
show.legend = FALSE
) +
ggtitle("CD49b Vs. DP") +
scale_colour_manual(values = c("grey30", "red"))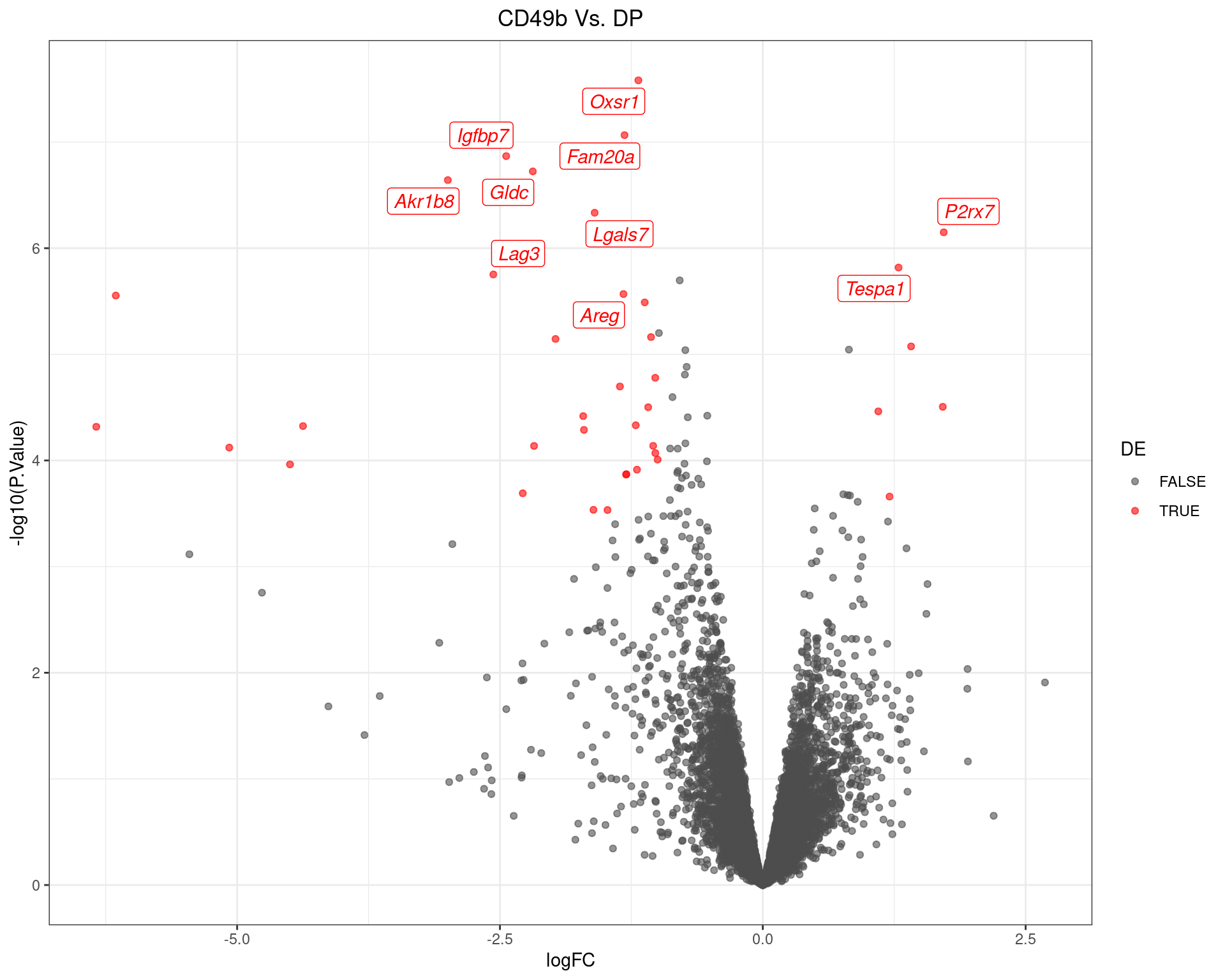
Volcano Plot for CD49b Vs. DP. The 10 most highly-ranked genes are labelled, with the blue line representing a spline through the data.
| Version | Author | Date |
|---|---|---|
| 8745ba2 | Steve Pederson | 2022-10-25 |
Heatmaps
grp_coef <- v$E %>%
as_tibble(rownames = "gene_id") %>%
pivot_longer(
cols = all_of(colnames(v)), names_to = "sample", values_to = "logCPM"
) %>%
left_join(v$targets) %>%
group_by(gene_id, condition) %>%
# summarise(logCPM = weighted.mean(logCPM, sample.weights)) %>%
summarise(logCPM = mean(logCPM)) %>%
pivot_wider(names_from = "condition", values_from = "logCPM") %>%
as.data.frame() %>%
column_to_rownames("gene_id") %>%
as.matrix()In order to visualise the data using heatmaps, the average expression within each cell type was calculated.
Top 100
All DE genes were combined across all comparisons and the 100 with the most extreme estimates of logFC were chosen for visualisation.
top_100 <- top_tables %>%
lapply(dplyr::filter, DE) %>%
bind_rows(.id = "comparison") %>%
arrange(desc(abs(logFC))) %>%
distinct(gene_id) %>%
dplyr::slice(1:100) %>%
pull("gene_id")
p <- grp_coef[top_100,] %>%
t() %>%
pheatmap(
color = hcl.colors(101, "inferno"),
labels_col = id2gene[top_100],
labels_row = c(DN = "DN", DP = "DP", "LAG_3" = "Lag3+", CD49b = "Cd49b+"),
cluster_rows = FALSE,
# annotation_col = top_tables %>%
# lapply(
# function(x) {
# up <- dplyr::filter(x, DE, logFC > 0)$gene_id
# down <- dplyr::filter(x, DE, logFC < 0)$gene_id
# case_when(
# top_100 %in% up ~ "Up",
# top_100 %in% down ~ "Down",
# TRUE ~ "Unchanged"
# )
# }
# ) %>%
# lapply(factor, levels = c("Up", "Down", "Unchanged")) %>%
# as.data.frame() %>%
# set_colnames(str_replace_all(colnames(.), "v", " Vs. ")) %>%
# set_rownames(top_100),
# annotation_colors = top_tables %>%
# setNames(str_replace_all(names(.), "v", " Vs. ")) %>%
# lapply(function(x) c("Unchanged" = "grey", "Up" = "red", "Down" = "blue")),
# annotation_legend = FALSE,
cutree_cols = 8,
cellheight = 15,
fontsize = 8,
silent = TRUE
) %>%
.[["gtable"]]
p$grobs[[3]]$gp <- gpar(fontsize = 8, fontface = "italic")
p$grobs[[4]]$gp <- gpar(fontsize = 10)
grid.newpage()
grid.draw(p)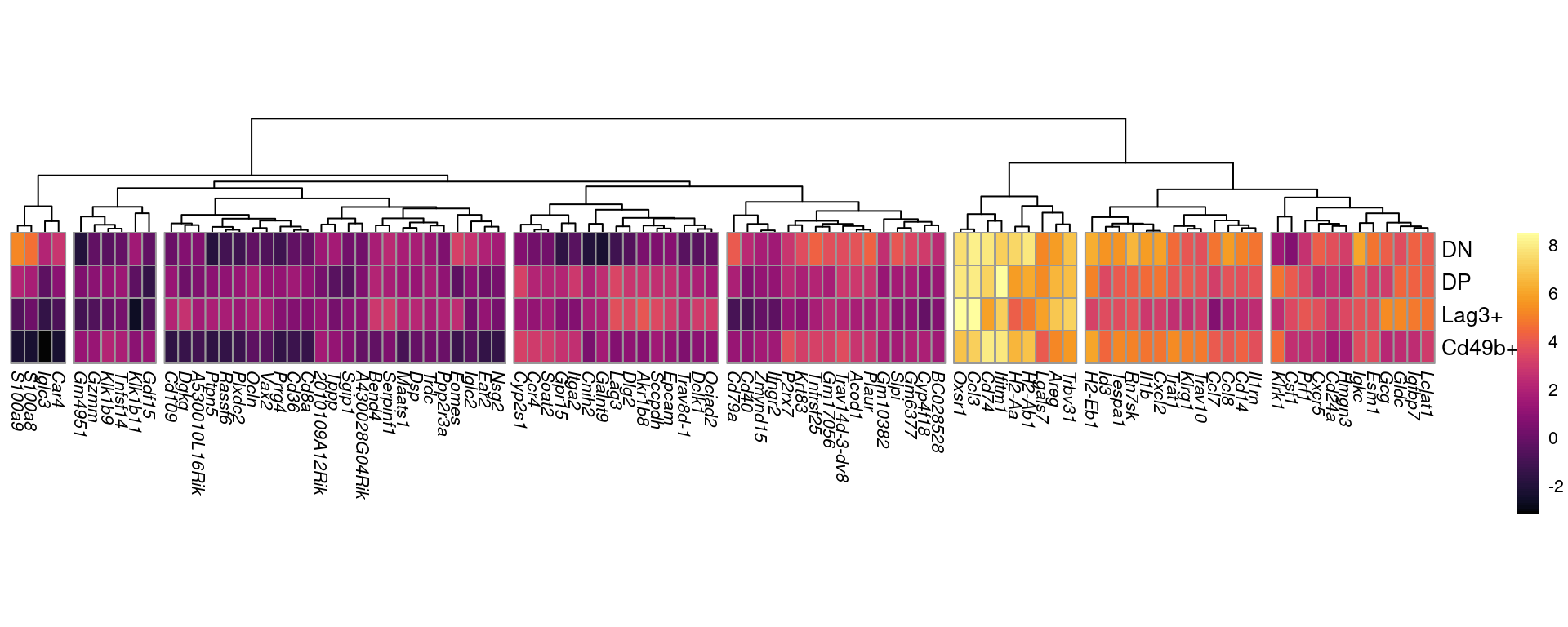
The 100 genes showing the most extreme fold-change across one or more comparisons
Data Export
write_rds(dgeFilt, here::here("output", "dgeFilt.rds"), compress = "gz")
write_rds(top_tables, here::here("output", "top_tables.rds"), compress = "gz")
write_rds(v, here::here("output", "v.rds"), compress = "gz")
write_rds(fit, here::here("output", "fit.rds"), compress = "gz")
sessionInfo()R version 4.2.1 (2022-06-23)
Platform: x86_64-pc-linux-gnu (64-bit)
Running under: Ubuntu 20.04.5 LTS
Matrix products: default
BLAS: /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/blas/libblas.so.3.9.0
LAPACK: /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/lapack/liblapack.so.3.9.0
locale:
[1] LC_CTYPE=en_AU.UTF-8 LC_NUMERIC=C
[3] LC_TIME=en_AU.UTF-8 LC_COLLATE=en_AU.UTF-8
[5] LC_MONETARY=en_AU.UTF-8 LC_MESSAGES=en_AU.UTF-8
[7] LC_PAPER=en_AU.UTF-8 LC_NAME=C
[9] LC_ADDRESS=C LC_TELEPHONE=C
[11] LC_MEASUREMENT=en_AU.UTF-8 LC_IDENTIFICATION=C
attached base packages:
[1] grid stats4 stats graphics grDevices utils datasets
[8] methods base
other attached packages:
[1] pander_0.6.5 glue_1.6.2 broom_1.0.0
[4] scales_1.2.0 ensembldb_2.20.2 AnnotationFilter_1.20.0
[7] GenomicFeatures_1.48.3 AnnotationDbi_1.58.0 Biobase_2.56.0
[10] GenomicRanges_1.48.0 GenomeInfoDb_1.32.2 IRanges_2.30.0
[13] S4Vectors_0.34.0 AnnotationHub_3.4.0 BiocFileCache_2.4.0
[16] dbplyr_2.2.1 BiocGenerics_0.42.0 pheatmap_1.0.12
[19] ggrepel_0.9.1 edgeR_3.38.1 limma_3.52.2
[22] magrittr_2.0.3 forcats_0.5.1 stringr_1.4.0
[25] dplyr_1.0.9 purrr_0.3.4 readr_2.1.2
[28] tidyr_1.2.0 tibble_3.1.8 ggplot2_3.3.6
[31] tidyverse_1.3.2 workflowr_1.7.0
loaded via a namespace (and not attached):
[1] readxl_1.4.0 backports_1.4.1
[3] lazyeval_0.2.2 splines_4.2.1
[5] BiocParallel_1.30.3 digest_0.6.29
[7] htmltools_0.5.3 fansi_1.0.3
[9] memoise_2.0.1 googlesheets4_1.0.0
[11] tzdb_0.3.0 Biostrings_2.64.0
[13] modelr_0.1.8 matrixStats_0.62.0
[15] vroom_1.5.7 prettyunits_1.1.1
[17] colorspace_2.0-3 blob_1.2.3
[19] rvest_1.0.2 rappdirs_0.3.3
[21] haven_2.5.0 xfun_0.31
[23] callr_3.7.1 crayon_1.5.1
[25] RCurl_1.98-1.7 jsonlite_1.8.0
[27] gtable_0.3.0 gargle_1.2.0
[29] zlibbioc_1.42.0 XVector_0.36.0
[31] DelayedArray_0.22.0 DBI_1.1.3
[33] Rcpp_1.0.9 xtable_1.8-4
[35] progress_1.2.2 bit_4.0.4
[37] httr_1.4.3 RColorBrewer_1.1-3
[39] ellipsis_0.3.2 farver_2.1.1
[41] pkgconfig_2.0.3 XML_3.99-0.10
[43] sass_0.4.2 here_1.0.1
[45] locfit_1.5-9.6 utf8_1.2.2
[47] labeling_0.4.2 tidyselect_1.1.2
[49] rlang_1.0.4 later_1.3.0
[51] munsell_0.5.0 BiocVersion_3.15.2
[53] cellranger_1.1.0 tools_4.2.1
[55] cachem_1.0.6 cli_3.3.0
[57] generics_0.1.3 RSQLite_2.2.15
[59] evaluate_0.15 fastmap_1.1.0
[61] yaml_2.3.5 processx_3.7.0
[63] knitr_1.39 bit64_4.0.5
[65] fs_1.5.2 KEGGREST_1.36.3
[67] nlme_3.1-159 whisker_0.4
[69] mime_0.12 xml2_1.3.3
[71] biomaRt_2.52.0 compiler_4.2.1
[73] rstudioapi_0.13 filelock_1.0.2
[75] curl_4.3.2 png_0.1-7
[77] interactiveDisplayBase_1.34.0 reprex_2.0.1
[79] statmod_1.4.36 bslib_0.4.0
[81] stringi_1.7.8 highr_0.9
[83] ps_1.7.1 lattice_0.20-45
[85] ProtGenerics_1.28.0 Matrix_1.5-1
[87] vctrs_0.4.1 pillar_1.8.0
[89] lifecycle_1.0.1 BiocManager_1.30.18
[91] jquerylib_0.1.4 bitops_1.0-7
[93] httpuv_1.6.5 rtracklayer_1.56.1
[95] R6_2.5.1 BiocIO_1.6.0
[97] promises_1.2.0.1 codetools_0.2-18
[99] assertthat_0.2.1 SummarizedExperiment_1.26.1
[101] rprojroot_2.0.3 rjson_0.2.21
[103] withr_2.5.0 GenomicAlignments_1.32.1
[105] Rsamtools_2.12.0 GenomeInfoDbData_1.2.8
[107] mgcv_1.8-40 parallel_4.2.1
[109] hms_1.1.1 rmarkdown_2.14
[111] MatrixGenerics_1.8.1 googledrive_2.0.0
[113] git2r_0.30.1 getPass_0.2-2
[115] shiny_1.7.2 lubridate_1.8.0
[117] restfulr_0.0.15